Abstract
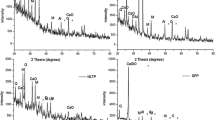
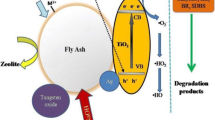
In this work, fly ash from a Brazilian thermal power plant was employed as a low-cost raw catalyst for Procion red degradation by photo-Fenton process. The ash was characterized by X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms (BET), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX). The material had an iron content of 4.10 wt%, distributed homogeneously on the solid surface. The ash particles showed mainly spherical morphology between 0.5 and 20 µm. The catalyst presented promising activity, reaching 93% of dye decolorization at 60 min of reaction, and 85% of organic load removal at 240 min. The predominant oxidizing species involved on the degradation of dye molecules during the photo-Fenton reaction were the hydroxyl radicals (HO·). The material showed remarkable stability and reusability after five successive cycles of reuse. The reaction intermediates were identified by LC/MS analysis and a reaction pathway was proposed.
Highlights
-
Reaction pathway for degradation of an emerging contaminant by photo-Fenton
-
Fly ash was a promising catalyst for the degradation of Procion red
-
The catalytic efficiency was 93.6% decolorization and 85% TOC removal
-
Fly ash presented good stability and low level of deactivation after five uses













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akay U, Demirtas EA (2015) Degradation of burazol blue ED by heterogeneous fenton process: simultaneous optimization by central composite design. Desalin Water Treatm 56:3346–3356. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.968630
Chang SH, Wang KS, Li HC, Wey MY, Chou JD (2009) Enhancement of Rhodamine B removal by low-cost fly ash sorption with Fenton pre-oxidation. J Hazard Mater 172:1131–1136
Chen J, Zhu L (2007) UV-Fenton discolouration and mineralization of Orange II over hydroxyl-Fe-pillared bentonite. J Photochem Photobiol A 188:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2006.11.018
Chen SH, Du DY (2014) Degradation of n-butyl xanthate using fly ash as heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. J Cent South Univ 21:1448–1452
Cho YK, Jung SH, Choi YC (2019) Effects of chemical composition of fly ash on compressive strength of fly ash cement mortar. Constr Build Mater 204:255–264
CONAMA, National Council on Environmental (Brazil). https://www2.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=646. Accessed 17 Jan 2020
Dao DS, Nguyen NV, Le ST, Nguyen HKD, Hoang HV et al (2017) Iron-modified fly ash as heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for decolorization of Reactive Blue 182 dye. In: Jacob Parker (ed) Fly ash: properties, analysis and performance. NOVA Scientific Publishers, Chap. 12. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/309730913_Ironmodified_fly_ash_as_heterogeneous_Fenton_catalyst_for_decolorization_of_Reactive_Blue_182_dye
Dash S, Chaudhuri H, Gupta R, Nair UG (2018) Adsorption study of modified coal fly ash with sulfonic acid as a potential adsorbent for the removal of toxic reactive dyes from aqueous solution: kinetics and thermodynamics. J Environ Chem Eng 6:5897–5905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.05.017
Depoi FS, Pozebon D, Kalkreuth WD (2008) Chemical characterization of feed coals and combustion-by-products from Brazilian power plants. Int J Coal Geol 76:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2008.07.013
Drumm FC, Oliveira JS, Foletto EL, Dotto GL, Flores EMM, Peters Enders MS, Müller EI (2018) Response surface methodology approach for the optimization of tartrazine removal by heterogeneous photo-Fenton process using mesostructured Fe2O3-suppoted ZSM-5 prepared by chitin-templating. Chem Eng Commun 205:445–455. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2017.1402009
Drumm FC, Grassi P, Sulkovski AA, Franco DSP, Georgin J, Dotto GL, Foletto EL, Jahn SL (2019) Applicability of coal bottom ash from thermoelectric power plant as an alternative heterogeneous catalyst in photo-Fenton reaction. Water Air Soil Pollut 230(12):274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4327-2
Fukasawa T, Karisma AD, Shibata D, Huang AN, Fukui K (2017) Synthesis of zeolite from coal fly ash by microwave hydrothermal treatment with pulverization process. Adv Powder Technol 28:798–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2016.12.006
Guo S, Zhang G, Wang J (2014) Photo-Fenton degradation of rhodamine B using Fe2O3–Kaolin as heterogeneous catalyst: characterization, process optimization and mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 433:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.07.017
