Abstract
Background
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is employed in the production of cosmetics, sunscreen, food, and drugs; however, TiO2 is toxic at the nanometric scale.
Objective
To analyze the in vitro toxic effect of TiO2 NPs on mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs).
Methods
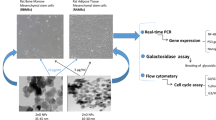
The hMSCs from Wharton`s jelly were exposed to 4, 62.5 and 500 μg/mL of TiO2 NPs. Viability and cell proliferation tests were carried out at 2, 5 and 7 days of exposure. Additionally, the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation capacity was evaluated.
Results
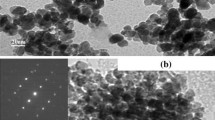
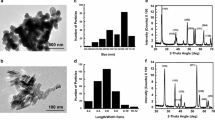
TiO2 NPs had a perinuclear arrangement and internalized in vesicles into cytosol, diminished significantly the viability (40% and 30% and 30%) and the proliferation cellular (35%, 50% and 55%), differentiation to osteoblast (38%) and adipoblasts (20%).
Conclusion
TiO2 NPs affect viability, proliferation, and differentiation of hMSCs. Our result suggests more regulation of the use of TiO2.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo-Olvera LF et al (2016) Effect of dehidroepiandrosterone on expression of BMP2, SPARC and RUNX2 in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Rev Mex Ing Quím 15:39–49
Almalki SG, Agrawal DK (2016) Key transcription factors in the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Differentiation 92:41–51
Arora S, Rajwade M, Paknikar K (2012) Nanotoxicology and in vitro studies: the need of the hour. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 258:151–165
Bunnell BA et al (2008) Adipose-derived stem cells: isolation, expansion and differentiation. Methods 45:115–120
Castro-Santos X et al (2017) Efecto del Medio Condicionado de la línea celular H9C2 Tratada con Dehidroepiandrosterona y Expuesta a Daño sobre la motilidad de Células Troncales Mesenquimales. Rev Mex Ing Biomed 38:265–272
Chang X et al (2013) Health effects of exposure to nano TiO2: a meta-analysis of experimental studies. Nanoscale Res Lett 8:51
Choi MG et al (2005) Effects of titanium particle size on osteoblast functions in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:4578–4583
Dankovic D, Kuempel E, Wheeler M (2007) An approach to risk assessment for TiO2. Inhal Toxicol 19:205–212
Dominici M et al (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells: the international society for cellular therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8:315–317
Donaldson K, Borm P (2006) Particle toxicology. CRC Press, New York
Elahi KC et al (2016) Human mesenchymal stromal cells from different sources diverge in their expression of cell surface proteins and display distinct differentiation patterns. Stem Cells Int 1:1
FDA (2002) Listing of color additives exempt from certification. In: Code of federal regulations
Van der Garde M et al (2015) Direct comparison of Wharton's jelly and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells to enhance engraftment of cord blood CD34(+) transplants. Stem Cells Dev 24:2649–2659
Gregory CA et al (2004) An Alizarin red-based assay of mineralization by adherent cells in culture: comparison with cetylpyridinium chloride extraction. Anal Biochem 329:77–84
Gupta SM, Manoj T (2011) A review of TiO2 nanoparticles. Chin Sci Bull 56:1639–1657
Hass R, Kasper C, Böhm S, Jacobs R (2011) Different populations and sources of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): a comparison of adult and neonatal tissue-derived MSC. Cell Commun Signal 9:12
Hou Y et al (2013) Effects of titanium nanoparticles on adhesion, migration, proliferation, and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Nanomed 8:3619–3630
Huerta-García E et al (2015) Internalization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles by glial cells is given at short times and is mainly mediated by actin reorganization-dependent endocytosis. NeuroToxicology 51:27–37
Jia X et al (2017) The potential liver, brain, and embryo toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on mice. Nanoscale Res Lett 12:478
Joerger-Messeril MS (2016) Mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton’s jelly and amniotic fluid. Best Pract Res clin Gynaecol 31:30–44
Kansara K et al (2015) TiO2 nanoparticles induce DNA double strand breaks and cell cycle arrest in human alveolar cells. Environ Mol Mutagen 56:204–217
Kelly D, Jacobs C (2010) The role of mechanical signals in regulating chondrogenesis and osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Birth Defects Res C 90(1):75–85
Khan M, Maskat M (2014) Interaction of titanium dioxide nanoparticle with human serum albumin: a spectroscopic approach. IJPPS 6:43–46
Levina AS et al (2012) High-performance method for specific effect on nucleic acids in cells using TiO2 DNA nanocomposites. Sci Rep-UK 2:1–6
Ma, L,. Liu, J. & Li., N. Oxidative stress in the brain of mice caused by translocated nanoparticulate TiO2 delivered to the abdominal cavity. Biomaterials. 31,99–105(2010).
