Abstract
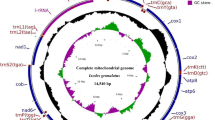
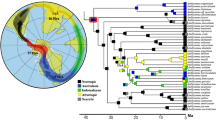
In this study, we sequenced two complete mitochondrial genomes of Amblyomma ovale, a tick of public health importance. Sequencing two distinct individuals, the resulting mitochondrial genomes were 14,756 and 14,760 bp in length and maintained the same gene order previously reported in Amblyomma. These were combined with RNA-seq derived mitochondrial sequences from three additional species, Amblyomma aureolatum, Amblyomma maculatum, and Amblyomma moreliae, to carry out mitogenome comparative and evolutionary analyses against all previously published tick mitochondrial genomes. We described a derivative genome rearrangement that isolates Ixodes from the remaining Ixodidae and consists of both a reverse translocation as well as an event of Tandem Duplication Random Loss. Genetic distance analyses indicated that cox2, nd1, nd5, and 16S are good candidates for future population studies in A. ovale. The phylogenetic analyses corroborated the utility of complete mitochondrial genomes as phylogenetic markers within the group. This study further supplements the genome information available for Amblyomma and facilitates future evolutionary and population genetic studies within the genus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalde S, Tenorio MJ, Uribe JE, Zardoya R (2019) Conidae phylogenomics and evolution. Zool Scr 48(2):194–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/zsc.12329
Abascal F, Zardoya R, Telford MJ (2010) TranslatorX: multiple alignment of nucleotide sequences guided by amino acid translations. Nucleic Acids Res 38:W7–W13. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq291
Adamson SW, Browning RE, Budachetri K, Ribeiro JM, Karim S (2013) Knockdown of selenocysteine-specific elongation factor in Amblyomma maculatum alters the pathogen burden of Rickettsia parkeri with epigenetic control by the Sin3 histone deacetylase corepressor complex. PLoS ONE 8(11):e82012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082012
Aguilar-Domínguez M, Sánchez-Montes S, Esteve-Gassent MD, Barrientos-Salcedo C, de León AP, Romero-Salas D (2019) Genetic structure analysis of Amblyomma mixtum populations in Veracruz State, Mexico. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 10(1):86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2018.09.004
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Alvarez V, Hernandez V, Hernandez J (2005) Catálogo de garrapatas suaves (Acari: Argasidae) y duras (Acari: Ixodidae) de Costa Rica. Brenesia 63:81–88
Aragão H, Fonseca FD (1961) Notas de ixodologia: IX. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, O complexo ovale do gênero Amblyomma. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0074-02761961000200002
Barker SC, Burger TD (2018) Two new genera of hard ticks, Robertsicus n. gen. and Archaeocroton n. gen., and the solution of the mystery of Hoogstraal´s ‘primitive’ tick from the Capathian Mountains. Zootaxa 4500(4):543–552. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4500.4.4
Barros-Battesti DM, Arzua M, Bechara GH (2006) Carrapatos de Importância Médico Veterinária da Região Neotropical: um Guia Ilustrado para Identificação de Espécies. Integrated consortium on ticks & tick-borne diseases. ICTTD/Butantan), São Paulo
Beati L, Klompen H (2019) Phylogeography of ticks (Acari: Ixodida). Annu Rev Entomol 64:379–397. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-020117-043027
Beati L, Nava S, Burkman EJ, Barros-Battesti DM, Labruna MB, Guglielmone AA, Cáceres AG, Guzmán-Cornejo CM, León R, Durden LA, Faccini JL (2013) Amblyomma cajennense (Fabricius, 1787) (Acari: Ixodidae), the Cayenne tick: phylogeography and evidence for allopatric speciation. BMC Evol Biol 13(1):267. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-13-267
Bermúdez SE, Eremeeva ME, Karpathy SE, Samudio F, Zambrano ML, Zaldivar Y, Motta JA, Dasch GA (2009) Detection and identification of rickettsial agents in ticks from domestic mammals in eastern panama. J Med Entomol 46:856–861. https://doi.org/10.1603/033.046.0417
Bermúdez C, Castro SE, Esser A, Liefting H, García Y, Miranda G RJ (2012) Ticks (Ixodida) on humans from central Panama, Panama (2010–2011). Exp Appl Acarol 58(1):81–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-012-9564-7
