Abstract
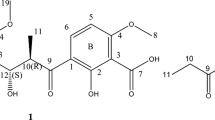
Four anthraquinone derivatives, termstrin A, B, C and D (1–4), were isolated and purified from termite-associated Streptomyces sp. BYF63. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analyses (HR-ESI-MS, 1D and 2D NMR). Compounds 1 and 4 were found to possess potent antibacterial activities against Staphylococcus aureus, with the zone of inhibition (ZOI) values of 12.85 and 11.17 mm, respectively, which were comparable to that of penicillin sodium with ZOI of 13.15 mm. Furthermore, metabolite 1 showed moderate cytotoxicities against melanoma cell line A375 and gastric cancer cell line MGC-803, with IC50 values of 22.76 and 36.65 μM, respectively, which were less than those of referenced adriamycin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brownlie JC, Johnson KN. Symbiont-mediated protection in insect hosts. Trends Microbiol. 2009;17:348–54.
Zhang YL, Ge HM, Li F, Song YC, Tan RX. New phytotoxic metabolites from Pestalotiopsis sp. HC02, a fungus residing in Chondracris rosee gut. Chem Biodivers. 2008;5:2402–7.
Zhang YL, Li S, Jiang DH, Kong LC, Zhang PH, Xu JD. Antifungal activities of metabolites produced by a termite-associated Streptomyces canus BYB02. J Agr Food Chem. 2013;61:1521–4.
Gosalbes MJ, Latorre A, Lamelas A, Moya A. Genomics of intracellular symbionts in insects. Int J Med Microbiol. 2010;300:271–8.
Scott JJ, Oh DC, Yuceer MC, Klepzig KD, Clardy J, Currie CR. Bacterial protection of beetle−fungus mutualism. Science. 2008;322:63–63.
Poulsen M, Oh DC, Clardy J, Currie CR. Chemical analyses of wasp-associated Streptomyces bacteria reveal a prolific potential for natural products discovery. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e16763 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016763
Van Arnam EB, Ruzzini AC, Sit CS, Horn H, Pinto-Tomas AA, Currie CR. Selvamicin an atypical antifungal polyene from two alternative genomic contexts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2016;113:12940–5.
Oh DC, Poulsen M, Currie CR, Clardy J. Dentigerumycin: a bacterial mediator of an ant-fungus symbiosis. Nat Chem Biol 2009;5:391–3.
Bode HB. Insects: true pioneers in anti-infective therapy and what we can learn from them. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;48:6394–6.
Crawford JM, Clardy J. Bacterial symbionts and natural products. Chem Commun. 2011;47:7559–66.
Li S, Shao MW, Lu YH, Kong LC, Jiang DH, Zhang YL. Phytotoxic and antibacterial metabolites from Fusarium proliferatum ZS07 isolated from the gut of long-horned grasshoppers. J Agr Food Chem. 2014;62:8997–9001.
Yin CP, Jin LP, Sun FF, Xu X, Shao MW, Zhang YL. Phytotoxic and antifungal metabolites from Curvularia crepinii QTYC-1 isolated from the gut of Pantala flavescens. Molecules. 2018;23:951 https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040951.
Darby AC, Chandler SM, Welburn SC, Douglas AE. Aphid-symbiotic bacteria cultured in insect cell lines. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005;71:4833–9.
Cerulli A, Lauro G, Masullo M, Cantone V, Olas B. Cyclic diarylheptanoids from Corylus avellana green leafy covers: determination of their absolute configurations and evaluation of their antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. J Nat Prod. 2017;80:1703–13.
Yang MD, Shen XB, Hu YS, Chen YY, Liu XH. Novel naphthalene-enoates: design and anticancer activity through regulation cell autophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;113:108747.
Huang H, Wang F, Luo M, Chen Y, Song Y, Zhang W, et al. Halogenated anthraquinones from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO F063. J Nat Prod. 2012;75:1346–52.
Wang M, Kornsakulkarn J, Srichomthong K, Fengl T, Liu JK. Antimicrobial anthraquinones from cultures of the ant pathogenic fungus Cordyceps morakotii BCC 56811. J Antibiot. 2019;72:141–7.
Takagi H, Nogawa T, Futamura Y, Takahashi S, Osada H. Kinanthraquinone, a new anthraquinone carboxamide isolated from Streptomyces reveromyceticus SN-593-44. J Antibiot. 2018;71:480–2.
Mohammed A, Ibrahim MA, Tajuddeen N, Aliyu AB, Isah MB. Antidiabetic potential of anthraquinones: a review. Phytother Res. 2020;34::486–504.
Kim KH, Ramadhar TR, Beemelmanns C, Cao SG, Poulsen M, Currie CR. Natalamycin A, an ansamycin from a termite-associated Streptomyces sp. Chem Em Sci. 2014;5:4333–8.
Klassen JL, Lee SR, Poulsen M, Beemelmanns C, Kim KH. Efomycins K and L from a termite-associated Streptomyces sp. M56 and their putative biosynthetic origin. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:1739 https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01739.
Beemelmanns C, Ramadhar TR, Kim KH, Klassen JL, Cao SG, Wyche TP. Macrotermycins A-D, glycosylated macrolactams from a termite-associated Amycolatopsis sp. M39. Org Lett. 2017;19:1000–3.
Bi SF, Li F, Song YC, Tan RX, Ge HM. New acrylamide and oxazolidin derivatives from a termite-associated Streptomyces sp. Nat Prod Commun. 2011;6:353–5.
Gyanchandani ND, Nigam IC. Anthraquinone drugs. II. inadvertent acetylation of aloe-emodin during preparation of aglycones from crude drugs-UV, IR, and NMR spectra of the products. J Pharm Sci. 1969;58:833–5.
Wijeratne EMK, Bashyal BP, Gunatilaka MK, Arnold AE, Gunatilaka AAL. Maximizing chemical diversity of fungal metabolites: biogenetically related heptaketides of the endolichenic fungus Corynespora sp. J Nat Prod. 2010;73:1156–9.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (31770007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Song, T., Wu, J. et al. Antibacterial and cytotoxic metabolites of termite-associated Streptomyces sp. BYF63. J Antibiot 73, 766–771 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-020-0334-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-020-0334-1