Abstract
Purpose
Atonic seizures are associated with a particularly poor response to medical treatment. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the efficacy of corpus callosotomy (CC) and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) in the management of atonic seizures in the pediatric population.
Methods
A literature search was performed in compliance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and recommendations, focusing on atonic seizures, CC, and VNS in pediatric populations. Pertinent clinical data were extracted and analyzed. Pooled effects between groups were calculated as standardized error (SE) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). To assess for statistical significance, the Z-test was performed, using the pooled effect size (ES) and 95% CI for each intervention.
Results
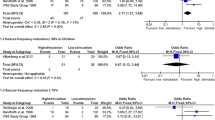
A total of 31 studies met the inclusion criteria, with 24 studies encompassing 425 children treated with CC and 7 studies encompassing 108 children treated with VNS. Twenty-four studies were included in a meta-analysis. There was a statistically significant difference in the primary outcome of atonic seizure control in favor of CC (overall effect size (ES) 0.73, 95% CI 0.69–0.77 for CC, ES 0.4, 95% CI 0.28–0.51 for VNS, p = 0.003). There was a higher rate of complications requiring reoperation in the CC cohort (6.6% vs. 3.8%) and a 14% rate of symptomatic disconnection syndrome.
Conclusions
While both techniques are safe, CC provides a much higher chance of effectively managing this morbid seizure type albeit with a higher risk of re-operation and disconnection syndrome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-El-Barr MM, Joseph JR, Schultz R, Edmonds JL, Wilfong AA, Yoshor D (2010) Vagus nerve stimulation for drop attacks in a pediatric population. Epilepsy Behav 19:394–399
Alexopoulos AV, Kotagal P, Loddenkemper T, Hammel J, Bingaman WE (2006) Long-term results with vagus nerve stimulation in children with pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Seizure 15:491–503
Asadi-Pooya AA (2015) Commissural reconnection: a possible reason for failure of corpus callosotomy in refractory epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 42:2
Asadi-Pooya AA (2018) Lennox–Gastaut syndrome: a comprehensive review. Neurol Sci 39:403–414
Berg AT, Smith SN, Frobish D, Beckerman B, Levy SR, Testa FM, Shinnar S (2004) Longitudinal assessment of adaptive behavior in infants and young children with newly diagnosed epilepsy: influences of etiology, syndrome, and seizure control. Pediatrics 114:645–650. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2003-1151-L
Berg AT, Kaiser K, Dixon-Salazar T, Elliot A, McNamara N, Meskis MA, Golbeck E, Tatachar P, Laux L, Raia C, Stanley J, Luna A, Rozek C (2019) Seizure burden in severe early-life epilepsy: perspectives from parents. Epilepsia Open 4:293–301. https://doi.org/10.1002/epi4.12319
Bower RS, Wirrell E, Nwojo M, Wetjen NM, Marsh WR, Meyer FB (2013) Seizure outcomes after corpus callosotomy for drop attacks. Neurosurgery 73:993–1000
Cukiert A, Cukiert CM, Burattini JA, Lima AM, Forster CR, Baise C, Argentoni-Baldochi M (2013) Long-term outcome after callosotomy or vagus nerve stimulation in consecutive prospective cohorts of children with Lennox–Gastaut or Lennox-like syndrome and non-specific MRI findings. Seizure 22:396–400
Cukiert A, Cukiert CM, Burattini JA, Lima AM, Forster CR, Baise C, Argentoni-Baldochi M (2013) A prospective long-term study on the outcome after vagus nerve stimulation at maximally tolerated current intensity in a cohort of children with refractory secondary generalized epilepsy. Neuromodulation 16:551–555
Englot DJ, Rolston JD, Wright CW, Hassnain KH, Chang EF (2016) Rates and predictors of seizure freedom with vagus nerve stimulation for intractable epilepsy. Neurosurgery 79:345–353
Hachem LD, Wong SM, Ibrahim GM (2018) The vagus afferent network: emerging role in translational connectomics. Neurosurg Focus 45:E2
Hodaie M, Musharbash A, Otsubo H, Snead IOC, Chitoku S, Ochi A, Holowka S, Hoffman HJ, Rutka JT (2001) Image-guided, frameless stereotactic sectioning of the corpus callosum in children with intractable epilepsy. Pediatr Neurosurg 34:286–294