Bernt M, Merkle D, Ramsch K, Fritzsch G, Perseke M, Bernhard D, Schlegel M, Stadler PF, Middendorf M (2007) CREx: inferring genomic rearrangements based on common intervals. Bioinformatics 23(21):2957–2958. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm468
Bernt M, Donath A, Jühling F, Externbrink F, Florentz C, Fritzsch G, Putz J, Middendorf M, Stadler PF (2013) MITOS: improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol Phylogenet Evol 69(2):313–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.08.023
Binetruy F, Buysse M, Lejarre Q, Barosi R, Villa M, Rahola N, Paupy C, Ayala D, Duron O (2020) Microbial community structure reveals instability of nutritional symbiosis during the evolutionary radiation of Amblyomma ticks. Mol Ecol 29(5):1016–1029. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.15373
Bitencourth K, Amorim M, De Oliveira SV, Caetano RL, Voloch CM, Gazêta GS (2017) Amblyomma sculptum: genetic diversity and rickettsias in the Brazilian Cerrado biome. Med Vet Entomol 31(4):427–437. https://doi.org/10.1111/mve.12249
Bitencourth K, Amorim M, de Oliveira SV, Voloch CM, Gazêta GS (2019) Genetic diversity, population structure and rickettsias in Amblyomma ovale in areas of epidemiological interest for spotted fever in Brazil. Med Vet Entomol 33(2):256–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/mve.12363
Black WC 4th, Roehrdanz RL (1998) Mitochondrial gene order is not conserved in arthropods: prostriate and metastriate tick mitochondrial genomes. Mol Biol Evol 15(12):1772–1785. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025903
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30(15):2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Boore JL, Macey JR, Medina M (2005) Sequencing and comparing whole mitochondrial genomes of animals. In: Zimmer EA, Roalson E (eds) Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, New York, pp 311–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(05)95019-2
Burger TD, Shao R, Beati L, Miller H, Barker SC (2012) Phylogenetic analysis of ticks (Acari: Ixodida) using mitochondrial genomes and nuclear rRNA genes indicates that the genus Amblyomma is polyphyletic. Mol Phylogenet Evol 64(1):45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.03.004
Burger TD, Shao R, Barker SC (2013) Phylogenetic analysis of the mitochondrial genomes and nuclear rRNA genes of ticks reveals a deep phylogenetic structure within the genus Haemaphysalis and further elucidates the polyphyly of the genus Amblyomma with respect to Amblyomma sphenodonti and Amblyomma elaphense. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 4(4):265–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.02.002
Burger TD, Shao R, Barker SC (2014) Phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial genome sequences indicates that the cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, contains a cryptic species. Mol Phylogenet Evol 76:241–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2014.03.017
Burnard D, Shao R (2019) Mitochondrial genome analysis reveals intraspecific variation within Australian hard tick species. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 10(3):677–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2019.02.013
Chang QC, Hu Y, Que TC, Liu YX, Zhu JG, Diao PW (2019) The complete mitochondrial genome of Amblyomma geoemydae (Ixodida: Ixodidae). Mitochondrial DNA B 4(2):2551–2552. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2019.1640643
Chang QC, Diao PW, Fu X, Wang XX, Qiu YY, Hu Y, Ma XX, Sun Y, Wang CR (2019b) The complete mitochondrial genome of Haemaphysalis japonica (Ixodida: Ixodidae). Mitochondrial DNA B 4(1):1006–1007. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2018.1535862
Chang QC, Wu TT, Cao H, Sun MQ, Zhang WT, Xue SJ (2020) The complete mitochondrial genome of Amblyomma testudinarium (Ixodida: Ixodidae). Mitochondrial DNA B 5(2):1485–1486. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2020.1742232
Criscuolo A, Gribaldo S (2010) BMGE (Block Mapping and Gathering with Entropy): a new software for selection of phylogenetic informative regions from multiple sequence alignments. BMC Evol Biol 10(1):210. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-10-210
de Lima PHC, Barcelos RM, Klein RC, Vidigal PMP, Montandon CE, Fabres-Klein MH, Dergamf JA, Mafra C (2017) Sequencing and comparative analysis of the Amblyomma sculptum mitogenome. Vet Parasitol 247:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2017.10.007
