Abstract
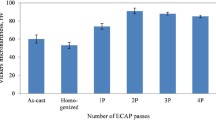
This research examines the effect of wear testing parameters on the wear behavior of AZ91 alloy prepared through rotary-die equal channel angular pressing (RD-ECAP). An AZ91 alloy was processed by RD-ECAP method at 573 K for up to 16 passes to reduce the grain size to ~ 5 µm. The properties of the alloys produced by RD-ECAP were compared with the as-received alloy. In order to measure the wear behavior of RD-ECAP manufactured alloy with the as-received alloy, wear tests were performed using ball-on-disk apparatus with specific loading conditions and varying sliding speeds. Surface analysis was used to show the presence of delamination, wear debris and plowing using scanning electron microscopes (SEM). The findings showed that, due to the grain refinement and homogeneity of the second phase distribution, RD-ECAP processed magnesium alloys possess increased wear resistance compared to the initial condition (unprocessed alloy), which makes them suitable for applications in aerospace, automotive and structural industries. Besides, the weight loss reduced with the increase of RD-ECAP pass numbers. Furthermore, increasing in applied load had a more dramatic effect on wear resistance compared to increasing sliding speed and sliding time.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.K. Kulekci, Magnesium and Its Alloys Applications in Automotive Industry, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2007, 39(9–10), p 851–865
K. Hirai, H. Somekawa, Y. Takigawa, and K. Higashi, Effects of Ca and Sr Addition on Mechanical Properties of a Cast AZ91 Magnesium Alloy at Room and Elevated Temperature, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 403(1–2), p 276–280
Y.J. Chen, Q.D. Wang, J.G. Peng, C.Q. Zhai, and W.J. Ding, Effects of Extrusion Ratio on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ31 Mg Alloy, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 182(1–3), p 281–285
A. Singh and S.P. Harimkar, Laser Surface Engineering of Magnesium Alloys: A Review, JOM, 2012, 64(6), p 716–733
J.X. Chen, L.L. Tan, X.M. Yu, I.P. Etim, M. Ibrahim, and K. Yang, Mechanical Properties of Magnesium Alloys for Medical Application: A Review, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2018, 87, p 68–79
X.B. Gong, H. Li, S.B. Kang, J.H. Cho, and S.Y. Li, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Twin-Roll Cast Mg-4.5Al-1.0Zn Sheets Processed by Differential Speed Rolling, Mater. Des., 2010, 31(3), p 1581–1587
X.B. Gong, S.B. Kang, S.Y. Li, and J.H. Cho, Enhanced Plasticity of Twin-Roll Cast ZK60 Magnesium Alloy Through Differential Speed Rolling, Mater. Des., 2009, 30(9), p 3345–3350
R.M. Wang, A. Eliezer, and E.M. Gutman, An Investigation on the Microstructure of an AM50 Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 355(1–2), p 201–207
B.C. Pai, U.T.S. Pillai, P. Manikandan, and A. Srinivasan, Modification of AZ91 Mg Alloys for High Temperature Applications, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2012, 65(6), p 601–606
E. Mostaed, M. Vedani, M. Hashempour, and M. Bestetti, Influence of ECAP Process on Mechanical and Corrosion Properties of Pure Mg and ZK60 Magnesium Alloy for Biodegradable Stent Applications, Biomatter, 2014, 4, p e28283
A.A. Luo, Magnesium Casting Technology for Structural Applications, Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2013, 1(1), p 2–22
M.V. Markushev, M.Y. Murashkin, P.B. Prangnell, A. Golinia, and O.A. Maiorova, Structure and Mechanical Behaviour of An Al-Mg alloy After Equal Channel Angular Extrusion, Nanostruct. Mater., 1999, 12, p 839–842
G.K. Manjunath, K. Udaya Bhat, G.V. Preetham Kumar, and M.R. Ramesh, Microstructure and Wear Performance of ECAP Processed Cast Al-Zn-Mg Alloys, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2018, 71(8), p 1919–1931
S. Surendarnath, K. Sankaranarayanasamy, and B. Ravisankar, A Comparative Study of Commercially Pure Aluminum Processed by ECAP Using Conventional and New Die, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2014, 29(10), p 1172–1178
G. Faraji, P. Yavari, S. Aghdamifar, and M. Mosavi Mashhadi, Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Ultra-fine Grained AZ91 Magnesium Alloy Tubes Processed via Multi Pass Tubular Channel Angular Pressing (TCAP), J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2014, 30(2), p 134–138
R.B. Figueiredo and T.G. Langdon, Principles of Grain Refinement in Magnesium Alloys Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, J. Mater. Sci., 2009, 44(17), p 4758–4762
J. Krolo, B. Lela, I. Dumanić, and F. Kozina, Statistical Analysis of the Combined ECAP and Heat Treatment for Recycling Aluminum Chips Without Remelting, Metals, 2019, 9(6), p 660
K.R. Gopi, H.S. Nayaka, and S. Sahu, Corrosion Behavior of ECAP-Processed AM90 Magnesium Alloy, Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 2018, 43(9), p 4871–4878
M.I. Abd El Aal, N. El Mahallawy, F.A. Shehata, M. Abd El Hameed, E.Y. Yoon, and H.S. Kim, Wear Properties of ECAP-Processed Ultrafine Grained Al-Cu Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(16–17), p 3726–3732
