Abstract
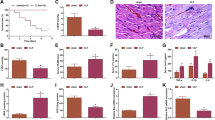
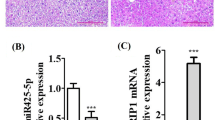
Sepsis is a whole-body inflammation and main cause of death in intensive care units worldwide. We aimed to investigate the roles of lncRNA MIAT and miR-330-5p in modulating inflammatory responses and oxidative stress in lipopolysachariden (LPS)-induced septic cardiomyopathy. Serum and heart tissue were collected from in vivo septic mice model, ELISA and qRT-PCR were used to measure the expression of pro-inflammation cytokines, MIAT and miR-330-5p, respectively. The knockdown of MIAT and overexpression of miR-330-5p were conducted to assess their effects on regulating inflammation response and intracellular oxidative stress in LPS-stimulated HL-1 cells. The reactive oxygen (ROS) level, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), GSH/GSSH ratio, and lipid peroxidation assessment (MDA) were used to evaluate the intracellular oxidative stress. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed to identify the association between MIAT and miR-330-5p, TRAF6 and miR-330-5p, respectively. In septic mice, the expression of MIAT and pro-inflammation cytokines was elevated while the expression of miR-330-5p decreased. Knockdown of MIAT or overexpression of miR-330-5p restrained inflammation and oxidative stress induced by LPS in vitro; MIAT directly targeted miR-330-5p to regulate NF-κB signaling, and miR-330-5p targeted against TRAF6 to suppress the activation of NF-κB signaling. We determined that lncRNA MIAT directly binds to miR-330-5p to activate TRAF6/NF-κB signaling axis and further promotes inflammation response as well as oxidative stress in LPS-induced septic cardiomyopathy. This finding suggests the potential therapeutic role of lncRNA MIAT and miR-330-5p in LPS-induced myocardial injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah M, Berthiaume JM, Willis MS (2017) Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 as a nuclear factor kappa B-modulating therapeutic target in cardiovascular diseases: at the heart of it all. Transl Res 195:48–61
An R et al (2018) miR-146a attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction by suppressing IRAK1 and TRAF6 via Targeting ErbB4 expression. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:7163057
Cui LH et al (2018) lncRNA PCAT6 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion through regulating miR-330-5p. Onco Targets Ther 11:7715–7724
Fang Y et al (2018) LncRNA H19 functions as an Aquaporin 1 competitive endogenous RNA to regulate microRNA-874 expression in LPS sepsis. Biomed Pharmacother 105:1183–1191
Greco S, Gorospe M, Martelli F (2015) Noncoding RNA in age-related cardiovascular diseases. J Mol Cell Cardiol 83:142–155
Gyuraszova M et al (2018) Markers of oxidative stress and antioxidant status in the plasma, urine and saliva of healthy mice. Physiol Res 67(6):921–934
Kalbitz M et al (2016) Complement-induced activation of the cardiac NLRP3 inflammasome in sepsis. FASEB J 30(12):3997–4006
Kong R et al (2017) Inhibition of NOB1 by microRNA-330-5p overexpression represses cell growth of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep 38(4):2572–2580
Lee Y et al (2016) BAT3 negatively regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-kappaB signaling through TRAF6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 478(2):784–790
Li Y et al (2018) LncRNA myocardial infarction-associated transcript (MIAT) contributed to cardiac hypertrophy by regulating TLR4 via miR-93. Eur J Pharmacol 818:508–517
Lin N, An Y (2017) Blockade of 146b–5p promotes inflammation in atherosclerosis-associated foam cell formation by targeting TRAF6. Exp Ther Med 14(5):5087–5092
Liu J, Huang GQ, Ke ZP (2018) Silence of long intergenic noncoding RNA HOTAIR ameliorates oxidative stress and inflammation response in ox-LDL-treated human macrophages by upregulating miR-330-5p. J Cell Physiol 234(4):5134–5142
Liu J, Huang GQ, Ke ZP (2019) Silence of long intergenic noncoding RNA HOTAIR ameliorates oxidative stress and inflammation response in ox-LDL-treated human macrophages by upregulating miR-330-5p. J Cell Physiol 234(4):5134–5142
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Lorigados CB, Soriano FG, Szabo C (2010) Pathomechanisms of myocardial dysfunction in sepsis. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 10(3):274–284
