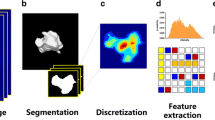
Abstract
Objectives
This work aims to study the variation, robustness, and feature redundancy of PET/MR radiomic features in the primary tumor of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
Procedures
PET/MR scans of 21 NPC patients were used in this study. The primary tumor volumes were defined using PET, T2-weighted-MR (T2-MR), and diffusion-weighted MR (DW-MR) images. A random-dilation-erosion method was used to simulate 10 sets of tumor volumes for identifying features invariant with manual segmentation uncertainties. Feature robustness was evaluated against imaging modalities, pixel sizes, slice thickness, and grey-level bin sizes using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and spearman correlation coefficient. Feature redundancy was analyzed using the hierarchical cluster analysis.
Results
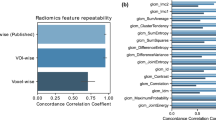
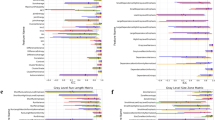
Voxel size of 0.5 × 0.5 × 1.0 mm3 was found optimal for robust feature extraction from PET and MR. Normalized grey level of 64 and 128 was suggested for PET and MR, respectively. The features from wavelet-transformed images were less stable than those from the original images. The robustness analysis and volume correlation analysis identified 335 (62.04 %) PET features, 240 (44.44 %) T2-MR features, and 366 (67.78 %) DW-MR features. The cluster analysis grouped PET, T2-MR, and DW-MR features into 106, 83, and 133 representative features, respectively.
Conclusions
The present study analyzed and identified robust features extracted from tumor volumes on PET/MR, which can provide guidance and promote standardization for PET/MR radiomic studies in NPC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
An X, Wang FH, Ding PR, Deng L, Jiang WQ, Zhang L, Shao JY, Li YH (2011) Plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA level strongly predicts survival in metastatic/recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with palliative chemotherapy. Cancer 117:3750–3757
Peng H, Tang L-L, Chen B-B, Chen L, Li WF, Mao YP, Liu X, Zhang Y, Liu LZ, Tian L, Guo Y, Sun Y, Ma J (2018) Optimizing the induction chemotherapy regimen for patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a big-data intelligence platform-based analysis. Oral Oncol 79:40–46
Tang X-R, Li Y-Q, Liang S-B, Jiang W, Liu F, Ge WX, Tang LL, Mao YP, He QM, Yang XJ, Zhang Y, Wen X, Zhang J, Wang YQ, Zhang PP, Sun Y, Yun JP, Zeng J, Li L, Liu LZ, Liu N, Ma J (2018) Development and validation of a gene expression-based signature to predict distant metastasis in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol 19:382–393
Lee AW, Zong JF, Pan JJ, Choi HC, Sze HC (2019) Staging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma based on the 8th edition of the AJCC/UICC staging system. In nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Elsevier, pp 179-203
Lai V, Khong PL (2014) Updates on MR imaging and 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol 50:539–548
Lambin P, Leijenaar RT, Deist TM et al (2017) Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:749–762
Shi L, Rong Y, Daly M, Dyer B, Benedict S, Qiu J, Yamamoto T (2020) Cone-beam computed tomography-based delta-radiomics for early response assessment in radiotherapy for locally advanced lung cancer. Phys Med Biol 65:015009
Zhang B, Tian J, Dong D, Gu D, Dong Y, Zhang L, Lian Z, Liu J, Luo X, Pei S, Mo X, Huang W, Ouyang F, Guo B, Liang L, Chen W, Liang C, Zhang S (2017) Radiomics features of multiparametric MRI as novel prognostic factors in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 23:4259–4269
Zhang L-L, Huang M-Y, Li Y, Liang JH, Gao TS, Deng B, Yao JJ, Lin L, Chen FP, Huang XD, Kou J, Li CF, Xie CM, Lu Y, Sun Y (2019) Pretreatment MRI radiomics analysis allows for reliable prediction of local recurrence in non-metastatic T4 nasopharyngeal carcinoma. EBioMedicine 42:270–280
