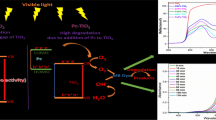
Abstract
There is a great deal of concern about the presence of pharmaceutical pollutants (PP) in water from various sources. The applications of heterogeneous photocatalysis using titanium dioxide (TiO2) for water treatment have been a feasible technology to overcome the occurrence of PP in water and wastewater. At the same time, polymer composite has proven as an excellent material due to its wide range of applications. Polymer modification of TiO2 enhances its effectiveness for visible light absorption employing sensitization. Hence, research interest, in the field of photocatalysis, has recently shifted to TiO2-based polymer nanocomposites, due to their exceptional optical, electrical, adsorptive, and catalytic properties. This article provides a review of various polymer-modified TiO2, as excellent adsorbent and photocatalytic materials for heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceutical and other organic pollutants. Discussions were also made on the basic principles of the heterogeneous photocatalytic process as it applies to the use of TiO2 and its modified forms (polymer–TiO2), as well as the kinetics and mechanism of polymer molecule–sensitized TiO2 catalyst for the degradation of selected pharmaceutical organic pollutants. Finally, some of the photocatalytic degradation intermediates for the selected pharmaceuticals were reviewed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Wahab AM, Al-Shirbini AS, Mohamed O, Nasr O (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of paracetamol over magnetic flower-like TiO2/Fe2O3 core-shell nanostructures. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 347:186–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.07.030
Ahmed MJ (2017) Adsorption of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from aqueous solution using activated carbons: review. J Environ Manag 190:274–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.073
Akpan UG, Hameed BH (2009) Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2-based photocatalysts: a review. J Hazard Mater 170:520–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.039
Ali F, Khan SB, Kamal T, Alamry KA, Asiri AM. (2018) Chitosan-titanium oxide fibers supported zero-valent nanoparticles: Highly efficient and easily retrievable catalyst for the removal of organic pollutants. Sci Rep. 8(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24311-4
Alhaji MH, Sanaullah K, Khan A, Hamza A, Muhammad A, Ishola MS, Rigit ARH, Bhawani SA (2017) Recent developments in immobilizing titanium dioxide on supports for degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater- a review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14:2039–2052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1349-4
Al-Hamdi AM, Sillanpää M, Dutta J (2015) Photocatalytic degradation of phenol by iodine doped tin oxide nanoparticles under UV and sunlight irradiation. J Alloys Compd 618:366–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.08.120
Al-Hamdi AM, Rinner U, Sillanpää M (2017) Tin dioxide as a photocatalyst for water treatment: a review. Process Saf Environ Prot 107:190–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.01.022
Al-Odaini NA, Zakaria MP, Yaziz MI, Surif S, Abdulghani M (2011) The occurrence of human pharmaceuticals in wastewater effluents and surface water of Langat River and its tributaries, Malaysia. Int J Environ Anal Chem 7319:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2011.592949
An T, Yang H, Li G, Song W, Cooper WJ, Nie X (2010) Kinetics and mechanism of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in degradation of ciprofloxacin in water. Appl Catal B Environ 94:288–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APCATB.2009.12.002
Ananpattarachai J, Seraphin S, Kajitvichyanukul P (2016) Formation of hydroxyl radicals and kinetic study of 2-chlorophenol photocatalytic oxidation using C-doped TiO2, N-doped TiO2, and C,N Co-doped TiO2 under visible light. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:3884–3896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5570-8
Antunes SC, Freitas R, Figueira E, Gonçalves F, Nunes B (2013) Biochemical effects of acetaminophen in aquatic species: edible clams Venerupis decussata and Venerupis philippinarum. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:6658–6666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1784-9
Ashfaq M, Nawaz Khan K, Saif Ur Rehman M, Mustafa G, Faizan Nazar M, Sun Q, Iqbal J, Mulla SI, Yu CP (2017) Ecological risk assessment of pharmaceuticals in the receiving environment of pharmaceutical wastewater in Pakistan. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 136:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.10.029
Ata R, Sacco O, Vaiano V, Rizzo L, Tore YG, Sannino D (2017) Visible light active N-doped TiO2 immobilized on polysrene as efficient system for wastewater treatment. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 348:255–262
Atul W, Gaikward G, Dondhe M, Khaty N (2013) Removal of organic pollutant from water by heterogeneous photocatalysis: a review. Res J Chem Environ 17:84–94
