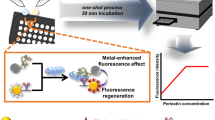
Abstract
Anti-PLA2R antibody is only expressed in podocytes from patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN). The detection of anti-PLA2R antibody in serum is therefore able to obtain essential information for rapid diagnosis and evaluation of the disease activity of IMN. In the present study, a polydopamine nanosphere-based fluorescent sensor was constructed for direct detection of anti-PLA2R antibodies in human serum. In this sensing system, the double-stranded DNA was phosphorylated under the action of anti-PLA2R antibody and the single-stranded DNA was cut by exonuclease. The single-stranded DNA was then adsorbed on polydopamine microspheres. The fluorescent groups labeled on the DNA were quenched, and the concentration of anti-PLA2R antibody was detected quantitatively by measuring the fluorescence signal changes before and after the reaction. The experimental results show that the method has a good linear detection range between 0.05 and 10 μg/mL for anti-PLA2R antibody and the detection limit is 0.02 μg/mL.

Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glassock RJ. Diagnosis and natural course of membranous nephropathy. Semin Nephrol. 2003;23(4):324–32.
Li LS, Liu ZH. Epidemiologic data of renal diseases from a Single unit in China: analysis based on 13 519 renal biopsies. Kidney Int. 2004;66(4):920–3.
Dou Y, Zhang L, Liu D, Wang C, Quan S, Ma S, et al. The accuracy of the anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody in the diagnosis of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a comparison of different cutoff values as measured by the ELISA method. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016;48(6):845–9.
Segal PE, Choi MJ. Recent advances and prognosis in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2012;19(2):114–9.
Laurence H, Ramon B, Gérard L, David M, David WP, Timothy DC, et al. M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(1):11–21.
Qin W, Beck LH, Zeng C, Chen Z, Li S, Zuo K, et al. Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody in membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22(6):1137–43.
Augert A, Payré C, de Launoit Y, Gil J, Lambeau G, Bernard D. The M-type receptor PLA2R regulates senescence through the p53 pathway. EMBO Rep. 2009;10(3):271–7.
Timmermans S, Ayalon R, Paassen P, Beck LH Jr, Rie H, Wirtz JJM, et al. Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibodies and malignancy in membranous nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(6):l223–I225.
Hofstra JM, Debiec H, Short CD, Pelle T, Kleta R, Mathieson PW, et al. Antiphospholipase A2 receptor antibody titer and subclass in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23(10):1735–l743.
Kanigicherla D, Gummadova J, McKenzie EA, Stephen AR, Shelley H, Milind N, et al. Anti-PLA2R antibodies measured by ELISA predict long-term outcome in a prevalent population of patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2013;83(5):940–8.
Yan J, Yang L, Lin MF, Ma J, Lu X, Lee PS. Polydopamine spheres as active templates for convenient synthesis of various nanostructures. Small. 2013;9:596–603.
Qiang W, Li W, Li X, Chen X, Xu D. Bioinspired polydopamine nanospheres: a superquencher for fluorescence sensing of biomolecules. Chem Sci. 2014;5:3018–24.
Liu Q, Pu Z, Asiri AM, Al-Youbi AO, Sun X. Polydopamine nanospheres: a biopolymer-based fluorescent sensing platform for DNA detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2014;191:567–71.
Fan D, Wu C, Wang K, Gu X, Liu Y, Wang E. A polydopamine nanosphere based highly sensitive and selective aptamer cytosensor with enzyme amplification. Chem Commun. 2016;52:406–9.
Qiang W, Wang X, Li W, Chen X, Li H, Xu D. A fluorescent biosensing platform based on the polydopamine nanospheres intergrating with exonuclease III-assisted target recycling amplification. Biosens.Bioelectron. 2015;71:143–9.
Karimi-Busheri F, Daly G, Robins P, Canas B, Pappin DJ, Sgouros J, et al. Molecular characterization of a human DNA kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:24187–94.
Lillehaug JR, Kleppe RK, Kleppe K. Phosphorylation of double-stranded DNAs by T4 polynucleotide kinase. Biochem. 1976;15:1858–65.
Funding
This study was funded by the financial support of Nature Sciences Funding of Fujian Province (2018J01293).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Lu, H., Ye, H. et al. A new fluorescence sensor developed with polydopamine nanospheres for the detection of anti-PLA2R antibody biomarkers of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Anal Bioanal Chem 412, 4549–4554 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02703-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02703-8