Hong J, Desai A, Thadani VM, Roberts DW (2018) Effcacy and safety of corpus callosotomy after vagal nerve stimulation in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy. J Neurosurg 128:277–286
Howland R (2014) Vagus nerve stimulation. Curr Behav Neurosci Rep 1:64–73
Iwasaki M, Uematsu M, Fukuyo NH, Osawa SI, Shimoda Y, Jin K, Nakasato N, Tominaga T (2016) Long-term seizure remission and developmental gains after total corpus callosotomy in children with intractable epilepsy. Childs Nerv Syst 32(10):1994
Jalilian L, Limbrick DD, Steger-May K, Johnston J, Powers AK, Smyth MD (2010) Complete versus anterior two-thirds corpus callosotomy in children: analysis of outcome. J Neurosurg Pediatr 6:257–266
Jea A, Vachhrajani S, Johnson KK, Rutka JT (2008) Corpus callosotomy in children with intractable epilepsy using frameless stereotactic neuronavigation: 12-year experience at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto. Neurosurg Focus 25:E7
Kasasbeh AS, Smyth MD, Steger-May K, Jalilian L, Bertrand M, Limbrick DD (2014) Outcomes after anterior or complete corpus callosotomy in children. Neurosurgery 74:17–28
Katagiri M, Iida K, Kagawa K, Hashizume A, Ishikawa N, Hanaya R, Arita K, Kurisu K (2016) Combined surgical intervention with vagus nerve stimulation following corpus callosotomy in patients with Lennox–Gastaut syndrome. Acta Neurochir 158:1005–1012
Kawai K, Shimizu H, Yagishita A, Maehara T, Tamagawa K (2004) Clinical outcomes after corpus callosotomy in patients with bihemispheric malformations of cortical development. J Neurosurg 101:7–15
Kelly KM, Chung SS (2011) Surgical treatment for refractory epilepsy: review of patient evaluation and surgical options. Epilepsy Res Treat 2011:303624–303610. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/303624
Kobylarek D, Iwanowski P, Lewandowska Z, Limphaibool N, Szafranek S, Labrzycka A, Kozubski W (2019) Advances in the potential biomarkers of epilepsy. Front Neurol 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00685
Kostov K, Kostov H, Tauboll E (2009) Long-term vagus nerve stimulation in the treatment of Lennox–Gastaut syndrome. Epilepsy Behav 16:321–324
Kwan SY, Wong TT, Chang KP, Chi CS, Yang TF, Lee YC, Guo WY, Su MS (2000) Seizure outcome after corpus callosotomy: the Taiwan experience. Childs Nerv Syst 16:87–92
Lancman G, Virk M, Shao H, Mazumdar M, Greenfield JP, Weinstein S, Schwartz TH (2013) Vagus nerve stimulation vs. corpus callosotomy in the treatment of Lennox–Gastaut syndrome: a meta-analysis. Seizure 22:3–8
Li S-T, Chiu N-C, Kuo Y-T, Shen E-Y, Tsai P-C, Ho C-S, Wu W-H, Chen J-C, Wang C-Y, Kuo Y-T, Wang H-S, Lin K-L, Hung P-C, Chang Y-C, Hung P-L, Fan P-C, Lee W-T, Yang R-C, Ko F-J, Lin L-C, Chou P-C, Tsai J-D, Hung K-L, Chen H-J, Chang K-P, Hsu T-R, Ho C-S, Chiu N-C, Chen S-J, Fan H-C, Lee H-T, Shen E-Y, Kuo H-T, Chang M-Y, Chang T-M, Li S-T, Yeh G-C (2017) Parenting stress in parents of children with refractory epilepsy before and after vagus nerve stimulation implantation. Pediatrics & Neonatology 58:516–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedneo.2017.03.001
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol 62:e1–e34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.006
Lin JS, Lew SM, Marcuccilli CJ, Mueller WM, Matthews AE, Koop JI, Zupanc ML (2011) Corpus callosotomy in multistage epilepsy surgery in the pediatric population. J Neurosurg Pediatr 7:189–200
Luat AF, Asano E, Kumar A, Chugani HT, Sood S (2017) Corpus callosotomy for intractable epilepsy revisited: the Children’s Hospital of Michigan Series. J Child Neurol 32:624–629
Mamelak AN, Barbaro NM, Walker JA, Laxer KD (1993) Corpus callosotomy: a quantitative study of the extent of resection, seizure control, and neuropsychological outcome. J Neurosurg 79:688–695. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1993.79.5.0688
Mithani K, Mikhail M, Morgan BR, Wong S, Weil AG, Deschenes S, Wang S, Bernal B, Guillen MR, Ochi A, Otsubo H, Yau I, Lo W, Pang E, Holowka S, Snead OC, Donner E, Rutka JT, Go C, Widjaja E, Ibrahim GM (2019) Connectomic profiling identifies responders to vagus nerve stimulation. Ann Neurol 08:08
