Abstract
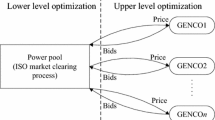
Global warming is one of the most alarming phenomena facing our planet today. There is a consensus among scientists that human-induced greenhouse gases (GHGs) should be regulated to slow down the heating of the Earth’s oceans and atmosphere. Energy consumption and CO2 emissions are continuously increasing in different countries, especially developing ones such as India, whose emerging economy and rapid economic development has caught the attention of the world. CO2 emission trading is executed by the various developed countries to alleviate the affect of GHG emissions. In this work, an optimal bidding strategy for a supplier has been developed, considering rival’s bidding behavior, in an hourly day-ahead pool market. Bidding problem has been formulated as a bi-level multi objective optimization problem (BLMOOP), where in the first level generator submit bid strategically to the ISO and in the next level a particle swarm optimization (PSO) approach has been employed for the maximization of social welfare with risk management. It is assumed that each generator should submit bid in sealed auction based on pay-as-bid MCP (market clearing price) mechanism with knowing the rival’s bidding behavior. The practicability of proposed optimization method is examined by an IEEE-30 bus system which consists of six suppliers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirschen D, Strbac G (2004) Fundamentals of power system economics, university of Manchester institute of science and technology. Wiley, New York
Stoft S (2002) Power system economics (designing markets for electricity), (chapter 1–3) Part 1. IEEE Press & Wiley, New York
Jamasb T, Thakur T, Bag B (2018) Smart electricity distribution networks, business models, and application for developing countries. Energy Policy 114:22–29
Liu Y, Wu FF (2006) Generator bidding in oligopolistic electricity markets using optimal control: fundamentals and application. IEEE Trans Power Syst 21(3):1050–1061
Shahdehpour M, Almoush M (2001) Restructured electrical power systems operation, trading and volatility. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
David AK, Wen F (2000) Strategic bidding in competitive electricity markets: a literature survey. In: Proceedings of IEEE power engineering society summer meeting, vol. 4, pp 2168–2173
David AK, Wen F (2001) Market power in electricity supply. IEEE Trans Energy Convers. 16(4):352–360
Kian Ashkan R, Cruz Jose B, Thomas RJ (2005) Bidding strategies in oligopolistic dynamic electricity double-sided auctions. IEEE Trans Power Syst 20(1):50–58
Srivastava AK, Kamalasadan S, Patel D, Sankar S, Al-Olimat KS (2011) Electricity markets: an overview and comparative study. Int J Energy Sec Manage 5(2):169–200
Shahidehpour M, Yamin H, Li Z (2002) Market operations in electric power systems: forecasting, scheduling, and risk management. IEEE Wiley-Inter Science, New York
Li G, Shi J, Qu X (2011) Modeling methods for GenCo bidding strategy optimization in the liberalized electricity spot markete—a state-of-the-art review. Energy 36:4686–4700
Mathur S, Arya A, Dubey M (2017) Optimal bidding strategy for price takers and customers in a competitive electricity market. Cogent Eng 1(4):1–15 (Taylor Francis)
Mathur S, Arya A, Dubey M (2018) Impact of emission trading on optimal bidding of price takers in a competitive energy market. Adv Intell Syst Comput 741:171–180 (Springer)
BUR (2016) India’s Biennial update reports to the United Nations Framework convention on climate change. Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India, New Delhi
CEA (2013) Performance review of thermal power stations 2013–14. Central Electricity Authority, Government of India, New Delhi
Arya A, Mathur SPS, Dubey M (2020) Impact of emission trading and renewable energy support scheme on the optimality of generator side bidding. In: E3S web of conferences, vol 167 (2020), 11th international conference on environmental science and development, Barcelona, Spain, February 10–12
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on neural networks, IV, Perth, Australia, pp. 1942–1948
Kumar A, Pant S, Singh SB (2016) Reliability optimization of complex system by using cuckoos search algorithm” mathematical concepts and applications in mechanical engineering and mechatronics, IGI global, pp 95–112
Pant S, Singh SB (2011) Particle swarm optimization to reliability optimization in complex system. In: IEEE international conference on quality and reliability, Bangkok, Thailand, Sept 14–17, pp 211–215
Raglend IJ, Padhy NP (2006) Solutions to practical unit commitment problems with operational, power flow and environmental constraints. In: IEEE power engineering society general meeting, pp 1–8
Azadeh A, Ghaderi SF, Nokhandan BP, Sheikhalishahi M (2012) A new genetic algorithm approach for optimizing bidding strategy viewpoint of profit maximization of a generation company. Expert Syst Appl 39(1):1565–1574
Acknowledgements
This Publication is an outcome of the R & D work undertaken in the project under the Young Faculty Research Fellowship, Visvesvaraya PhD Scheme of Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology, Government of India, being implemented by Digital India Corporation (formerly Media Lab Asia). We would also like to show our gratitude to Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal for providing us the required facilities during the course of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arya, A., Mathur, S.P.S. & Dubey, M. Optimal generator side bidding with carbon emission trading and risk management. CSIT 8, 235–240 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-020-00298-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-020-00298-0