Zhang L, Dong D, Li H, Tian J, Ouyang F, Mo X, Zhang B, Luo X, Lian Z, Pei S, Dong Y, Huang W, Liang C, Liu J, Zhang S (2019) Development and validation of a magnetic resonance imaging-based model for the prediction of distant metastasis before initial treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. EBioMedicine 40:327–335
Wang G, He L, Yuan C, Huang Y, Liu Z, Liang C (2018) Pretreatment MR imaging radiomics signatures for response prediction to induction chemotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur J Radiol 98:100–106
Lv W, Yuan Q, Wang Q, et al. (2019) Radiomics analysis of PET and CT components of PET/CT imaging integrated with clinical parameters: application to prognosis for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Imaging Biol 1–11
Peng H, Dong D, Fang M, et al. (2019) Prognostic value of deep learning PET/CT-based radiomics: potential role for future individual induction chemotherapy in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 3065.2018
Chan S-C, Yeh C-H, Yen T-C, Ng SH, Chang JTC, Lin CY, Yen-Ming T, Fan KH, Huang BS, Hsu CL, Chang KP, Wang HM, Liao CT (2018) Clinical utility of simultaneous whole-body 18 F-FDG PET/MRI as a single-step imaging modality in the staging of primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45:1297–1308
Naqa IE (2014) The role of quantitative PET in predicting cancer treatment outcomes. Clin Translat Imaging 2:305–320
Niu T, Yang P, Sun X, Mao T, Xu L, Yue N, Kuang Y, Shi L, Nie K (2018) Variations of quantitative perfusion measurement on dynamic contrast enhanced CT for colorectal cancer: implication of standardized image protocol. Phys Med Biol 63:165009
Rizzo S, Botta F, Raimondi S, Origgi D, Fanciullo C, Morganti AG, Bellomi M (2018) Radiomics: the facts and the challenges of image analysis. Eur Radiol Exp 2:36–36
Hatt M, Laurent B, Ouahabi A, Fayad H, Tan S, Li L, Lu W, Jaouen V, Tauber C, Czakon J, Drapejkowski F, Dyrka W, Camarasu-Pop S, Cervenansky F, Girard P, Glatard T, Kain M, Yao Y, Barillot C, Kirov A, Visvikis D (2018) The first MICCAI challenge on PET tumor segmentation. Med Image Anal 44:177–195
Orlhac F, Nioche C, Soussan M, Buvat I (2017) Understanding changes in tumor texture indices in PET: a comparison between visual assessment and index values in simulated and patient data. J Nucl Med 58:387–392
Hatt M, Tixier F, Pierce L, Kinahan PE, Le Rest CC, Visvikis D (2017) Characterization of PET/CT images using texture analysis: the past, the present… any future? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 44:151–165
Sanduleanu S, Woodruff HC, de Jong EEC, van Timmeren JE, Jochems A, Dubois L, Lambin P (2018) Tracking tumor biology with radiomics: a systematic review utilizing a radiomics quality score. Radiother Oncol 127:349–360
Sala E, Mema E, Himoto Y, Veeraraghavan H, Brenton JD, Snyder A, Weigelt B, Vargas HA (2017) Unravelling tumour heterogeneity using next-generation imaging: radiomics, radiogenomics, and habitat imaging. Clin Radiol 72:3–10
Lu L, Lv W, Jiang J, Ma J, Feng Q, Rahmim A, Chen W (2016) Robustness of radiomic features in [11 C] choline and [18 F] FDG PET/CT imaging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: impact of segmentation and discretization. Mol Imaging Biol 18:935–945
Belli ML, Mori M, Broggi S, Cattaneo GM, Bettinardi V, Dell'Oca I, Fallanca F, Passoni P, Vanoli EG, Calandrino R, di Muzio N, Picchio M, Fiorino C (2018) Quantifying the robustness of [18F] FDG-PET/CT radiomic features with respect to tumor delineation in head and neck and pancreatic cancer patients. Phys Med 49:105–111
Berenguer R, Pastor-Juan MDR, Canales-Vazquez J et al (2018) Radiomics of CT features may be nonreproducible and redundant: influence of CT acquisition parameters. Radiology 288:407–415