Ono T, Baba H, Toda K, Ono K (2011) Callosotomy and subsequent surgery for children with refractory epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 93:185–191
Ozanne A, Verdinelli C, Olsson I, Edelvik A, Graneheim UH, Malmgren K (2018) Callosotomy in children—parental experiences reported at long-term follow-up. Epilepsy Behav 86:91–97
Pitkanen A, Engel J Jr (2014) Past and present definitions of epileptogenesis and its biomarkers. Neurotherapeutics 11:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-014-0257-2
Rahimi SY, Park YD, Witcher MR, Lee KH, Marrufo M, Lee MR (2007) Corpus callosotomy for treatment of pediatric epilepsy in the modern era. Pediatr Neurosurg 43:202–208
Rathore C, Abraham M, Rao RM, George A, Sankara Sarma P, Radhakrishnan K (2007) Outcome after corpus callosotomy in children with injurious drop attacks and severe mental retardation. Brain and Development 29:577–585
Rolston JD, Englot DJ, Wang DD, Shih T, Chang EF (2012) Comparison of seizure control outcomes and the safety of vagus nerve, thalamic deep brain, and responsive neurostimulation: evidence from randomized controlled trials. Neurosurg Focus 32:E14. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.1.FOCUS11335
Rolston JD, Englot DJ, Wang DD, Garcia PA, Chang EF (2015) Corpus callosotomy versus vagus nerve stimulation for atonic seizures and drop attacks: a systematic review. Epilepsy Behav 51:13–17
Rosenfeld WE, Roberts DW (2009) Tonic and atonic seizures: what’s next—VNS or callosotomy? Epilepsia 50:25–30
Ruiz-Falco M, Garcia-Penas J, Lara Herguedas J, Duat-Rodriguez A, Lopez-Marin L, Cantarin-Extremera V, Gutierrez N, Gutierrez-Solana L, Garcia M, Perez-Jimenez M, Villarejo F (2009) Vagus nerve stimulation in pediatric epileptic syndromes. Epilepsia 50:147
Shahwan A, Bailey C, Maxiner W, Harvey AS (2009) Vagus nerve stimulation for refractory epilepsy in children: more to VNS than seizure frequency reduction. Epilepsia 50:1220–1228
Shim KW, Lee YM, Kim HD, Lee JS, Choi JU, Kim DS (2008) Changing the paradigm of 1-stage total callosotomy for the treatment of pediatric generalized epilepsy. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2:29–36
Shimizu H (2005) Our experience with pediatric epilepsy surgery focusing on corpus callosotomy and hemispherotomy. Epilepsia 46:30–31
Stigsdotter-Broman L, Olsson I, Flink R, Rydenhag B, Malmgren K (2014) Long-term follow-up after callosotomy—a prospective, population based, observational study. Epilepsia 55:316–321
Turani G, Yalnizoglu D, Genc-Acikgoz D, Akalan N, Topcu M (2006) Outcome and long term follow-up after corpus callosotomy in childhood onset intractable epilepsy. Childs Nerv Syst 22:1322–1327
Wong TT, Kwan SY, Chang KP, Hsiu-Mei W, Yang TF, Chen YS, Yi-Yen L (2006) Corpus callosotomy in children. Childs Nerv Syst 22:999–1011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0133-4
Yang PF, Lin Q, Mei Z, Chen ZQ, Zhang HJ, Pei JS, Tian J, Jia YZ, Zhong ZH (2014) Outcome after anterior callosal section that spares the splenium in pediatric patients with drop attacks. Epilepsy Behav 36:47–52
Yonekawa T, Nakagawa E, Takeshita E, Inoue Y, Inagaki M, Kaga M, Sugai K, Sasaki M, Kaido T, Takahashi A, Otsuki T (2011) Effect of corpus callosotomy on attention deficit and behavioral problems in pediatric patients with intractable epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 22:697–704
You SJ, Kang HC, Ko TS, Kim HD, Yum MS, Hwang YS, Lee JK, Kim DS, Park SK (2008) Comparison of corpus callosotomy and vagus nerve stimulation in children with Lennox–Gastaut syndrome. Brain Dev 30:195–199
Zamponi N, Passamonti C, Cesaroni E, Trignani R, Rychlicki F (2011) Effectiveness of vagal nerve stimulation (VNS) in patients with drop-attacks and different epileptic syndromes. Seizure 20:468–474
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, V.C., Mansouri, A., Warsi, N.M. et al. Atonic seizures in children: a meta-analysis comparing corpus callosotomy to vagus nerve stimulation. Childs Nerv Syst 37, 259–267 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04698-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04698-0