Abstract
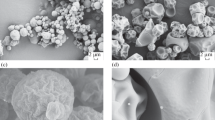
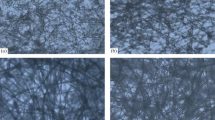
Using a twin-screw microextruder, fibers are synthesized from polylactide with the addition of two types of chitin nanofibrils—both original and modified with poly(ethylene glycol). The fibers are subjected to the additional high-temperature orientational drawing by a factor of 4 and 6. Composite materials are investigated by a complex of thermophysical and structural methods, and their physicomechanical properties are determined. It is shown that the modification of chitin nanoparticles with poly(ethylene glycol) allows one to obtain bioresorbable composite materials with improved physicomechanical properties.











Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
European Commission (2013) Plastic Waste-Strategy and Background. http://ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/ plastic_waste.htm. Cited February 15, 2017.
FICCI (2014) Potential of Plastics Industry in Northern India with Special Focus on Plastic Culture and Food Processing. http://www.ficci.in. Cited 2020.
A. D. Tripathi, A. Yadav, A. Jha, and S. K. J. Srivastava, J. Polym. Environ. 20, 446 (2012).
D. R. Lu, C. M. Xiao, and S. J. Xu, eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 3, 366 (2009).
G. E. Luckachan and C. K. S. Pillai, Carbohydr. Polym. 64, 254 (2006).
L. S. Nair and C. T. Laurencin, Prog. Polym. Sci. 32, 762 (2007).
R. A. Gross and B. Kalra, Science 297 (5582), 803 (2002).
V. Podzorova, Yu. V. Tertyshnaya, and A. A. Popov, Polym. Sci., Ser. D 10, 289 (2017).
R. E. Drumright, P. R. Gruber, D. E. Henton, Adv. Mater. 12, 1841 (2000).
L. Yu, K. Dean, and L. Li, Prog. Polym. Sci. 31, 576 (2006).
D. Garlotta, J. Polym. Environ. 9, 63 (2001).
A. Valdés, A. C. Mellinas, M. Ramos, M. Garriigós, and A. Jiménez, Front. Chem. 2, 1 (2014).
L. Cabedo, J. L. Feijoo, M. P. Villanueva, J. M. Lagarón, and E. Giménez, Macromol. Symp. 233, 191 (2006).
B. Baxand J. Müssig, Compos. Sci. Technol. 68, 1601 (2009).
S. Cheng, K.-T. Lau, T. Liu, Y. Zhao, P.-M. Lam, and Y. Yin, Composites, Part B 40, 650 (2009).
A. P. Mathew, K. Oksman, and M. Sain, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 97, 2014 (2005).
I. S. M. A. Tawakkal, R. A. Talib, K. Abdan, and C. N. Ling, BioResources 7, 1643 (2012).
M. Jamshidian, E. Arab Tehrany, M. Imran, M. Jacquot, and S. Desobry, Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 9, 552 (2010).
M. Persson, G. S. Lorite, H. E. Kokkonen, S.-W. Cho, P. P. Lehenkari, M. Skrifars, and J. Tuukkanen, Colloids Surf., B 121, 409 (2014).
Melt Spinning Process. Feature of Melt Spinning. Advantages and Disadvantages of Melt Spinning. http://textilelearner.blogspot.com/2013/10/melt-spinning-process-feature-of-melt.html. Cited December 12, 2018.
M. Jacob John, R. Anandjiwala, K. Oksman, and A. P. Mathew, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 127, 274 (2013).
K. V. Malafeev, O. A. Moskalyuk, V. E. Yudin, P. Morganti, E. M. Ivan’kova, E. N. Popova, and Y. U. Elo-khovskii, J. Appl. Cosmetol. 35, 163 (2017).
M. Sheth, R. Ananda Kumar, V. Davé, R. A. Gross, and S. P. McCathy, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 66, 1495 (1997).
H. Otsuka, Y. Nagasaki, and K. Kataoka, Biomacromolecules 1, 39 (2000).
I. P. Dobrovol’skaya, in Nauch.-Tekhn. Ved. SPb Gos. Politekhn. Univ. Fiz.-Mat. Nauki, No. 4 (206), 74 (2014).
M. B. Coltelli, P. Cinelli, V. Gigante, L. Aliotta, P. Morganti, L. Panariello, and A. Lazzeri, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 504 (2019).
H. Bai, C. Huang, H. Xiu, Q. Zhang, and Q. Fu, Polymer 55, 6924 (2014).
I. Kola and J. Landis, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 3, 711 (2004).
X. Niu, Q. Feng, M. Wang, X. Guo, and C. Zheng, Polym. Degrad. Stab. 94, 176 (2009).
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project code 19-73-30003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malafeev, K.V., Moskalyuk, O.A., Yudin, V.E. et al. Study of Physicomechanical Properties of Composite Fibers Based on Polylactide and Modified Chitin Nanofibrils. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 62, 249–259 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X20030104
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X20030104