Hatt M, Majdoub M, Vallieres M, Tixier F, le Rest CC, Groheux D, Hindie E, Martineau A, Pradier O, Hustinx R, Perdrisot R, Guillevin R, el Naqa I, Visvikis D (2015) 18F-FDG PET uptake characterization through texture analysis: investigating the complementary nature of heterogeneity and functional tumor volume in a multi-cancer site patient cohort. J Nucl Med 56:38–44
Yang X-L, Wang Y, Liang S-B, He SS, Chen DM, Chen HY, Lu LX, Chen Y (2018) Comparison of the seventh and eighth editions of the UICC/AJCC staging system for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: analysis of 1317 patients treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy at two centers. BMC Cancer 18:606
Cao C, Yang P, Xu Y, Niu T, Hu Q, Chen X (2019) Feasibility of multiparametric imaging with PET/MR in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a pilot study. Oral Oncol 93:91–95
Tustison NJ, Avants BB, Cook PA, Yuanjie Zheng, Egan A, Yushkevich PA, Gee JC (2010) N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29:1310–1320
Rasmussen JH, Nørgaard M, Hansen AE, Vogelius IR, Aznar MC, Johannesen HH, Costa J, Engberg AME, Kjær A, Specht L, Fischer BM (2017) Feasibility of multiparametric imaging with PET/MR in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Nucl Med 58:69–74
Frings V, van Velden FHP, Velasquez LM, Hayes W, van de Ven PM, Hoekstra OS, Boellaard R (2014) Repeatability of metabolically active tumor volume measurements with FDG PET/CT in advanced gastrointestinal malignancies: a multicenter study. Radiology 273:539–548
Koçak B, Durmaz EŞ, Ateş E, Kılıçkesmez Ö (2019) Radiomics with artificial intelligence: a practical guide for beginners. Diagn Interv Radiol 25:485–495
Shi L, He Y, Yuan Z et al (2018) Radiomics for response and outcome assessment for non-small cell lung cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat 17:1533033818782788–1533033818782788
Koo TK, Li MY (2016) A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med 15:155–163
Kim YJ, Lee H-J, Kim KG, Lee SH (2019) The effect of CT scan parameters on the measurement of CT radiomic features: a lung nodule phantom study. Comput Math Methods Med 2019:1–12
Lu L, Lv W, Jiang J et al (2016) Robustness of textural features in 11C-choline and 18F-FDG PET/CT scans of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Nucl Med 57:1896
Shen X, Yang F, Yang P, et al. (2020) A contrast-enhanced computed tomography based radiomics approach for preoperative differentiation of pancreatic cystic neoplasm subtypes: a feasibility study Front Oncol 10
Vallières M, Freeman CR, Skamene SR, El Naqa I (2015) A radiomics model from joint FDG-PET and MRI texture features for the prediction of lung metastases in soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities. Phys Med Biol 60:5471–5496
Papp L, Rausch I, Grahovac M, Hacker M, Beyer T (2019) Optimized feature extraction for radiomics analysis of 18F-FDG PET imaging. J Nucl Med 60:864–872
Xu M, Fang M, Zou J, Yang S, Yu D, Zhong L, Hu C, Zang Y, Dong D, Tian J, Fang X (2019) Using biparametric MRI radiomics signature to differentiate between benign and malignant prostate lesions. Eur J Radiol 114:38–44
Zhao L, Lu Z, Jiang J, Zhou Y, Wu Y, Feng Q (2019) Automatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma segmentation using fully convolutional networks with auxiliary paths on dual-modality PET-CT images. J Digit Imaging 32:462–470
Ma Z, Wu X, Song Q, Luo Y, Wang Y, Zhou J (2018) Automated nasopharyngeal carcinoma segmentation in magnetic resonance images by combination of convolutional neural networks and graph cut. Exp Ther Med 16:2511–2521
Sun R, Limkin EJ, Vakalopoulou M, Dercle L, Champiat S, Han SR, Verlingue L, Brandao D, Lancia A, Ammari S, Hollebecque A, Scoazec JY, Marabelle A, Massard C, Soria JC, Robert C, Paragios N, Deutsch E, Ferté C (2018) A radiomics approach to assess tumour-infiltrating CD8 cells and response to anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy: an imaging biomarker, retrospective multicohort study. Lancet Oncol 19:1180–1191