Augugliaro V, Bellardita M, Loddo V, Palmisano G, Palmisano L, Yurdakal S (2012) Overview on oxidation mechanisms of organic compounds by TiO2 in heterogeneous photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol C: Photochem Rev 13:224–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPHOTOCHEMREV.2012.04.003
Autónoma U, De Química F, Concordia CA, Carmen C (2011) Photocatalytic degradation of acetaminophen. Int J Environ Res 5:1071–1078
Awofiranye OS, Modise SJ, Naidoo EB (2020) Design and synthesis of polyvinyl alcohol derived conjugated polyene modified TiO2 for visible-light degradation of chloramphenicol. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103755
Balakrishna K, Rath A, Praveenkumarreddy Y, Guruge KS, Subedi B (2017) A review of the occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in Indian water bodies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 137:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.11.014
Behnajady MA, Modirshahla N, Hamzavi R (2006) Kinetic study on photocatalytic degradation of C.I. acid yellow 23 by ZnO photocatalyst. J Hazard Mater 133:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2005.10.022
Bijanzad K, Tadjarodi A, Moghaddasi Khiavi M, Akhavan O (2015) Microwave-assisted synthesis of bismuth oxybromochloride nanoflakes for visible light photodegradation of pollutants. Phys B Condens Matter 475:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2015.06.013
Boreen AL, Arnold WA, McNeill K (2003) Photodegradation of pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: a review. Aquat Sci 65:320–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-003-0672-7
Boukhatem H, Khalaf H, Djouadi L, Gonzalez FV, Navarro RM, Santaballa JA, Canle M (2017) Photocatalytic activity of mont-La (6%)-Cu0.6Cd0.4S catalyst for phenol degradation under near UV visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 211:114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.03.074
Bubacz K, Kusiak-Nejman E, Tryba B, Morawski AW (2013) Investigation of OH radicals formation on the surface of TiO2/N photocatalyst at the presence of terephthalic acid solution. Estimation of optimal conditions. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 261:7–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPHOTOCHEM.2013.04.003
Calamari D, Zuccato E, Castiglioni S, Bagnati R, Fanelli R (2003) Strategic survey of therapeutic drugs in the rivers Po and Lambro in northern Italy. Environ Sci Technol 37:1241–1248. https://doi.org/10.1021/es020158e
Chen PH, Jenq CH (1998) Kinetics of photocatalytic oxidation of trace organic compounds over titanium dioxide. Environ Int 24:871–879. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(98)00077-4
Chen X, Lu W, Xu T, Li N, Zhu Z, Wang G, Chen W (2017) Visible-light-assisted generation of high-valent iron-oxo species anchored axially on g-C3N4 for efficient degradation of organic pollutants. Chem Eng J 328:853–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.110
Chen Z, Wu C, Zhang Z, Wu W, Wang X, Yu Z (2018) Synthesis, functionalization, and nanomedical applications of functional magnetic nanoparticles. Chin Chem Lett 29:1601–1608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2018.08.007
Cheshme Khavar AH, Moussavi G, Mahjoub AR (2018) The preparation of TiO2@rGO nanocomposite efficiently activated with UVA/LED and H2O2for high rate oxidation of acetaminophen: catalyst characterization and acetaminophen degradation and mineralization. Appl Surf Sci 440:963–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.238
Daghrir R, Drogui P, Robert D (2013) Modified TiO2 for environmental photocatalytic applications: a review. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:3581–3599. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie303468t
Dankovich TA, Smith JA (2014) Incorporation of copper nanoparticles into paper for poit-of-use water purification. Water Research 63:245–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.06.022
Díez AM, Moreira FC, Marinho BA, Espíndola JCA, Paulista LO, Sanromán MA, Pazos M, Boaventura RAR, Vilar VJP (2018) A step forward in heterogeneous photocatalysis: process intensification by using a static mixer as catalyst support. Chem Eng J 343:597–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.041
Dong S, Li Y, Sun J, Sun J, Yu C, Li Y (2014) Facile synthesis of novel ZnO/RGO hybrid nanocomposites with enhanced catalytic performance for visible-light-driven photodegradation of metronidazole. Mater Chem Phys 145:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.02.024
Dong H, Qiang Z, Hu J, Qu J (2017) Degradation of chloramphenicol by UV/chlorine treatment: kinetics, mechanism and enhanced formation of halonitromethanes. Water Res 121:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.05.030
Eibes G, Lú-Chau T, Feijoo G, Moreira MT, Lema JM (2005) Complete degradation of anthracene by manganese peroxidase in organic solvent mixtures. Enzym Microb Technol 37:365–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENZMICTEC.2004.02.010
Fagan R, McCormack DE, Dionysiou DD, Pillai SC (2016) A review of solar and visible light active TiO2photocatalysis for treating bacteria, cyanotoxins and contaminants of emerging concern. Mater Sci Semicond Process 42:2–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.07.052