da Paixão Sevá A, Martins TF, Muñoz-Leal S, Rodrigues AC, Pinter A, Luz HR, Angerami RN, Labruna MB (2019) A human case of spotted fever caused by Rickettsia parkeri strain Atlantic rainforest and its association to the tick Amblyomma ovale. Parasite Vector 12(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3730-2
Donath A, Jühling F, Al-Arab M, Bernhart SH, Reinhardt F, Stadler PF, Middendorf M, Bernt M (2019) Improved annotation of protein-coding genes boundaries in metazoan mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 47(20):10543–10552. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz833
Duan DY, Tang JM, Chen Z, Liu GH, Cheng TY (2019) Mitochondrial genome of Amblyomma javanense: a hard tick parasite of the endangered Malayan pangolin (Manis javanica). Med Vet Entomol 34(2):229–235. https://doi.org/10.1111/mve.12403
Edler D, Klein J, Antonelli A, Silvestro D (2019) raxmlGUI 2.0 beta: a graphical interface and toolkit for phylogenetic analyses using RAxML. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/800912
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01734359
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 3:294–299
Forlano M, Scofield A, Elisei C, Fernandes KR, Ewing SA, Massard CL (2005) Diagnosis of Hepatozoon spp. in Amblyomma ovale and its experimental transmission in domestic dogs in Brazil. Vet Parasitol 134:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.05.066
Fournier GF, Pinter A, Santiago R, Muñoz-Leal S, Martins TF, Lopes MG, McCoy KD, Toty C, Horta MC, Labruna MB, Dias RA (2019) A high gene flow in populations of Amblyomma ovale ticks found in distinct fragments of Brazilian Atlantic rainforest. Exp Appl Acarol 77(2):215–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-019-00350-y
Gaur RK (2014) Amino acid frequency distribution among eukaryotic proteins. IIOABJ 5(2):6
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q, Chen Z (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29(7):644. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1883
Guglielmone AA, Estrada-Peña A, Mangold AJ, Barros-Battesti DM, Labruna MB, Martins JR, Venzal JM, Arzua M, Keirans JE (2003) Amblyomma aureolatum (Pallas, 1772) and Amblyomma ovale Koch, 1844 (Acari: Ixodidae): hosts, distribution and 16S rDNA sequences. Vet Parasitol 113(3–4):273–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4017(03)00083-9
Guglielmone AA, Beati L, Barros-Battesti DM, Labruna MB, Nava S, Venzal JM, Mangold AJ, Szabó MPJ, Martins JR, González-Acuña D, Estrada-Peña A (2006) Ticks (Ixodidae) on humans in South America. Exp Appl Acarol 40:83–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-006-9027-0
Guglielmone AA, Robbins RG, Apanaskevich DA, Petney TN, Estrada-Peña A, Horak I (2014) The hard ticks of the world. Springer, Dordrecht, p 738. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7497-1
Guo DH, Zhang Y, Fu X, Gao Y, Liu YT, Qiu JH, Chang QC, Wang CR (2016) Complete mitochondrial genomes of Dermacentor silvarum and comparative analyses with another hard tick Dermacentor nitens. Exp Parasitol 169:22–27
Harvey E, Rose K, Eden JS, Lo N, Abeyasuriya T, Shi M, Doggett SL, Holmes EC (2019) Extensive diversity of RNA viruses in Australian ticks. J Virol 93(3):e01358–e01318. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01358-18
Irisarri I, Uribe JE, Eernisse DJ, Zardoya R (2020) A mitogenomic phylogeny of chitons (Mollusca: Polyplacophora). BMC Evol Biol 20(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-019-1573-2
Jones EK, Clifford CM, Keirans JE, Kohls GM (1972) The ticks of Venezuela (Acarina: Ixodoidea) with a key to the species of Amblyomma in the Western Hemisphere. Brigham Young Univ sci bull Biol 17(4):1
Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TKF, von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat Methods 14(6):587. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285
Katoh K, Kuma KI, Toh H, Miyata T (2005) MAFFT version 5: improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Res 33(2):511–518. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki198
Katoh K, Rozewicki J, Yamada KD (2019) MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief Bioinform 20(4):1160–1166. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx108