Q. Xu, A.B. Ma, Y.H. Li, B. Saleh, Y.C. Yuan, J.H. Jiang, and C.Y. Ni, Enhancement of Mechanical Properties and Rolling Formability in AZ91 Alloy by RD-ECAP Processing, Materials, 2019, 12(21), p 3503
K.R. Gopi, Nayaka H. Shivananda, and S. Sahu, Microstructural Evolution and Strengthening of AM90 Magnesium Alloy Processed by ECAP, Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 2017, 42(11), p 4635–4647
M. Saravanan, R.M. Pillai, B.C. Pai, M. Brahmakumar, and K.R. Ravi, Equal Channel Angular Pressing of Pure Aluminium-An Analysis, Bull. Mater. Sci., 2006, 29, p 679–684
K. Máthis, J. Gubicza, and N.H. Nam, Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of AZ91 Mg Alloy Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, J. Alloys Compd., 2005, 394(1–2), p 194–199
M. Chegini, A. Fallahi, and M.H. Shaeri, Effect of Equal Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP) on Wear Behavior of Al-7075 Alloy, Procedia Mater. Sci., 2015, 11, p 95–100
S.R. Kumar, K. Gudimetla, P. Venkatachalam, B. Ravisankar, and K. Jayasankar, Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Al 7075 Alloy Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 533, p 50–54
L.L. Gao and X.H. Cheng, Microstructure and Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Cu-10%Al-4%Fe Alloy Produced by Equal Channel Angular Extrusion, Wear, 2008, 265(7–8), p 986–991
C.T. Wang, N. Gao, R.J.K. Wood, and T.G. Langdon, Wear Behavior of An Aluminum Alloy Processed by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, J. Mater. Sci., 2010, 46(1), p 123–130
A.W. El-Morsy, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Hot Deformed Magnesium AZ61 Alloy as Influenced by the Sliding Conditions, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 473(1–2), p 330–335
G.A. Zhang, C.Y. Ma, and Q. Zhou, Semi-Solid Billets of AZ91D Magnesium Alloy Prepared by Forward Extrusion/Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, Adv. Mater. Res., 2011, 299–300, p 380–384
M. Srinivasan, C. Loganathan, M. Kamaraj, Q.B. Nguyen, M. Gupta, and R. Narayanasamy, Sliding Wear Behaviour of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy and Nano-composite, Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China, 2012, 22(1), p 60–65
J. Xu, X.W. Wang, X.C. Zhu, M. Shiooyeh, J. Wongsa-Ngam, D.B. Shan, and T.G. Langdon, Dry Sliding Wear of An AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Processed by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, J. Mater. Sci., 2013, 48(11), p 4117–4127
K.R. Gopi and H.S. Nayaka, Tribological and Corrosion Properties of AM70 Magnesium Alloy Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, J. Mater. Res., 2017, 32(11), p 1–8
J.H. Chen, Y.C. Shen, C.G. Chao, and T.F. Liu, Wear Behavior and Microstructure of Mg-Sn Alloy Processed by Equal Channel Angular Extrusion, Materials (Basel), 2017, 10(11), p 1315
G.M. Naik, S. Narendranath, and S.S. Satheesh Kumar, Effect of Grain Refinement on the Performance of AZ80 Mg Alloys During Wear and Corrosion, Adv. Mater. Res., 2018, 7(2), p 105–118
H.Y. Wang, E.B. Zhang, X.L. Nan, L. Zhang, Z.P. Guan, and Q.C. Jiang, A Comparison of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-9Al-1Zn Sheets Rolled from As-cast, Cast-rolling and As-extruded alloys, Mater. Des., 2016, 89, p 167–172
L.F. Wang, E. Mostaed, X.J. Cao, G.S. Huang, A. Fabrizi, F. Bonollo, C.Z. Chi, and M. Vedani, Effects of Texture and Grain Size on Mechanical Properties of AZ80 Magnesium Alloys at Lower Temperatures, Mater. Des., 2016, 89, p 1–8
B. Saleh, J.H. Jiang, Q. Xu, R. Fathi, A.B. Ma, Y.H. Li, and L.S. Wang, Statistical Analysis of Dry Sliding Wear Process Parameters for AZ91 Alloy Processed by RD-ECAP Using Response Surface Methodology, Met. Mater. Int., 2020, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00624-w
W.J. Kim, C.W. An, Y.S. Kim, and S.I. Hong, Mechanical Properties and Microstructures of an AZ61 Mg Alloy Produced by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Scripta Mater., 2002, 47, p 39–44
W.J. Kim, S.I. Hong, Y.S. Kim, S.H. Min, H.T. Jeong, and J.D. Lee, Texture Development and Its Effect on Mechanical Properties of An AZ61 Mg Alloy Fabricated by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(11), p 3293–3307
Acknowledgments
The study was founded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51979099 51774109 and 51701065), the Key Research and Development Project of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BE2017148) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2018B48414). Q.X. is grateful for the support from the China Scholarship Council and the W. M. Keck Center for Advanced Microscopy and Microanalysis at University of Delaware.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Ma, A., Saleh, B. et al. Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of AZ91 Alloy Processed by Rotary-Die Equal Channel Angular Pressing. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 3961–3973 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04883-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04883-x