Feder HM, Osier C (2016) Chloramphenicol: a review of its use in clinical practice. Author(s): Henry M. Feder, Jr., Carl Osier and Eufronio G. Maderazo Source: Reviews of infectious diseases. Vol. 3, No. 3 (May - Jun, 1981), pp. 479–491. Published by: Oxford Univ 3, 479–491
Gao B, Chen W, Dong S, Liu J, Liu T, Wang L, Sillanpää M (2017) Polypyrrole/ZnIn2S4 composite photocatalyst for enhanced mineralization of chloramphenicol under visible light. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 349:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.09.018
Ghosh A, Nayak AK, Pal A (2017) Nano-particle-mediated wastewater treatment: a review. Curr Pollut Rep 3:17–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-016-0045-1
Hammad HM, Zia F, Bakhat HF, Fahad S, Ashraf MR, Wilkerson CJ, Shah GM, Nasim W, Khosa I, Shahid M (2018) Uptake and toxicological effects of pharmaceutical active compounds on maize. Agric Ecosyst Environ 258:143–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2018.02.022
Hassani A, Khataee A, Karaca S, Fathinia M (2017) Degradation of mixture of three pharmaceuticals by photocatalytic ozonation in the presence of TiO2/montmorillonite nanocomposite: simultaneous determination and intermediates identification. J Environ Chem Eng 5:1964–1976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.03.032
He Y, Sutton NB, Rijnaarts HHH, Langenhoff AAM (2016) Degradation of pharmaceuticals in wastewater using immobilized TiO2 photocatalysis under simulated solar irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 182:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.09.015
Hernández-Uresti DB, Vázquez A, Sanchez-Martinez D, Obregón S (2016) Performance of the polymeric g-C3N4 photocatalyst through the degradation of pharmaceutical pollutants under UV-vis irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 324:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.01.031
Hoffmann MR, Hoffmann MR, Martin ST, Choi W, Bahnemannt DW (1995) Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem Rev 95:69–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00033a004
Hou H, Xu G, Tan S, Zhu Y (2017) A facile sol-gel strategy for the scalable synthesis of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles with enhanced infrared radiation property: influence of the synthesis conditions. Infrared Phys Technol 85:261–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2017.07.008
Igberase E, Osifo P (2015) Equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic and desorption studies of cadmium and lead by polyaniline grafted cross-linked chitosan beads from aqueous solution. J Ind Eng Chem 26:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JIEC.2014.12.007
Jallouli N, Elghniji K, Trabelsi H, Ksibi M (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of paracetamol on TiO2nanoparticles and TiO2/cellulosic fiber under UV and sunlight irradiation. Arab J Chem 10:S3640–S3645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.03.014
Jallouli N, Pastrana-Martínez LM, Ribeiro AR, Moreira NFF, Faria JL, Hentati O, Silva AMT, Ksibi M (2018) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of ibuprofen in ultrapure water, municipal and pharmaceutical industry wastewaters using a TiO2/UV-LED system. Chem Eng J 334:976–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.045
Jia Q, Wang W, Zhao J, Xiao J, Lu L, Fan H (2017) Synthesis and characterization of TiO2/polyaniline/graphene oxide bouquet-like composites for enhanced microwave absorption performance. J Alloys Compd 710:717–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2017.03.234
Jin Q, Wang H, Hu C, Chen Z, Wang X (2018) Effects of NOM on the degradation of chloramphenicol by UV/H2O2 and the characteristics of degradation products. Sep Purif Technol 191:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.09.014
Jyothi KP, Yesodharan S, Yesodharan EP (2016) Contaminant salts as enhancers of sonocatalytic degradation of organic water pollutants: effect of concentration, reaction time and adsorption on the efficiency of enhancement and the fate of concurrently formed H2O2. J Environ Chem Eng 6:3574–3589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.12.053
Kaur A, Umar A, Kansal SK (2015) Sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug based on TiO2 quantum dots. J Colloid Interface Sci 459:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.08.010
Kaur A, Umar A, Kansal SK (2016) Heterogeneous photocatalytic studies of analgesic and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Appl Catal A Gen 510:134–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2015.11.008
Khataee A, Kıranşan M, Karaca S, Sheydaei M (2017) Photocatalytic ozonation of metronidazole by synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles immobilized on montmorillonite. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 74:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.02.014
Kim Phuong NT, Beak M-W, Huy BT, Lee YI (2016) Adsorption and photodegradation kinetics of herbicide 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid with MgFeTi layered double hydroxides. Chemosphere 146:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.008