Grassi P, Drumm FC, Georgin J, Franco DSP, Foletto EL, Dotto GL, Jahn SL (2020) Water treatment plant sludge as iron source to catalyze a heterogeneous photo-Fenton reaction. Environ Technol Innov 17:100544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100544
Hsu TC (2008) Adsorption of an acid dye onto coal fly ash. Fuel 87:3040–3045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2008.03.026
Ifelebuegu AO, Ukpebor J, Nzeribe-Nwedo B (2016) Mechanistic evaluation and reaction pathway of UV photo-assisted Fenton-like degradation of progesterone in water and wastewater. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:2757–2766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1103-3
Koshy N, Singh DN (2016) Fly ash zeolites for water treatment applications. J Environ Chem Eng 4:1460–1472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.02.002
Kutchko BG, Kim AG (2006) Fly ash characterization by SEM–EDS. Fuel 85:2537–2544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.05.016
Li JT, Bai B, Song YL (2010) Degradation of Acid orange 3 in aqueous solution by combination of Fly ash/H2O2 and ultrasound irradiation. Indian J Chem Technol 17:198–203
Liu H, Sun Q, Wang B, Wang P, Zou J (2016) Morphology and composition of microspheres in fly ash from the Luohuang Power Plant, Chongqing, Southwestern China. Minerals 6:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020030
Luo Y, Zheng S, Ma S, Liu C, Wang X (2017) Ceramic tiles derived from coal fly ash: preparation and mechanical characterization. Ceram Int 43:11953–11966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.06.045
Mossmann A, Dotto GL, Hotza D, Jahn SL, Foletto EL (2019) Preparation of polyethylene–supported zero–valent iron buoyant catalyst and its performance for Ponceau 4R decolorization by photo–Fenton process. J Environ Chem Eng 7(2):102963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.102963
Mazumder NA, Rano R (2015) An efficient solid base catalyst from coal combustion fly ash for green synthesis of dibenzylideneacetone. J Ind Eng Chem 29:359–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.04.015
Mushtaq F, Zahid M, Bhatti IA, Nasir S, Hussain T (2019) Possible applications of coal fly ash in wastewater treatment. J Environ Manag 240:27–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.054
Nascimento M, Soares PSM, Souza VP (2009) Adsorption of heavy metal cations using coal fly ash modified by hydrothermal method. Fuel 88:1714–1719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2009.01.007
Oliveira JSD, Mazutti MA, Urquieta-González EA, Foletto EL, Jahn SL (2016) Preparation of mesoporous Fe2O3-supported ZSM-5 zeolites by carbon-templating and their evaluation as photo-Fenton catalysts to degrade organic pollutant. Mater Res 19:1399–1406. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2016-0367
Pan C, Zhu Y (2010) New type of BiPO4 oxy-acid salt photocatalyst with high photocatalytic activity on degradation of dye. Environ Sci Technol 44:5570–5574. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101223n
Patra G, Barnwal R, Behera SK, Meikap BC (2018) Removal of dyes from aqueous solution by sorption with fly ash using a hydrocyclone. J Environ Chem Eng 6:5204–5211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.08.011
Pires M, Querol X (2004) Characterization of Candiota (South Brazil) coal and combustion by-product. Int J Coal Geol 60:57–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2004.04.00
Rajput H, Verma A, Kaur M, Kaur T, Toor AP (2016) Heterogeneous solar photo-fenton degradation of reactive black 5 using foundry sand and fly ash: value addition to waste. J Environ Eng Landsc Manag 24:124–132. https://doi.org/10.3846/16486897.2015.1109517
Ramírez-Franco JH, Galeano LA, Vicente MA (2019) Fly ash as photo-Fenton catalyst for the degradation of amoxicillin. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103274
Rendon JL, Serna CJ (1981) IR spectra of powder hematite: effects of particle size and shape. Clay Miner 16:375–382. https://doi.org/10.1180/claymin.1981.016.4.06
Salla SJ, Silvestri S, Flores EMM, Foletto EL (2018) A Novel application of Cu2FeSnS4 particles prepared by solvothermal route as solar photo-Fenton catalyst. Mater Lett 228:160–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.06.004
Schmachtenberg N, Silvestri S, Salla JS, Dotto GL, Hotza D, Jahn SL, Foletto EL (2019) Preparation of delafossite–type CuFeO2 powders by conventional and microwave–assisted hydrothermal routes for use as photo–Fenton catalysts. J Environ Chem Eng 7:102954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.102954
Severo EDC, Anchieta CG, Foletto VS, Kuhn RC, Collazzo GC, Mazutti MA, Foletto EL (2016) Degradation of Amaranth azo dye in water by heterogeneous photo-Fenton process using FeWO4 catalyst prepared by microwave irradiation. Water Sci Technol 73:88–94. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.469