Wu J, Gensheimer MF, Dong X et al (2016) Robust intratumor partitioning to identify high-risk subregions in lung cancer: a pilot study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 95:1504–1512
Popovtzer A, Ibrahim M, Tatro D, Feng FY, Ten Haken RK, Eisbruch A (2014) MRI to delineate the gross tumor volume of nasopharyngeal cancers: which sequences and planes should be used? Radiol Oncol 48:323–330
Anderson CM, Sun W, Buatti JM et al (2014) Interobserver and intermodality variability in GTV delineation on simulation CT, FDG-PET, and MR images of head and neck cancer. Jacobs J Radiat Oncol 1:006–006
Fave X, Mackin D, Yang J, Zhang J, Fried D, Balter P, Followill D, Gomez D, Kyle Jones A, Stingo F, Fontenot J, Court L (2015) Can radiomics features be reproducibly measured from CBCT images for patients with non-small cell lung cancer? Med Phys 42:6784–6797
Larue RTHM, Van De Voorde L, van Timmeren JE et al (2017) 4DCT imaging to assess radiomics feature stability: an investigation for thoracic cancers. Radiother Oncol 125:147–153
Zhang L, Zhou H, Gu D, Tian J, Zhang B, Dong D, Mo X, Liu J, Luo X, Pei S, Dong Y, Huang W, Chen Q, Liang C, Lian Z, Zhang S (2019) Radiomic nomogram: pretreatment evaluation of local recurrence in nasopharyngeal carcinoma based on MR imaging. J Cancer 10:4217–4225
Hatt M, Vallieres M, Visvikis D, Zwanenburg A (2018) IBSI: an international community radiomics standardization initiative. J Nucl Med 59:287
Papp L, Rausch I, Grahovac M, Hacker M, Beyer TJJNM (2019) Optimized feature extraction for radiomics analysis of 18F-FDG. PET Imaging 60:864–872
Whybra P, Parkinson C, Foley K, Staffurth J, Spezi E (2019) Assessing radiomic feature robustness to interpolation in 18F-FDG PET imaging. Sci Rep 9:9649
Lu L, Lv W, Jiang J, Ma J, Feng Q, Rahmim A, Chen W (2016) Robustness of radiomic features in [11C]choline and [18F]FDG PET/CT imaging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: impact of segmentation and discretization. Mol Imaging Biol 18:935–945
Su C, Jiang J, Zhang S, Shi J, Xu K, Shen N, Zhang J, Li L, Zhao L, Zhang J, Qin Y, Liu Y, Zhu W (2019) Radiomics based on multicontrast MRI can precisely differentiate among glioma subtypes and predict tumour-proliferative behaviour. Eur Radiol 29:1986–1996
Shafiq-ul-Hassan M, Zhang GG, Latifi K, Ullah G, Hunt DC, Balagurunathan Y, Abdalah MA, Schabath MB, Goldgof DG, Mackin D, Court LE, Gillies RJ, Moros EG (2017) Intrinsic dependencies of CT radiomic features on voxel size and number of gray levels. Med Phys 44:1050–1062
Huang SY, Franc BL, Harnish RJ, Liu G, Mitra D, Copeland TP, Arasu VA, Kornak J, Jones EF, Behr SC, Hylton NM, Price ER, Esserman L, Seo Y (2018) Exploration of PET and MRI radiomic features for decoding breast cancer phenotypes and prognosis. NPJ Breast Cancer 4:24
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Caineng Cao and Xiaozhong Chen, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital and Yuanfan Xu, Hangzhou Universal Medical Imagine Diagnostion for generously providing the PET/MR dataset.
Funding
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFE0114800), Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC Grant Nos. 81871351, 81827804, 81950410632), and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LY17E050008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 43 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, P., Xu, L., Cao, Z. et al. Extracting and Selecting Robust Radiomic Features from PET/MR Images in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Mol Imaging Biol 22, 1581–1591 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-020-01507-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-020-01507-7