Kosera VS, Cruz TM, Chaves ES, Tiburtius ERL (2017) Triclosan degradation by heterogeneous photocatalysis using ZnO immobilized in biopolymer as catalyst. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 344:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.05.014
Kshirsagar AS, Gautam A, Khanna PK (2017) Efficient photo-catalytic oxidative degradation of organic dyes using CuInSe2/TiO2 hybrid hetero-nanostructures. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 349:73–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.08.058
Kumar SG, Devi LG (2011) Review on modified TiO2 photocatalysis under UV/visible light: selected results and related mechanisms on interfacial charge carrier transfer dynamics. J Phys Chem A 115:13211–13241. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp204364a
Lan Y, Zhou L, Tong Z, Pang Q, Wang F, Gong F (2011) Synthesis and characterization of polythiophene-modified TiO2 nanotube arrays. Bull Mater Sci 34:1173–1177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-011-0243-9
Lassoued A, Lassoued MS, Dkhil B, Ammar S, Gadri A (2018) Synthesis, photoluminescence and magnetic properties of iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles through precipitation or hydrothermal methods. Physica E 101:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2018.04.009
Leung HW, Minh TB, Murphy MB, Lam JCW, So MK, Martin M, Lam PKS, Richardson BJ (2012) Distribution, fate and risk assessment of antibiotics in sewage treatment plants in Hong Kong, South China. Environ Int 42:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVINT.2011.03.004
Li WC (2014) Occurrence, sources, and fate of pharmaceuticals in aquatic environment and soil. Environ Pollut 187:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.01.015
Li X, Wang G, Li X, Lu D (2004) Surface properties of polyaniline/nano-TiO2 composites. Appl Surf Sci 229:395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2004.02.022
Li Q, Su H, Tan T (2008) Synthesis of ion-imprinted chitosan-TiO2 adsorbent and its multi-functional performances. Biochem Eng J 38:212–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BEJ.2007.07.007
Li H, Li Y, Xiang L, Huang Q, Qiu J, Zhang H, Sivaiah MV, Baron F, Barrault J, Petit S, Valange S (2015) Heterogeneous photo-Fenton decolorization of Orange II over Al-pillared Fe-smectite: response surface approach, degradation pathway, and toxicity evaluation. J Hazard Mater 287:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2015.01.023
Li S, Zhao S, Qiang S, Chen G, Chen Y, Chen Y (2018a) A novel zein/poly (propylene carbonate)/nano-TiO2 composite films with enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Process Biochem 70:198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2018.03.029
Li T, Zhang CZ, Ding D, Fan X, Li Y (2018b) Experimental and theoretical study on degradation of oxidized C60 in water via photo-Fenton method. Chem Eng J 334:587–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.062
Liang B, Cheng HY, Kong DY, Gao SH, Sun F, Cui D, Kong FY, Zhou AJ, Liu WZ, Ren NQ, Wu WM, Wang AJ, Lee DJ (2013) Accelerated reduction of chlorinated nitroaromatic antibiotic chloramphenicol by biocathode. Environ Sci Technol 47:5353–5361. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400933h
Lima JM, Silva GC, Lopes CBJ, Dias MM, Faria LJ (2017) Homogeneous and heterogeneous photo-Fenton degradation of antibiotics using an innovative static mixer photoreactor. Chem Eng J 310:342–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.032
Lin Y-Y, Chu T-H, Li S-S, Chuang C-H, Chang C-H, Su W-F, Chang C-P, Chu M-W, Chen C-W (2009) Interfacial nanostructuring on the performance of polymer / TiO2 nanorod bulk heterojunction solar cells. J Am Chem Soc 131:3644–3649. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja8079143
Lin JCT, Deluna MDG, Aranzamendez GL, Lu MC (2016) Degradation of acetaminophen via a K2S2O8-doped TiO2 photocatalyst under visible light irradiation. Chemo. 155:388–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.059
Liu G, Zhao Y, Sun C, Li F, Lu GQ, Cheng HM (2008) Synergistic effects of B/N doping on the visible-light photocatalytic activity of mesoporous TiO2. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:4516–4520. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200705633
Liu P, Zhang H, Feng Y, Yang F, Zhang J (2014) Removal of trace antibiotics from wastewater: a systematic study of nanofiltration combined with ozone-based advanced oxidation processes. Chem Eng J 240:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2013.11.057
Liu Y, Wei S, Gao W (2015) Ag/ZnO heterostructures and their photocatalytic activity under visible light: effect of reducing medium. J Hazard Mater 287:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.12.045
Liu X, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Luo L, Yang Y, Huang H, Peng H, Tang L, Mu Y (2018) Insight into electro-Fenton and photo-Fenton for the degradation of antibiotics: mechanism study and research gaps. Chem Eng J 347:379–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.142
Loaiza-Ambuludi S, Panizza M, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2014) Removal of the anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen from water using homogeneous photocatalysis. Catal Today 224:29–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2013.12.018