Mafi R et al (2011) Sources of adult mesenchymal stem cells applicable for musculoskeletal applications: a systematic review of the literature. TOOJ 5:242–248
Mekala NK et al (2012) Osteoblast differentiation of umbilical blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and enhanced cell adhesion by fibronectin. Tissue Eng Regen Med 9:259–264
Meng B, Yang X (2013) Titanium particles enhanced osteoclast differentiation and osteoclast bone resorption activity in vitro. J Dent Oral Hyg 5:7–12
Montiel-Dávalos A et al (2012) TiO2 nanoparticles induce dysfunction and activation of human endothelial cells. Chem Res Toxicol 25:920–930
NIOSH, Departament of Health and Human Services (2011) Occupational exposure to titanium dioxide. Curr Intell Bull 63:1–85
Nemmar A, Melghit K, Ali BH (2008) The acute proinflammatory and prothrombotic effects of pulmonary exposure to rutile TiO2 nanorods in rats. Exp Biol Med 233:610–619
Nemmar A et al (2013) Recent advances in particulate matter and nanoparticle toxicology: a review of the in vivo and in vitro studies. BioMed Res Int
Niinomi M (2008) Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 1:30–42
Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E, Oberdörster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113:823–839
Oprea A, Mihai A (2017) Nanotechnology applications in food: flavor, stability, nutrition and safety. Academic Press, UK
O’Brien J, Wilson I, Terry O, Pognan F (2000) Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur J Biochem 267:5421–5426
Parra-Barrera A et al (2017) Comparación entre Células Troncales Mesenquimales obtenidas de Médula Ósea, Tejido Adiposo y Gelatina de Wharton en base a los criterios de la ISCT. Rev Mex Ing Biomed 38:280–287
Pavlović M, Radotić K (2017) Animal and plant stem cells. In: Essential characteristics of stem cells: self-renewal, and plasticity. Springer, Switzerland
Piccinno F, Gottshchalk F, Seeger S, Nowack B (2012) Industrial production quantities and uses of ten engineered nanomaterials in Europe and the world. J Nanopart Res 14:1109
Rampersad SN (2012) Multiple applications of alamar blue as an indicator of metabolic function and cellular health in cell viability bioassays. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 12:12347–12360
Rihane N et al (2016) Microglial cells (BV-2) internalize titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles: toxicity and cellular responses. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:9690–9699
Rodríguez-Pardo VM et al (2010) Aislamiento y caracterización de células "stem" mesenquimales de médula ósea humana según criterios de la Sociedad Internacional de Terapia Celular. Univ Sci (Bogotá) 15:224–239
Sabapathy V, Sundaram B, Kumar S (2017) Therapeutic application of Human Wharton Jelly mesenchymal stem cells in skin injury of SCID. Methods Mol Biol 1553:115–132
Shi H, Magaye R, Castranova V, Zhao J (2013) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a review of current toxicological data. Part Fibre Toxicol 10:15
Soto-Alvaredo A et al (2014) Evaluation of the biological effect of Ti generated debris from metal implants: ions and nanoparticles. J R Soc Chem Metallom 6:1702–1708
Sunil SJ, Vivek V (2016) Industrial catalytic processes for fine and specialty chemicals. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Vergaro V et al (2015) Interaction between human serum albumin and different anatase TiO2 nanoparticles: a nano-bio interface study. Nanomater Nanotechnol 5:30
Vishwakarma A, Karp J (2017) Biology and engineering of stem cells niches. Ed (Elsevier. Estados Unidos)
Warheit DB et al (2006) Pulmonary instillation studies with nanoscale TiO2 rods and dots in rats: toxicity is not dependent upon particle size and surface area. Toxicol Sci 91:227–236
Wilczyńska-Michalik W et al (2015) Fine and ultrafine TiO2 particles in aerosol in Kraków (Poland). Mineralogy 45:65–77
Zachri M et al (2014) Evaluation of the alamar blue assay for adherent cell irradiation experiments. Dose-Response 12:246–258
Zhongshan W et al (2015) Microarc-oxidized titanium surfaces functionalized with microRNA-21-loaded chitosan/hyaluronic acid nanoparticles promote the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Nanomed 10:6675–6687
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the departamento de posgrado de la Escuela Superior de Medicina-Instituto Politécnico Nacional and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT, CV# 744347 and transcript# A160392). This study received financial support from BEIFI and SIP (project #20180261).
Funding
CONACyT, CV# 744347 and transcript# A160392, BEIFI and SIP project #20180261.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contribute as follows: PVAB: technical work and writing, PBA: direction of the work, writing and review of the manuscript, RGMP: supervision of the technical work and writing, LMR: supervision of the technical work and writing, AGJ: writing and review of the manuscript, GGI: supervision of the technical work, writing and chief of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The current protocol was approved by the Ethics in Research Committee (CEI-02/31-05-2017) and Biosecurity Committee (CBS-06/11-09-2017) of the Escuela Superior de Medicina, Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Mexico.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adriana-Berenice, PV., Alberto, PB., del Pilar, RG.M. et al. Toxic effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on human mesenchymal stem cells. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 16, 321–330 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-020-00084-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-020-00084-8