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Labruna MB, Whitworth T, Bouyer DH, McBride J, Camargo LMA, Camargo EP, Popov V, Walker DH (2004) Rickettsia bellii and Rickettsia amblyommii in Amblyomma Ticks from the State of Rondônia, Western Amazon. Brazil J Med Entomol 41(6):1073–1081. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-838246320140623
Labruna MB, Mattar S, Nava S, Bermudez S, Venzal JM, Dolz G, Abarca L, Romero L, Sousa R, Oteo J, Zavala-Castro J (2011) Rickettsioses in Latin America, Caribbean, Spain and Portugal. Rev MVZ Cordoba 16(2):2435–2457
Lamattina D, Tarragona EL, Nava S (2018) Molecular detection of the human pathogen Rickettsia parkeri strain Atlantic rainforest in Amblyomma ovale ticks in Argentina. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 9(5):1261–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2018.05.007
Lartillot N, Rodrigue N, Stubbs D, Richer J (2013) PhyloBayes MPI: phylogenetic reconstruction with infinite mixtures of profiles in a parallel environment. Syst Biol 62(4):611–615. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syt022
Laslett D, Canbäck B (2008) ARWEN: a program to detect tRNA genes in metazoan mitochondrial nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 24(2):172–175. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm573
Le VS, Dang CC, Le QS (2017) Improved mitochondrial amino acid substitution models for metazoan evolutionary studies. BMC Evol Biol 17(1):136. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-017-0987-y
Liu GH, Chen F, Chen YZ, Song HQ, Lin RQ, Zhou DH, Zhu XQ (2013) Complete mitochondrial genome sequence data provides genetic evidence that the brown dog tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Acari: Ixodidae) represents a species complex. Int J Biol Sci 9(4):361–369. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.6081
Liu J, Zhu D, Ma G, Liu M, Wang M, Jia R, Chen S, Sun K, Yang Q, Wu Y, Chen X, Cheng A (2016) Genome-wide analysis of the synonymous codon usage patterns in Riemerella anatipestifer. Int J Mol Sci 17(8):1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081304
Liu ZQ, Liu YF, Kuermanali N, Wang DF, Chen SJ, Guo HL, Zhao L, Wang JW, Han T, Wang YZ, Wang J (2018) Sequencing of complete mitochondrial genomes confirms synonymization of Hyalomma asiaticum asiaticum and kozlovi, and advances phylogenetic hypotheses for the Ixodidae. PloS one 13(5):e0197524. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197524
Londoño AF, Díaz FJ, Valbuena G, Gazi M, Labruna MB, Hidalgo M, Mattar S, Contreras V, Rodas JD (2014) Infection of Amblyomma ovale by Rickettsia sp. strain Atlantic rainforest, Colombia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 5(6):672–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2014.04.018
Lopes MG, Junio JM, Foster RJ, Harmsen BJ, Sanchez E, Martins TF, Quigley H, Marcili A, Labruna MB (2016) Ticks and rickettsiae in Belize, Central America. Parasite Vector 9(1):62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1348-1
Mans BJ, Featherston J, Kvas M, Pillay KA, de Klerk DG, Pienaar R, de Castro MH, Schwan TG, Lopez JE, Teel P, Pérez de León AA, Sonenshine DE, Egekwu NI, Bakkes DK, Heyne H, Kanduma EG, Nyangiwe N, Bouattour A, Latif AAP (2019) Argasid and ixodid systematics: implications for soft tick evolution and systematics, with a new argasid species list. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 10(1):219–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2018.09.010
Marrelli MT, Souza LF, Marques RC, Labruna MB, Matioli SR, Tonon AP, Ribolla PEM, Marinotti O, Schumaker TTS (2007) Taxonomic and phylogenetic relationships between neotropical species of ticks from Genus Amblyomma (Acari: Ixodidae) inferred from second internal transcribed spacer sequences of rDNA. J Med Entomol 44(2):222–228. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/44.2.222
Martins TF, Barbieri ARM, Costa FB, Terassini FA, Camargo LMA, Peterka CRL, Pacheco RC, Dias RA, Nunes PH, Marcili A, Scofiled A, Campos AK, Horta MC, Guilloux AGA, Benatti HR, Ramirez DG, Barros-Battesti DM, Labruna MB (2016) Geographical distribution of Amblyomma cajennense (sensu lato) ticks (Parasitiformes: Ixodidae) in Brazil, with description of the nymph of A. cajennense (sensu stricto). Parasite Vector 9:186. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1460-2