López Zavala MÁ, Estrada EE (2016) Degradation of acetaminophen and its transformation products in aqueous solutions by using an electrochemical oxidation cell with stainless steel electrodes. Water (Switzerland) 8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090383
Ma J, Chen K (2018) Silica-free hydrothermal synthesis of ε-Fe2O3 nanoparticles and their oriented attachment to nanoflakes with unique magnetism evolution. Ceram Int 44:19338–19344. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2018.07.162
Magureanu M, Mandache NB, Parvulescu VI (2015) Degradation of pharmaceutical compounds in water by non-thermal plasma treatment. Water Res 81:124–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.05.037
Manzo V, Honda L, Navarro O, Ascar L, Richter P (2014) Microextraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from waste water samples by rotating-disk sorptive extraction. Talanta 128:486–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.06.003
Marsoni M, De Mattia F, Labra M, Bruno A, Bracale M, Vannini C (2014) Uptake and effects of a mixture of widely used therapeutic drugs in Eruca sativa L. and Zea mays L. plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 108:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2014.05.029
Martelli A, Mattioli F, Pastorino G, Robbiano L, Allavena A, Brambilla G (1991) Genotoxicity testing of chloramphenicol in rodent and human cells. Mutat Res 260:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1218(91)90081-V
Mezohegyi G, Gonçalves F, Órfão JJM, Fabregat A, Fortuny A, Font J, Bengoa C, Stuber F (2010) Tailored activated carbons as catalysts in biodecolourisation of textile azo dyes. Appl Catal B Environ 94:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APCATB.2009.11.007
Minh TB, Leung HW, Loi IH, Chan WH, So MK, Mao JQ, Choi D, Lam JCW, Zheng G, Martin M, Lee JHW, Lam PKS, Richardson BJ (2009) Antibiotics in the Hong Kong metropolitan area: ubiquitous distribution and fate in Victoria Harbour. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1052–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2009.02.004
Mirzaei A, Chen Z, Haghighat F, Yerushalmi L (2016) Removal of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds from water by zinc oxide-based photocatalytic degradation: a review. Sustain Cities Soc 27:407–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2016.08.004
Moctezuma E, Leyva E, Aguilar CA, Luna RA, Montalvo C (2012) Photocatalytic degradation of paracetamol: intermediates and total reaction mechanism. J Hazard Mater 243:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.10.010
Mohapatra L, Parida KM (2012) Zn–Cr layered double hydroxide: visible light responsive photocatalyst for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Sep Purif Technol 91:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2011.10.028
Muxika A, Etxabide A, Uranga J, Guerrero P, de la Caba K (2017) Chitosan as a bioactive polymer: processing, properties and applications. Int J Biol Macromol 105:1358–1368. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2017.07.087
Nasirian M, Lin YP, Bustillo-Lecompte CF, Mehrvar M (2018) Enhancement of photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide using non-metal doping methods under visible light: a review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:2009–2032. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1618-2
Nassar MY, Ahmed IS, Samir I (2014) A novel synthetic route for magnesium aluminate (MgAl2O4) nanoparticles using sol-gel auto combustion method and their photocatalytic properties. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 131:329–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.04.040
Olaleye MT, Rocha BTJ (2008) Acetaminophen-induced liver damage in mice: effects of some medicinal plants on the oxidative defense system. Exp Toxicol Pathol 59:319–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2007.10.003
Oseghe EO, Ofomaja AE (2018) Facile microwave synthesis of pine cone derived C-doped TiO2 for the photodegradation of tetracycline hydrochloride under visible-LED light. J Environ Manag 223:860–867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.07.003
Oturan MA, Aaron JJ (2014) Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: principles and applications. A review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44:2577–2641. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2013.829765
Parsley LC, Consuegra EJ, Kakirde KS, Land AM, Harper WF, Liles MR (2010) Identification of diverse antimicrobial resistance determinants carried on bacterial, plasmid, or viral metagenomes from an activated sludge microbial assemblage. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3753–3757. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03080-09
Peng X, Wang Z, Kuang W, Tan J, Li K (2006) A preliminary study on the occurrence and behavior of sulfonamides, ofloxacin and chloramphenicol antimicrobials in wastewaters of two sewage treatment plants in Guangzhou, China. Sci Total Environ 371:314–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2006.07.001
