Abstract
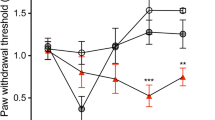
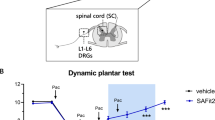
Despite the importance of microglial cells in chronic pain, the mechanisms of microglial engagement remain controversial. In this study, we examined the changes in immune-related factors in the mesenteric lymph node and spinal cord over time as a treatment regimen for paclitaxel-induced neuropathy (2 mg/kg/day for 5 days). Our data showed that expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, Tbx21 (Th1) and Rorc (RORγ; Th17), were increased at 7 days but subsequently normalized after paclitaxel treatment. Monocyte/macrophage functional phenotypes also exhibited a similar pattern in mesenteric lymph node. In the spinal cord, expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines were decreased at 7 days and recovered at 21 days in paclitaxel-treated mice. Although, mRNA level of TNF-α was transiently increased at 1 day, expression of genes related to microglial homeostatic function (Cx3cr1, Cd200r, TGF-β, IGF-1, and P2ry12) was significantly reduced at 7 and 14 days and restored at 21 days, suggesting the impairment of microglial homeostatic function. In addition, lipofuscin accumulation was increased at 7-14 days and partly normalized at 21 days in the spinal cord. The partly restoration of lipofuscin accumulation at 21 days seems to be related to a reduction in expression of genes involved in cell cycle arrest such as p16 and p21. Collectively, we propose that a process involving dysfunctional microglia, lipofuscin accumulation, and promotion of cell proliferation may explain the onset of paclitaxel-induced neuropathy and recovery after washout.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Johannes, C.B., Le, T.K., Zhou, X., Johnston, J.A., and Dworkin, R.H., J Pain, 2010, vol. 11, pp. 1230–1239.
Ji, R.R., Xu, Z.Z., and Gao, Y.J., Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, vol. 13, pp. 533–548.
Kuner, R., Nat. Med., 2010, vol. 16, pp. 1258–1266.
Chen, G., Zhang, Y.Q., Qadri, Y.J., Serhan, C.N., and Ji, R.R., Neuron, 2018, vol. 100, pp. 1292–1311.
Saijo, K., and Glass, C.K., Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 775–787.
Noh, M.Y., Lim, S.M., Oh, K.W., Cho, K.A., Park, J., Kim, K.S., Lee, S.J., Kwon, M.S., and Kim, S.H., Stem Cells Transl. Med., 2016, vol. 5, pp. 1538–1549.
Rangaraju, S., Dammer, E.B., Raza, S.A., Rathakrishnan, P., Xiao, H., Gao, T., Duong, D.M., Pennington, M.W., Lah, J.J., Seyfried, N.T., and Levey, A.I., Mol. Neurodegener., 2018, vol. 13, p. 24.
Ransohoff, R.M., Nat. Neurosci., 2016, vol. 19, pp. 987–991.
Butovsky, O., and Weiner, H.L., Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2018, vol. 19, pp. 622–635.
Jaggi, A.S., and Singh, N., Toxicology, 2012, vol. 291, pp. 1–9.
Li, Y., Zhang, H., Kosturakis, A.K., Jawad, A.B., and Dougherty, P.M., J Pain, 2014, vol. 15, pp. 712–725.
Kawasaki, Y., Zhang, L., Cheng, J.K., and Ji, R.R., J. Neurosci., 2008, vol. 28, pp. 5189–5194.
Grace, P.M., Hutchinson, M.R., Maier, S.F., and Watkins, L.R., Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2014, vol. 14, pp. 217–231.
Liu, C.C., Lu, N., Cui, Y., Yang, T., Zhao, Z.Q., Xin, W.J., and Liu, X.G., Mol. Pain., 2010, vol. 6, p. 76.
Zhang, H., Yoon, S.Y., and Dougherty, P.M., J Pain. 2012, vol. 13, pp. 293–303.
Ochi-ishi, R., Nagata, K., Inoue, T., Tozaki-Saitoh, H., Tsuda, M., and Inoue, K., Mol. Pain., 2014, vol. 10, p. 53.
Park, H.S., Park, M.J., and Kwon, M.S., Int. Neurourol. J., 2016, vol. 20, pp. S8–S14.