Martins LA, Galletti MF, Ribeiro JM, Fujita A, Costa FB, Labruna MB, Daffre S, Fogaça AC (2017) The distinct transcriptional response of the midgut of Amblyomma sculptum and Amblyomma aureolatum ticks to Rickettsia rickettsii correlates to their differences in susceptibility to infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:129. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00129
Miller HC, Conrad AM, Barker SC, Daugherty CH (2007) Distribution and phylogenetic analyses of an endangered tick, Amblyomma sphenodonti. New Zeal J Zool 34:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1080/03014220709510068
Montagna M, Sassera D, Griggio F, Epis S, Bandi C, Gissi C (2012) Tick-box for 3′-end formation of mitochondrial transcripts in Ixodida, basal Chelicerates and Drosophila. PloS ONE 7(10):e47538. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047538
Nava S, Szabó MPJ, Mangold AJ, Guglielmone AA (2008) Distribution, hosts, 16S rDNA sequences and phylogenetic position of the Neotropical tick Amblyomma parvum (Acari: Ixodidae). Ann Trop Med Parasit 102:409–425
Nava S, Beati L, Labruna MB, Cáceres AG, Mangold AJ, Guglielmone AA (2014) Reassessment of the taxonomic status of Amblyomma cajennense (Fabricius, 1787) with the description of three new species, Amblyomma tonelliae n. sp., Amblyomma interandinum n. sp. and Amblyomma patinoi n. sp., and reinstatement of Amblyomma mixtum Koch, 1844 and Amblyomma sculptum Berlese, 1888 (Ixodida: Ixodidae). Ticks Tick Borne Dis 5:252–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.11.004
Nava S, Venzal JM, González-Acuña D, Martins TF, Guglielmone AA (2017) Ticks of the southern cone of America: diagnosis, distribution and hosts with taxonomy, ecology and sanitary importance. Elsevier, London, 348 pp
Nguyen LT, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ (2014) IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 32:268–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu300
Pacheco R, Rosa S, Richtzenhain L, Szabà MPJ, Labruna MB (2008) Isolation of Rickettsia bellii from Amblyomma ovale and Amblyomma incisum ticks from southern. Brazil Rev MVZ Cordoba 13:1273–1279
Palumbi S, Martin A, McMillan W, Stice L, Grabowski G (1991) The simple fool’s guide to PCR. http://palumbi.stanford.edu/SimpleFoolsMaster.pdf. pp 1–45. Accessed 12 April 2020
Rambaut A, Drummond AJ, Xie D, Baele G, Suchard MA (2018) Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst Biol 67(5):901. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syy032
Rannala B, Yang Z (1996) Probability distribution of molecular evolutionary trees: a new method of phylogenetic inference. J Mol Evol 43(3):304–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02338839
Sabatini G, Pinter A, Nieri-Bastos F, Marcili A, Labruna MB (2010) Survey of ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) and their Rickettsia in an Atlantic rain forest reserve in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. J Med Entomol 47(5):913–916. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/47.5.913
Sánchez-Montes S, Ballados-González GG, Hernández-Velasco A, Zazueta-Islas HM, Solis-Cortés M, Miranda-Ortiz H, Canseco-Méndez JC, Fernández-Figueroa EA, Colunga-Salas P, López-Pérez AM, la Mora JD, Licona-Enriquez JD, la Mora DD, Karpathy SE, Paddock CD, Rangel-Escareño C (2019) Molecular Confirmation of Rickettsia parkeri/em in emAmblyomma ovaleticks, Veracruz, Mexico. Emerg Infect Dis 25:2315. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2512.190964
Schwarz G (1978) Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Stat 6:461–464
Shao R, Fukunaga M, Barker SC (2005) The mitochondrial genomes of ticks and their kin: a review plus the description of the mitochondrial genomes of Amblyomma triguttatum and Ornithodoros porcinus. In: Proceedings of the 5th international conference on TTP7. Université de Neuchâtel Switzerland
Silva N, Eremeeva ME, Rozental T, Ribeiro GS, Paddock CD, Ramos EAG, Favacho ARM, Reis MG, Dasch GA, de Lemos ERS, Ko AI (2011) Eschar-associated spotted fever rickettsiosis, Bahia, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis 17:275–278. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1702.100859
Silvestro D, Michalak I (2012) raxmlGUI: a graphical front-end for RAxML. Org Divers Evol 12:(4):335–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13127-011-0056-0
Spolidorio MG, Labruna MB, Mantovani E, Brandao PE, Richtzenhain LJ, Yoshinari NH (2010) Novel spotted fever group rickettsiosis, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis 16:521–523. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1603.091338
