Abstract
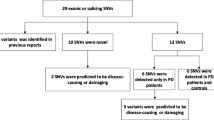
In the past two decades, genetic studies of familial forms of Parkinson’s disease (PD) have shown evidence that PD has a significant genetic component. Indeed, 12 genes are strongly involved in PD causality, three of them having dominant inheritance and 9 causing early-onset autosomal recessive forms, including 3 with a typical PD and 6 with an atypical parkinsonism. The aim of this study was to determine the genetic basis of familial PD in Moroccan patients. We selected 18 Moroccan index case with familial forms of PD. Patients were first screened for exon-rearrangements by MLPA kit. They were then analyzed by gene panel next-generation sequencing (NGS). Functional variants with minor allele frequencies < 0.5% in public databases were considered potential candidate variants to PD. In the 18 PD patients with a positive family history that were analyzed, MLPA assays identified PRKN deletions in two patients: a homozygous exon 3–5 deletion and a heterozygous exon 4 deletion. Sixteen rare SNV were identified by NGS, four of them were novel. Seven mutations were categorized as pathogenic, five as likely pathogenic, two to be of uncertain significance, and 3 were predicted to be likely benign but may give a weaker pathogenic effect and could contribute to PD since they were found in late-onset PD patients. Rare or novel mutations that could be related to the disease were identified in 72% of these patients (13/18), including nine with bi-allelic pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants in genes causing recessive PD, particularly PRKN and PINK1. Mutations in genes with dominant inheritance were found in 4/18 patients (22%).

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Aarsland D, Taylor JP, Weintraub D (2014) Psychiatric issues in cognitive impairment. Mov Disord 29:651–662
Bhatia KP, Daniel SE, Marsden CD (1993) Familial parkinsonism with depression: a clinicopathological study. Ann Neurol 34:842–847
Bouhouche A, Tesson C, Regragui W, Rahmani M, Drouet V, Tibar H, Souirti Z, Ben El Haj R, Bouslam N, Yahyaoui M, Brice A, Benomar A, Lesage S (2017a) Mutation analysis of consanguineous Moroccan patients with Parkinson’s disease combining microarray and gene panel. Front Neurol l8:567
Bouhouche A, Tibar H, Ben El Haj R, El Bayad K, Razine R, Tazrout S, Skalli A, Bouslam N, Elouardi L, Benomar A, Yahyaoui M, Regragui W (2017b) LRRK2 G2019S mutation: prevalence and clinical features in Moroccans with Parkinson’s disease. Park Dis 2017:2412486
De Virgilio A, Greco A, Fabbrini G, Inghilleri M, Rizzo MI, Gallo A, Conte M, Rosato C, Ciniglio Appiani M, de Vincentiis M (2016) Parkinson’s disease: autoimmunity and neuroinflammation. Autoimmun Rev 15:1005–1011
Deng H, Wang P, Jankovic J (2018) The genetics of Parkinson disease. Ageing Res Rev 42:72–85
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:181–184
Kasten M, Hartmann C, Hampf J, Schaake S, Westenberger A, Vollstedt EJ, Balck A, Domingo A, Vulinovic F, Dulovic M, Zorn I, Madoev H, Zehnle H, Lembeck CM, Schawe L, Reginold J, Huang J, König IR, Bertram L, Marras C, Lohmann K, Lill CM, Klein C (2018) Genotype-phenotype relations for the Parkinson’s disease genes Parkin, PINK1, DJ1: MDSGene systematic review. Mov Disord 33:730–741
Kumar R, Jangir DK, Verma G, Shekhar S, Hanpude P, Kumar S, Kumari R, Singh N, Sarovar Bhavesh N, Ranjan Jana N, Kanti Maiti T (2017) S-nitrosylation of UCHL1 induces its structural instability and promotes α-synuclein aggregation. Sci Rep 7:44558
Lechevalier B, Schupp C, Fallet-Bianco C, Viader F, Eustache F, Chapon F, Morin P (1992) Familial parkinsonian syndrome with athymhormia and hypoventilation. Rev Neurol (Paris) 148:39–46
Leroy E, Boyer R, Auburger G, Leube B, Ulm G, Mezey E, Harta G, Brownstein MJ, Jonnalagada S, Chernova T, Dehejia A, Lavedan C, Gasser T, Steinbach PJ, Wilkinson KD, Polymeropoulos MH (1998) The ubiquitin pathway in Parkinson's disease. Nature 395:451–452
Lesage S, Dürr A, Tazir M, Lohmann E, Leutenegger AL, Janin S, Pollak P, Brice A (2006) LRRK2 G2019S as a cause of Parkinson’s disease in north African Arabs. N Engl J Med 354:422–423
Lunati A, Lesage S, Brice A (2018) The genetic landscape of Parkinson's disease. Rev Neurol (Paris) 174:628–643