Pera-Titus M, García-Molina V, Baños MA, Giménez J, Esplugas S (2004) Degradation of chlorophenols by means of advanced oxidation processes: a general review. Appl Catal B Environ 47:219–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APCATB.2003.09.010
Pourakbar M, Moussavi G, Shekoohiyan S (2016) Homogenous VUV advanced oxidation process for enhanced degradation and mineralization of antibiotics in contaminated water. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 125:72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2015.11.040
Qiao X, Zheng X, Xie Q, Yang X, Xiao J, Xue W, Chen J (2014) Faster photodegradation rate and higher dioxin yield of triclosan induced by cationic surfactant CTAB. J Hazard Mater 275:210–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2014.05.012
Qin W, Song Y, Dai Y, Qiu G, Ren M, Zeng P (2015) Treatment of berberine hydrochloride pharmaceutical wastewater by O3/UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation process. Environ Earth Sci 73:4939–4946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4192-2
Qiu J, Zhang X, Feng Y, Zhang X, Wang H, Yao J (2018) Modified metal-organic frameworks as photocatalysts. Appl Catal B Environ 231:317–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.03.039
Ri K, Lgh LR, Uurolgrqh YLQO, Dv D, Dqg DJ, Dwlrq K (2016) $ 6lpsoh &khplfdo 3uhflslwdwlrq 0hwkrg ri 7lwdqlxp ‘lr[lgh 1dqrsduwlfohv 8vlqj 3ro\ylq\o 3\uurolgrqh dv d &dsslqj $jhqw dqg 7khlu &kdudfwhul]dwlrq. 10, 556–559
Saud PS, Pant B, Alam A-M, Ghouri ZK, Park M, Kim H-Y (2015) Carbon quantum dots anchored TiO2 nanofibers: effective photocatalyst for waste water treatment. Ceram Int 41:11953–11959. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2015.06.007
Schartel B, Dittrich B, Wartig K, Hofmann D, Rolf M (2015) The influence of layered, spherical, and tubular carbon nanomaterials’ concentration on the flame retardancy of polypropylene. Polym Compos 2:1230–1241. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.23027
Shih IK (1971) Photodegradation products of chloramphenicol in aqueous solution. J Pharm Sci 60:1889–1890. https://doi.org/10.1002/JPS.2600601231
Shokri A, Mahanpoor K, Soodbar D (2016) Evaluation of a modified TiO2(GO-B-TiO2) photo catalyst for degradation of 4-nitrophenol in petrochemical wastewater by response surface methodology based on the central composite design. J Environ Chem Eng 4:585–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.11.007
Sirés I, Brillas E (2012) Remediation of water pollution caused by pharmaceutical residues based on electrochemical separation and degradation technologies: a review. Environ Int 40:212–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2011.07.012
Slamani S, Abdelmalek F, Ghezzar MR, Addou A (2018) Initiation of Fenton process by plasma gliding arc discharge for the degradation of paracetamol in water. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 359:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.03.032
Šojić Merkulov DV, Despotović VN, Banić ND, Armaković SJ, Finčur NL, Lazarević MJ, Četojević-Simin DD, Orčić DZ, Radoičić MB, Šaponjić ZV, Čomor MI, Abramović BF (2018) Photocatalytic decomposition of selected biologically active compounds in environmental waters using TiO2/polyaniline nanocomposites: kinetics, toxicity and intermediates assessment. Environ Pollut 239:457–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.039
Soon AN, Hameed BH (2011) Heterogeneous catalytic treatment of synthetic dyes in aqueous media using Fenton and photo-assisted Fenton process. Desalination 269:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.002
Srikanth B, Goutham R, Narayan RB, Ramprasath A, Gopinath KP, Sankaranarayanan AR. (2017) Recent advancements in supporting materials for immobilised photocatalytic applications in waste water treatment. J Environ Manage. 200:60–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.063
Su WY, Lin W-H, Hsu Y-J, Wei K-H (2014) Conjugated polymer/nanocrustal nanocomposites for renewable energy applications in photovoltaics and photocatalysis. Small J 10:4427–4442. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201401508
Sun L, Shi Y, Li B, Li X, Wang Y (2013) Preparation and characterization of polypyrrole / TiO2 nanocomposites by reverse microemulsion polymerization and its photocatalytic activity for the degradation of methyl orange under natural light. Polym Compos 34:1076–1080. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.22515
Talane TE, Mbule PS, Noto LL, Shingange K, Mhlongo GH, Mothudi BM, Dhlamini MS (2018) Sol-gel preparation and characterization of Er3+ doped TiO2 luminescent nanoparticles. Mater Res Bull 108:234–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.09.007
Tan KB, Abdullah AZ, Horri BA, Salamatinia B (2016) Adsorption mechanism of microcrystalline cellulose as green adsorbent for the removal of cationic methylene blue dye. J Chem Soc Pak 38:651
Teh CY, Wu TY, Juan JC (2017) An application of ultrasound technology in synthesis of titania-based photocatalyst for degrading pollutant. Chem Eng J 317:586–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.001
Thi VHT, Lee BK (2017) Effective photocatalytic degradation of paracetamol using La-doped ZnO photocatalyst under visible light irradiation. Mater Res Bull 96:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.04.028
