Abstract
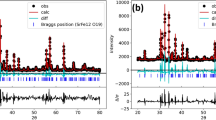
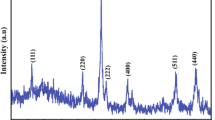
A series of Cu-Co-substituted manganese ferrites (Mn1-xCuxFe2-yCoyO4; x = 0.0–0.1, y = 0.00–0.25) were synthesized via microemulsion method. The values of structural parameters, i.e., lattice constant and crystallite size, were increased with the inclusion of Co and Cu ions. FTIR studies revealed first band at 400–500 cm−1 and second band at 561–588 cm−1. The values of dielectric parameters have been increased with the increase of Cu and Co concentrations. The magnetic parameters, i.e., saturation magnetization (Ms), coercivity (Hc), and remanence (Mr), have been investigated from M-H loops. The values of Ms and Mr were observed to increase from 5.00 to 36.02 emu/g and from 4.6 to 13.2 emu/g, respectively. The value of coercivity had been decreased from 466 to 261 Oe. The increase in saturation magnetization as well as decrease in dielectric losses proposed that synthesized nanoferrites may be potential candidates for high frequency and microwave applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giustini, A.J., et al.: Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia in cancer treatment. Nano Life. 1(01n02), 17–32 (2010)
Leslie-Pelecky, D.L., Rieke, R.D.: Magnetic properties of nanostructured materials. Chem. Mater. 8(8), 1770–1783 (1996)
Debnath, S., et al.: X-ray diffraction analysis for the determination of elastic properties of zinc-doped manganese spinel ferrite nanocrystals (Mn0.75Zn0.25Fe2O4), along with the determination of ionic radii, bond lengths, and hopping lengths. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 134, 105–114 (2019)
Alivisatos, A.P.: Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science. 271(5251), 933 (1996)
Roduner, E.: Size matters: why nanomaterials are different. Chem. Soc. Rev. 35(7), 583–592 (2006)
Junaid, M., et al.: Structural, spectral, dielectric and magnetic properties of Tb–Dy doped Li-Ni nano-ferrites synthesized via micro-emulsion route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 338–344 (2016)
Aravind, G., Raghasudha, M., Ravinder, D.: Electrical transport properties of nano crystalline Li–Ni ferrites. J. Mater. 1(4), 348–356 (2015)
Yuvaraj, S., Manikandan, N., Vinitha, G.: Structural and nonlinear optical properties of nickel substituted manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 44(18), 22592–22600 (2018)
Arshad, M., et al.: Structural and magnetic properties variation of manganese ferrites via Co-Ni substitution. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 474, 98–103 (2019)
Goodarz Naseri, M., et al.: Synthesis and characterization of manganese ferrite nanoparticles by thermal treatment method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323(13), 1745–1749 (2011)
Malaescu, I., et al.: Experimental investigations of the structural transformations induced by the heat treatment in manganese ferrite synthesized by ultrasonic assisted co-precipitation method. Ceram. Int. 42(15), 16744–16748 (2016)
Debnath, S., Das, R.: Study of the optical properties of Zn doped Mn spinel ferrite nanocrystals shows multiple emission peaks in the visible range –a promising soft ferrite nanomaterial for deep blue LED. J. Mol. Struct. 1199, 127044 (2020)
Xu, Z., et al.: Calcination induced phase transformation in MnZn ferrite powders. J. Alloys Compd. 814, 152307 (2020)
Naik, P.P., et al.: Altering saturation magnetization of manganese zinc ferrite nanoparticles by doping with rare earth Nd+3 ions. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 584, 412111 (2020)
Gul, M., Akhtar, K.: Synthesis and characterization of Al_doped manganese ferrite uniform particles for high-frequency applications. J. Alloys Compd. 765, 1139–1147 (2018)
Desai, I., et al.: Synthesis and characterization of magnetic manganese ferrites. Mater Sci for Energy Technol. 2(2), 150–160 (2019)
Lazarova, T., et al.: Tunable nanosized spinel manganese ferrites synthesized by solution combustion method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 496, 143571 (2019)
Zahraei, M., et al.: Hydrothermal synthesis of fine stabilized superparamagnetic nanoparticles of Zn2+ substituted manganese ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 393, 429–436 (2015)