Ha, J.W., You, M.J., Park, H.S., Kim, J.W., and Kwon, M.S., Arch. Pharm. Res., 2019, vol. 42, pp. 359–368.
Jung, T., Hohn, A., and Grune, T., Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, vol. 594, pp. 173–193.
Moreno-García, A., Kun, A., Calero, O., Medina, M., and Calero, M., Front. Neurosci., 2018, vol. 12, p. 464.
Warburton, S., Davis, W.E., Southwick, K., Xin, H., Woolley, A.T., Burton, G.F., and Thulin, C.D., Mol. Vis., 2007, vol. 13, pp. 318–329.
Deczkowska, A., Amit, I., and Schwartz, M., Nat. Neurosci. 2018, vol. 21, pp. 779–786.
Hickman, S., Izzy, S., Sen, P., Morsett, L., and El Khoury, J., Nat. Neurosci., 2018, vol. 21, pp. 1359–1369.
Eijkelkamp, N., Steen-Louws, C., Hartgring, S.A., Willemen, H.L., Prado, J., Lafeber, F.P., Heijnen, C.J., Hack, C.E., van Roon, J.A., and Kavelaars, A., J. Neurosci., 2016, vol. 36, pp. 7353–7363.
Scripture, C.D., Figg, W.D., and Sparreboom, A., Curr. Neuropharmacol., 2006, vol. 4, pp. 165–172.
Staff, N.P., Grisold, A., Grisold, W., and Windebank, A.J., Ann. Neurol., 2017, vol. 81, pp. 772–781.
Childs, B.G., Baker, D.J., Kirkland, J.L., Campisi, J., and van Deursen, J.M., EMBO Rep., 2014, vol. 15, pp. 1139–1153.
Jung, T., Bader, N., and Grune, T., Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 2007, vol. 1119, pp. 97–111.
Gosselin, D., Link, V.M., Romanoski, C.E., Fonseca, G.J., Eichenfield, D.Z., Spann, N.J., Stender, J.D., Chun, H.B., Garner, H., Geissmann, F., and Glass, C.K., Cell, 2014, vol. 159, pp. 1327–1340.
Krasemann, S., Madore, C., Cialic, R., Baufeld, C., Calcagno, N., El Fatimy, R., Beckers, L., O’Loughlin, E., Xu, Y., Fanek, Z., Greco, D.J., Smith, S.T., Tweet, G., Humulock, Z., Zrzavy, T., Conde-Sanroman, P., Gacias, M., Weng, Z., Chen, H., Tjon, E., Mazaheri, F., Hartmann, K., Madi, A., Ulrich, J.D., Glatzel, M., Worthmann, A., Heeren, J., Budnik, B., Lemere, C., Ikezu, T., Heppner, F.L., Litvak, V., Holtzman, D.M., Lassmann, H., Weiner, H.L., Ochando, J., Haass, C., and Butovsky, O., Immunity, 2017, vol. 47, pp. 566–581, e569.
Lund, H., Pieber, M., Parsa, R., Grommisch, D., Ewing, E., Kular, L., Han, J., Zhu, K., Nijssen, J., Hedlund, E., Needhamsen, M., Ruhrmann, S., Guerreiro-Cacais, A.O., Berglund, R., Forteza, M.J., Ketelhuth, D.F.J., Butovsky, O., Jagodic, M., Zhang, X.M., and Harris, R.A., Nat. Immunol., 2018, vol. 19, pp. 1–7.
Park, M.J., Park, H.S., You, M.J., Yoo, J., Kim, S.H., and Kwon, M.S., Mol. Neurobiol., 2019, vol. 56, pp. 1421–1436.
Funding
This study was funded by by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (grant number: 2017R1C1B5018178).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kim JW has received research grants from NRF; and wrote manuscript. Park HS conducted lipofuscin study and wrote a draft. You MJ conducted immunohistochemistry in the spinal cord. Yang BH and Jang KB conducted qPCR in the lymph node and spinal cord. Kwon MS suggested experimental design and interpreted all data. All authors critically revised the manuscript and approved the final article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted (IACUC approval No. 180009).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jong Wan Kim, Park, HS., You, MJ. et al. Time Course of Peripheral and Central Immune System Alterations in Paclitaxel-Treated Mice: Possible Involvement of Dysfunctional Microglia. Neurochem. J. 14, 204–214 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712420020063
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712420020063