Mishima T, Fujioka S, Kurisaki R, Yanamoto S, Higuchi MA, Tsugawa J, Fukae J, Neshige R, Tsuboi Y (2015) Impulse control disorders and punding in Perry syndrome. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 21:1381–1382
Mishima T, Fujioka S, Tomiyama H, Yabe I, Kurisaki R, Fujii N, Neshige R, Ross OA, Farrer MJ, Dickson DW, Wszolek ZK, Hattori N, Tsuboi Y (2018) Establishing diagnostic criteria for Perry syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 89:482–487
Monfrini E, Di Fonzo A (2017) Leucine-rich repeat kinase (LRRK2) genetics and Parkinson’s disease. Adv Neurobiol 14:3–30
Perry TL, Bratty PJ, Hansen S, Kennedy J, Urquhart N, Dolman CL (1975) Hereditary mental depression and parkinsonism with taurine deficiency. Arch Neurol 32:108–113
Postuma RB, Berg D (2017) New diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Int Rev Neurobiol 132:55–78
Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M, Poewe W, Olanow CW, Oertel W, Obeso J, Marek K, Litvan I, Lang AE, Halliday G, Goetz CG, Gasser T, Dubois B, Chan P, Bloem BR, Adler CH, Deuschl G (2015) MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30:1591–1601
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, Voelkerding K, Rehm HL (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 17:405–424
Riederer P, Berg D, Casadei N, Cheng F, Classen J, Dresel C, Jost W, Krüger R, Müller T, Reichmann H, Rieß O, Storch A, Strobel S, van Eimeren T, Völker HU, Winkler J, Winklhofer KF, Wüllner U, Zunke F, Monoranu CM (2019) α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: causal or bystander? J Neural Transm (Vienna) 126:815–840
Tran HH, Dang SNA, Nguyen TT, Huynh AM, Dao LM, Kamei K, Yamaguchi M, Dang TTP (2018) Drosophila ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase knockdown model of Parkinson’s disease. Sci Rep 8:4468
Trinh J, Zeldenrust FMJ, Huang J, Kasten M, Schaake S, Petkovic S, Madoev H, Grünewald A, Almuammar S, König IR, Lill CM, Lohmann K, Klein C, Marras C (2018) Genotype-phenotype relations for the Parkinson’s disease genes SNCA, LRRK2, VPS35: MDSGene systematic review. Mov Disord 33:1857–1870
Tsuboi Y, Wszolek ZK, Kusuhara T, Doh-ura K, Yamada T (2002) Japanese family with parkinsonism, depression, weight loss, and central hypoventilation. Neurology 58:1025–1030
Tysnes OB, Storstein A (2017) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 124:901–905
Wang J, Liu Y, Chen T (2017) Identification of key genes and pathways in Parkinson’s disease through integrated analysis. Mol Med Rep 16:3769–3776
Wider C, Wszolek ZK (2008) Rapidly progressive familial parkinsonism with central hypoventilation, depression and weight loss (Perry syndrome)-a literature review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14:1–7
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all patients for their participation in this study and to Dr. Leslie Hunter for improving the English language of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported by the “Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur, de la Recherche Scientifique et de la Formation des Cadres” (MESRSFC) of Morocco and the “Centre National de Recherche Scientifique et Technique” (CNRST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
All research was approved by the ethics committee of biomedical research of Medical School and Pharmacy of Rabat (CERB).
Consent to Participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all of the participants in the study.
Consent for Publication
Written informed consent for publication of clinical details and clinical images was obtained from all of the participants.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary Fig. 1
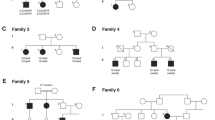
Family pedigree of the eighteen index PD cases studied. a Families with probably autosomal dominant inheritance; b families with probably autosomal recessive inheritance; c families with unspecified inheritance. (PPT 925 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Comparison between the two NGS gene panels used in this study. (DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smaili, I., Tesson, C., Regragui, W. et al. Gene Panel Sequencing Identifies Novel Pathogenic Mutations in Moroccan Patients with Familial Parkinson Disease. J Mol Neurosci 71, 142–152 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01635-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01635-3