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30(9):1312–1313. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
Trout RT, Steelman CD, Szalanski AL, Loftin K (2010) Establishment of Amblyomma maculatum (Gulf Coast tick) in Arkansas, USA. Fla Entomol 93(1):120–122. https://doi.org/10.1653/024.093.0117
Uddin A, Chakraborty S (2017) Synonymous codon usage pattern in mitochondrial CYB gene in pisces, aves, and mammals. Mitochondrial DNA A 28(2):187–196. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2015.1115842
Uribe JE, Gutiérrez-Rodríguez J (2016) The complete mitogenome of the trilobite beetle, Platerodrilus sp. (Elateroidea: Lycidae). Mitochondrial DNA B 1(1):658–659. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2016.1219626
Uribe JE, Irisarri I, Templado J, Zardoya R (2019) New patellogastropod mitogenomes help counteracting long-branch attraction in the deep phylogeny of gastropod mollusks. Mol Phylogenet Evol 133:12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2018.12.019
Valverde JR, Batuecas B, Moratilla C, Marco R, Garesse R (1994) The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the crustacean Artemia franciscana. J Mol Evol 39(4):400–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00160272
Wang Q, Tang G (2017) Genomic and phylogenetic analysis of the complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of walnut leaf pest Paleosepharia posticata (Coleoptera: Chrysomeloidea). J Asia Pac Entomol 20:840–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aspen.2017.05.010
Wang T, Zhang S, Pei T, Yu Z, Liu J (2019) Tick mitochondrial genomes: structural characteristics and phylogenetic implications. Parasite Vector 12(1):451. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3705-3
Williams-Newkirk AJ, Burroughs M, Changayil SS, Dasch GA (2015) The mitochondrial genome of the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum). Ticks Tick Borne Dis 6(6):793–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2015.07.006
Yang Z, Rannala B (1997) Bayesian phylogenetic inference using DNA sequences: a Markov Chain Monte Carlo method. Mol Biol Evol 14(7):717–724. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025811
Yu Z, Zhang S, Wang T, Yang X, Wang H, Liu J (2018) The mitochondrial genome and phylogenetic analysis of the tick Dermacentor everestianus Hirst, 1926 (Acari: Ixodidae). Syst Appl Acarol 23(7):1313–1321. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.23.7.8
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Adriana Santodomingo and Andrea Cotes for their collaboration in the collection of the A. ovale (Colombia) specimen, and Makiri Sei and Herman Wirshing for their help in the molecular laboratory. All laboratory work, sequencing, and analyses were conducted in and with the support of the Laboratories of Analytical Biology (LAB) facilities of the National Museum of Natural History.
Funding
JEU was supported by Peter Buck Postdoctoral Fellowship Program from the Smithsonian Institution (2017–2019) and Atracción Talento de la Comunidad de Madrid Fellowship Program (REFF 2019-T2/AMB-13166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LRC, ELT and SN collected the material; JEU and KRM generated the molecular data; JEU analyzed the data; JEU, SN and LRC wrote the first draft of the manuscript and all authors contributed to writing the final version. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10493_2020_512_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Electronic supplementary material 1 Supplementary Material. Alternative topology. Phylogenetic relationships of Amblyomma based on mitochondrial protein-coding genes analyzed at the amino-acid level. The tree is a maximum-likelihood phylogram using Ixodes as its root. Numbers at nodes are statistical support values for ML analyses, bootstrap. Asterisks indicate species for which transcriptomes were used. Scale bar = 0.2 substitutions/site. (PDF 58 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uribe, J.E., Nava, S., Murphy, K.R. et al. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Amblyomma ovale, comparative analyses and phylogenetic considerations. Exp Appl Acarol 81, 421–439 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-020-00512-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-020-00512-3