Meng Z et al (2013) Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces inflammatory responses in cultured human mast cells via toll-like receptor 4. Cell Physiol Biochem 31:842–853
Meydan C, Bekenstein U, Soreq H (2018) Molecular regulatory pathways link sepsis with metabolic syndrome: non-coding RNA elements underlying the sepsis/metabolic cross-talk. Front Mol Neurosci 11:189
Mo XY et al (2019) Hydrogen-rich saline protects rat from oxygen glucose deprivation and reperusion-induced apoptosis through VDAC1 via Bcl-2. Brain Res 1706:110–115
Montini L et al (2016) Prognostic value of the reactive oxygen species in severe sepsis and septic shock patients: a pilot study. Minerva Anestesiol 82(12):1306–1313
Okazaki S et al (2014) Redox evaluation in sepsis model mice by the in vivo ESR technique using acyl-protected hydroxylamine. Free Radic Biol Med 68:72–79
Oliveira YPAD et al (2017) Oxidative stress in sepsis Possible production of free radicals through an erythrocyte-mediated positive feedback mechanism. Braz J Infect Dis 21(1):19–26
Pearson MJ, Jones SW (2016) Review: long noncoding RNAs in the regulation of inflammatory pathways in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68(11):2575–2583
Qureshi IA, Mehler MF (2012) Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in brain evolution, development, plasticity and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:528
Rapicavoli NA et al (2013) A mammalian pseudogene lncRNA at the interface of inflammation and anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Elife 2:e00762
Rudiger A, Singer M (2007) Mechanisms of sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med 35(6):1599
Shao S et al (2018) LncRNA myocardial infarction-associated transcript promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis by targeting miR-330-5p in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Arch Med Sci 14(6):1263–1270
Takasu O et al (2013) Mechanisms of cardiac and renal dysfunction in patients dying of sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 187(5):509–517
Tang HM et al (2016) Translational assessment of cardiac contractility by echocardiography in the telemetered rat. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 77:24–32
Tsolaki V et al (2017) Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: oxidative implications in the initiation and resolution of the damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:7393525–7393525
van de Sandt AM et al (2013) Endothelial NOS (NOS3) impairs myocardial function in developing sepsis. Basic Res Cardiol 108(2):330
Wang R et al (2018) LncRNA DGCR5 contributes to CSC-like properties via modulating miR-330-5p/CD44 in NSCLC. J Cell Physiol 233(9):7447–7456
Wu H et al (2016) LncRNA-HOTAIR promotes TNF-α production in cardiomyocytes of LPS-induced sepsis mice by activating NF-κB pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 471(1):240–246
Xiao S et al (2018) miR-330-5p targets SPRY2 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression via MAPK/ERK signaling. Oncogenesis 7(11):90
Yan B et al (2015) lncRNA-MIAT regulates microvascular dysfunction by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Circ Res 116(7):1143–1156
Yang F et al (2013) Long noncoding RNA CCAT1, which could be activated by c-Myc, promotes the progression of gastric carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139(3):437–445
Zou X et al (2014) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagy protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis in HL-1 cardiomyocytes. Exp Physiol 99(10):1348–1358
Funding
The study was supported by Project of Beijing Medical Health Public Welfare Foundation (Grant No. B185040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this study declared no conflict of interests.
Ethics Approval
All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital East.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, PC., An, P., Hu, GY. et al. LncRNA MIAT Promotes Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Sepsis-Induced Cardiac Injury by Targeting miR-330-5p/TRAF6/NF-κB Axis. Biochem Genet 58, 783–800 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-020-09976-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-020-09976-9