Shaheen SM, Hooda PS, Tsadilas CD (2014) Opportunities and challenges in the use of coal fly ash for soil improvements—a review. J Environ Manag 145:249–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.07.005
Sideris K, Justnes H, Soutsos M, Sui T (2018) Fly ash. Properties of fresh and hardened concrete containing supplementary cementitious materials. Springer, Cham, pp 55–98
Silvestri S, Hennemann B, Zanatta N, Foletto EL (2018) Photocatalytic efficiency of TiO2 supported on raw red clay disks to discolour reactive red 141. Water Air Soil Pollut 229:40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3700-x
Singh K, Gupta AB, Sharma AK (2016) Fly ash as low cost adsorbent for treatment of effluent of handmade paper industry-Kinetic and modelling studies for direct black dye. J Clean Prod 112:1227–1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.058
Sivalingam S, Sen S (2019) Swift sono-hydrothermal synthesis of pure NaX nanocrystals with improved sorption capacity from industrial resources. Appl Surf Sci 463:190–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.019
Sohrabi MR, Khavaran A, Shariati S, Shariati S (2017) Removal of Carmoisine edible dye by Fenton and photo Fenton processes using Taguchi orthogonal array design. Arab J Chem 10:S3523–S3531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.02.019
Somna K, Jaturapitakkul C, Kajitvichyanukul P, Chindaprasirt P (2011) NaOH-activated ground fly ash geopolymer cured at ambient temperature. Fuel 90:2118–2124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.01.018
Soon AN, Hameed BH (2013) Degradation of Acid Blue 29 in visible light radiation using iron modified mesoporous silica as heterogeneous Photo-Fenton catalyst. Appl Catal A 450:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2012.10.025
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Olivier JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, Sing KS (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 87:1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Wang N, Chen J, Zhao Q, Xu H (2017) Study on preparation conditions of coal fly ash catalyst and catalytic mechanism in a heterogeneous Fenton-like process. RSC Adv 83:52524–52532. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA09925H
Wang NN, Hu Q, Hao LL, Zhao Q (2019a) Degradation of Acid Organic 7 by modified coal fly ash-catalyzed Fenton-like process: kinetics and mechanism study. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1965-7
Wang N, Hu Q, Du X, Xu H, Hao L (2019b) Study on decolorization of Rhodamine B by raw coal fly ash catalyzed Fenton-like process under microwave irradiation. Adv Powder Technol 30:2369–2378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2019.07.020
Xu T, Zhu R, Zhu G, Zhu J, Liang X, Zhu Y, He H (2017) Mechanisms for the enhanced photo-Fenton activity of ferrihydrite modified with BiVO4 at neutral pH. Appl Catal B 212:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.04.064
Yao ZT, Ji XS, Sarker PK, Tang JH, Ge LQ, Xia MS, Xi YQ (2015) A comprehensive review on the applications of coal fly ash. Earth Sci Rev 141:105–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.11.016
Zhang A, Wang N, Zhou J, Jiang P, Liu G (2012) Heterogeneous Fenton-like catalytic removal of p-nitrophenol in water using acid-activated fly ash. J Hazard Mater 201:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.033
Zhang H, Xue G, Chen H, Li X (2018) Magnetic biochar catalyst derived from biological sludge and ferric sludge using hydrothermal carbonization: preparation, characterization and its circulation in Fenton process for dyeing wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 191:64–71
Zhou G, Chen Z, Fang F, He Y, Sun H, Shi H (2015) Fenton-like degradation of Methylene Blue using paper mill sludge-derived magnetically separable heterogeneous catalyst: characterization and mechanism. J Environ Sci 35:20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.01.026
Zhuang J, Dai W, Tian Q, Li Z, Xie L, Wang J, Liu P, Shi X, Wang D (2010) Photocatalytic degradation of RhB over TiO2 bilayer films: effect of defects and their location. Langmuir 26:9686–9694. https://doi.org/10.1021/la100302m
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support given by research funding agencies CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel-Brazil) and CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Technological Development-Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grassi, P., Drumm, F.C., da Silveira Salla, J. et al. Investigation of the reaction pathway for degradation of emerging contaminant in water by photo-Fenton oxidation using fly ash as low-cost raw catalyst. Int J Environ Res 14, 427–438 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00266-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00266-1