Tiwari B, Sellamuthu B, Ouarda Y, Drogui P, Tyagi RD, Buelna G (2017) Review on fate and mechanism of removal of pharmaceutical pollutants from wastewater using biological approach. Bioresour Technol 224:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.11.042
Tobajas M, Belver C, Rodriguez JJ (2017) Degradation of emerging pollutants in water under solar irradiation using novel TiO2-ZnO/clay nanoarchitectures. Chem Eng J 309:596–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2016.10.002
Tong H, Zhan X, Tian X, Li J, Qian D, Wu D (2018) Understanding the energy level matching relationships between semiconductor photocatalysts and organic pollutants for effective photocatalytic degradations. J Colloid Interface Sci 526:384–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.05.009
Tran HTT, Kosslick H, Ibad MF, Fischer C, Bentrup U, Vuong TH, Nguyen LQ, Schulz A (2017) Photocatalytic performance of highly active brookite in the degradation of hazardous organic compounds compared to anatase and rutile. Appl Catal B Environ 200:647–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.017
Trandafilović LV, Jovanović DJ, Zhang X, Ptasińska S, Dramićanin MD (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange by ZnO:Eu nanoparticles. Appl Catal B Environ 203:740–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.10.063
Turchi CS, Ollis DF (1990) Photocatalytic degradation of organic water contaminants: mechanisms involving hydroxyl radical attack. J Catal 122:178–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9517(90)90269-P
Unni M, Uhl AM, Savliwala S, Savitzky BH, Dhavalikar R, Garraud N, Arnold DP, Kourkoutis LF, Andrew JS, Rinaldi C (2017) Thermal decomposition synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles with diminished magnetic dead layer by controlled addition of oxygen. ACS Nano 11:2284–2303. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b00609
Vaiano V, Sacco O, Sannino D, Ciabelli P, Longo S, Venditto V, Guerra G (2014) N-doped TiO2/s-PS aerogels for photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes in wastewater under visible light irradiation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89:1175–1181
Wang Y, Jamal R, Wang M, Yang L, Liu F, Abdiryim T (2017) A donor–acceptor–donor-type conjugated polymer-modified TiO2 with enhanced photocatalytic activity under simulated sunlight and natural sunlight. J Mater Sci 52:4820–4832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0717-7
Wia̧cek AE, Gozdecka A, Jurak M (2018) Physicochemical characteristics of chitosan-TiO2 biomaterial. 1. Stability and swelling properties. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:1859–1870. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b04257
Xi C, Zhang Y, Marrs CF, Ye W, Simon C, Foxman B, Nriagu J (2009) Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in drinking water treatment and distribution systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5714–5718. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00382-09
Xiang Q, Yu J, Jaroniec M (2012) Synergetic effect of MoS 2 and graphene as cocatalysts for enhanced photocatalytic H2 production activity of TiO2 nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 134:6575–6578. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja302846n
Xu W, Zhang G, Zou S, Li X, Liu Y (2007) Determination of selected antibiotics in the Victoria Harbour and the Pearl River, South China using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Environ Pollut 145:672–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2006.05.038
Xu S, Gu L, Wu K, Yang H, Song Y, Jiang L, Dan Y (2012) The influence of the oxidation degree of poly(3-hexylthiophene) on the photocatalytic activity of poly(3-hexylthiophene)/TiO2 composites. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 96:286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOLMAT.2011.09.022
Xu B, Ding T, Zhang Y, Wen Y, Yang Z, Zhang M (2017) A new efficient visible-light-driven composite photocatalyst comprising ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles and conjugated polymer from the dehydrochlorination of polyvinyl chloride. Mater Lett 187:123–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.10.094
Yan C, Yang Y, Zhou J, Liu M, Nie M, Shi H, Gu L (2013) Antibiotics in the surface water of the Yangtze estuary: occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Environ Pollut 175:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2012.12.008
Yang L, Yu LE, Ray MB (2008) Degradation of paracetamol in aqueous solutions by TiO2 photocatalysis. Water Res 42:3480–3488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.04.023
Yang Y, Wen J, Xiong R, Shi J, Plan C (2013) Polypyrrole decorated Ag-TiO2 nanofibers exhibiting enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible-light illumination. Appl Mater Interfaces 5(13):6201–6207. https://doi.org/10.10221/am401167g
Yang S, Li L, Xiao T, Zhang Y, Zheng D (2016) Promoting effect of ammonia modification on activated carbon catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation. Sep Purif Technol 160:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.01.020