Kaewmanee, T., et al.: Effect of oleic acid content on manganese-zinc ferrite properties. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 103, 87–92 (2019)
Vignesh, V., et al.: Electrochemical investigation of manganese ferrites prepared via a facile synthesis route for supercapacitor applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 538, 668–677 (2018)
Jabbar, R., Sabeeh, S.H., Hameed, A.M.: Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Mn+2 doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 494, 165726 (2020)
Ahmad Tokeer, Ruby Phul: Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as contrast agents: hydrothermal synthesis, characterization and properties. Solid State Phenom. 232, 111–114 (2015)
K. Ahalya, N. Suriyanarayanan, S. Sangeetha. : Effect of pH and annealing temperatures on structural, magnetic, electrical, dielectric and adsorption properties of manganese ferrite nano particles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 27, 672–681 (2014)
K. Ahalya, N. Suriyanarayanan, V. Ranjithkumar. : Effect of cobalt substitution on structural and magnetic properties and chromium adsorption of manganese ferrite nano particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 372, 208–213 (2014)
Zhang, C.F., et al.: Effects of cobalt doping on the microstructure and magnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrites prepared by the co-precipitation method. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 404(16), 2327–2331 (2009)
Nejati, K., Zabihi, R.: Preparation and magnetic properties of nano size nickel ferrite particles using hydrothermal method. Chem. Cent. J. 6(1), 1–6 (2012)
Elmoussaoui, H., et al.: New results on magnetic properties of tin-ferrite nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 25(6), 1995–2002 (2012)
Ghatage, A., et al.: X-ray, infrared and magnetic studies of chromium substituted nickel ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 15(17), 1548–1550 (1996)
Slamovich, E.B., Aksay, I.A.: Structure evolution in hydrothermally processed (< 100 C) BaTiO3 films. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79(1), 239–247 (1996)
Li, S., et al.: FTIR and Raman spectral study of the preparation of lead zirconate (PbZrO3) by a solgel process in a non-flowing air atmosphere. J. Mater. Sci. 24(11), 3873–3877 (1989)
Maxwell, J.C.: A treatise on electricity and magnetism, vol. 1. Clarendon Press, London (1873)
Ali, R., et al.: Structural, magnetic and dielectric behavior of Mg 1− x Ca x Ni y Fe 2− y O 4 nano-ferrites synthesized by the micro-emulsion method. Ceram. Int. 40(3), 3841–3846 (2014)
Koops, C.: On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83(1), 121 (1951)
Batoo, K.M., et al.: Influence of Al doping on electrical properties of Ni–Cd nano ferrites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9(4), 826–832 (2009)
El Hiti, M.: Dielectric behavior and ac electrical conductivity of Zn-substituted Ni ▪ Mg ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 164(1), 187–196 (1996)
Dar, M.A., et al.: Low dielectric loss of Mg doped Ni–Cu–Zn nano-ferrites for power applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(14), 5342–5347 (2012)
Bottger, H., Bryksin, V.: Hopping conductivity in solids. Akademie-Verlag, Berlin (1985)
M. A. Amer. : Mössbauer, infrared, and X-ray studies of Ti-doped CoCr1. 2Fe0. 8O4 ferrites. Phys. status solidi B. 237(2), 459– 471 (2003)
Hossain, A.A., et al.: Effect of Li substitution on the magnetic properties of Li x Mg 0.40 Ni 0.60− 2x Fe 2+ x O 4 ferrites. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 406(8), 1506–1512 (2011)
Sertkol, M., et al.: Microwave synthesis and characterization of Zn-doped nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 486(1), 325–329 (2009)
Ali, R., et al.: Impacts of Ni–co substitution on the structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of magnesium nano-ferrites fabricated by micro-emulsion method. J. Alloys Compd. 584, 363–368 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Junaid, M., Jacob, J., Nadeem, M. et al. Structural, Spectroscopic, Dielectric, and Magnetic Properties of Cu-Co–Co-substituted Manganese Soft Ferrites. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 3171–3177 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05567-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05567-2