Yang L, Yu Y, Zhang J, Chen F, Meng X, Qiu Y, Dan Y, Jiang L (2018) In-situ fabrication of diketopyrrolopyrrole-carbazole based conjugated polymer/TiO2 heterojunction for enhanced visible light photocatalysis. Appl Surf Sci 434:796–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.176
Yao B, Peng C, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Niu J, Zhao J (2015) A novel Fe(III) porphyrin-conjugated TiO2 visible-light photocatalyst. Appl Catal B Environ 174–175:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.02.030
Yu TH, Lin AYC, Panchangam SC, Hong PKA, Yang PY, Lin CF (2011) Biodegradation and bio-sorption of antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs using immobilized cell process. Chemosphere 84:1216–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.045
Zeghioud H, Khellaf N, Djelal H, Amrane A, Bouhelassa M (2016) Photocatalytic reactors dedicated to the degradation of hazardous organic pollutants: kinetics, mechanistic aspects, and design – a review. Chem Eng Commun 203:1415–1431. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2016.1202243
Zhang L, Jaroniec M (2018) Toward designing semiconductor-semiconductor heterojunctions for photocatalytic applications. Appl Surf Sci 430:2–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.192
Zhang XX, Zhang T, Fang HHP (2009) Antibiotic resistance genes in water environment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:397–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1829-z
Zhang L, Li L, Mou Z, Li X (2012) Study on microstructure and catalytic performance of B, C, N co-doped TiO2. Proc Eng 27:552–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROENG.2011.12.486
Zhang N, Yang MQ, Tang ZR, Xu YJ (2014a) Toward improving the graphene-semiconductor composite photoactivity via the addition of metal ions as generic interfacial mediator. ACS Nano 8:623–633. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn405242t
Zhang Q, Liang T, Wang L, Cai Y, Okoli CP (2014b) Cross-linked starch-based polymer as an SPE material for the determination of nitrophenols at trace levels in environmental water. J Sep Sci 37:257–264. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201300934
Zhang D, Yin J, Zhao J, Zhu H, Wang C (2015a) Adsorption and removal of tetracycline from water by petroleum coke-derived highly porous activated carbon. J Environ Chem Eng 3:1504–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.05.014
Zhang H, Zhang P, Ji Y, Tian J, Du Z (2015b) Photocatalytic degradation of four non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in water under visible light by P25-TiO2/tetraethyl orthosilicate film and determination via ultra performance liquid chromatography electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Chem Eng J 262:1108–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.019
Zhang G, Chen L, Fu X, Wang H (2018) Cellulose microfiber-supported TiO2@Ag nanocomposites: a dual-functional platform for photocatalysis and in situ reaction monitoring. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:4277–4286. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b00006
Zhao J, Ji M, Di J, Ge Y, Zhang P, Xia J, Li H (2017a) Synthesis of g-C3N4/Bi4O5Br2 via reactable ionic liquid and its cooperation effect for the enhanced photocatalytic behavior towards ciprofloxacin degradation. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 347:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.07.023
Zhao Y, Tao C, Xiao G, Su H (2017b) Controlled synthesis and wastewater treatment of Ag2O/TiO2 modified chitosan-based photocatalytic film. RSC Adv 7:11211–11221. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra27295a
Zhao Y, Wang Y, Xiao G, Su H (2019) Fabrication of biomaterial/TiO2 composite photocatalysts for the selective removal of trace environmental pollutants. Chin J Chem Eng 27:1416–1428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2019.02.003
Ziylan-Yavaş A, Ince NH (2018) Catalytic ozonation of paracetamol using commercial and Pt-supported nanocomposites of Al2O3: the impact of ultrasound. Ultrason Sonochem 40:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.02.017
Zuorro A, Fidaleo M, Fidaleo M, Lavecchia R (2014) Degradation and antibiotic activity reduction of chloramphenicol in aqueous solution by UV/H2O2 process. J Environ Manag 133:302–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2013.12.012
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Vaal University of Technology for the Ph.D. research opportunity given to OS Awofiranye.
Funding
The funding for this project was provided for Awofiranye OS (217044050) for his Ph.D. research study, by the research directorate, Vaal University of Technology, South Africa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Awofiranye: writing of the original draft, Modise: supervision and project administration, and Naidoo: review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awofiranye, O.S., Modise, S.J. & Naidoo, E.B. Overview of polymer–TiO2 catalyst for aqueous degradation of pharmaceuticals in heterogeneous photocatalytic process. J Nanopart Res 22, 168 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-04877-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-04877-9