Abstract
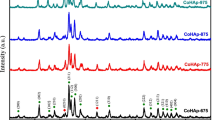
In this paper, experimental method and first-principles calculations were combined to study the properties of pure hydroxyapatite and Zn-doped hydroxyapatite. Pure and Zn-doped hydroxyapatite (HA) powders were synthesized using the hydrothermal method. The FTIR spectra show that the adding of Zn atoms makes the intensity of PO43− stretching peaks become weaken and obscure. In addition, the O-H bending peaks at 3570 and 632 cm−1 become weaker and broader. The XRD patterns show that the replacement of Zn ion in the HA structure leads to the distortion in HA lattice, which is shown and proved by the TEM analysis. First-principles calculations based on density functional theory (DFT) method were applied to investigate the Zn-doped hydroxyapatite. The elastic properties of HA, HA with Ca2+(II) vacancy, and Zn doped HA systems were calculated. Through the calculation, we found that the doping of Zn atoms made the elastic modulus of HA crystal becoming soft. The elastic properties dropped dramatically when there is a vacancy in the Ca2+(II) position. Compared with the HA-VCa2+ structure, the Zn-doped HA has better elastic properties and stability. The local structure of the substitution position was presented and analyzed. In the Zn-doped HA structure, the OH− group adjacent to Zn2+ is significantly displaced from the c axis toward to the Zn2+, making the lattice distorted. The distortion of the crystal lattice is responsible for the weakness of the P-O stretching peaks and O-H bending peaks in the FTIR spectra of the Zn doped HA crystal. The softness of the elastic modulus is also caused by the distortion of the lattice and the weak bonding force between Zn atom and O atom.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Busse, B., Jobke, B., Hahn, M., Priemel, M., Niecke, M.: Effects of strontium ranelate administration on bisphosphonate-altered hydroxyapatite: matrix incorporation of strontium is accompanied by changes in mineralization and microstructure. Acta Biomater. 6, 4513–4521 (2010)
Bhadangab, K.A., Holding, C.A., Thissen, H., McLean, K.M., Forsythe, J.S., Haynesc, D.R.: Biological responses of human osteoblasts and osteoclasts to flame-sprayed coatings of hydroxyapatite and fluorapatite blends. Acta Biomater. 6, 1575–1583 (2010)
Basar, B., Tezcaner, A., Keskin, D., Evis, Z.: Improvements in microstructural, mechanical, and biocompatibility properties of nano-sized hydroxyapatites doped with yttrium and fluoride. Ceram. Int. 36, 1633–1643 (2010)
Lee, Y.J., Elzinga, E.J., Reeder, R.J.: Sorption mechanisms of zinc on hydroxyapatite: systematic uptake studies and EXAFS spectroscopy analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 4042–4048 (2005)
Matsunaga, K., Murata, H., Mizoguchi, T., Nakahira, A.: Mechanism of incorporation of zinc into hydroxyapatite. Acta Biomater. 6, 2289–2293 (2010)
Guerra-López, J.R., Echeverría, G.A., Güida, J.A., Viña, R., Punte, G.: Synthetic hydroxyapatites doped with Zn(II) studied by X-ray diffraction, infrared Raman and thermal analysis. J. Physics. Chemi. Solids. 81, 57–65 (2015)
Wang, T., Zhang, J., Chen, Y., Xiao, P., Yang, M.: Effect of zinc ion on the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of mouse primary bone marrow stromal cells and the adipocytic trans-differentiation of mouse primary osteoblasts. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 21, 84–91 (2007)
Tank, K.P., Chudasama, K.S., Thaker, V.S., Joshi, M.J.: Pure and zinc doped nano-hydroxyapatite: synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial and hemolytic studies. J. Cryst. Growth. 401, 474–479 (2014)
Hamioud, F., AlGhamdi, G.S., Al-Omari, S., Mubarak, A.A.: Ab initio investigation of the structural, electronic, magnetic and optical properties of the perovskite TlMnX3 (X = F, Cl) compounds. Int. J. Mod. Phys B. 30, 301650031 (2016)
Sajid, A., Alay-e-abbas, S.M., Afaq, A., Shaukat, A.: Structural, electronic and optical properties of MgSxSe1-x, MgSxTe1-x and MgSexTe1-x (0 ≤x ≤1) alloys from first principles. Int. J. Mod. Phys B. 26, 1250098 (2012)
Antonov, V., Georgieva, I., Trendafilova, N., Kovacheva, D., Krezhov, K.: First principles study of structure and properties of La- and Mn-modified BiFeO3. Physica B. 14, 782–788 (2012)
Ching, W.Y., Rulis, P., Misra, A.: Ab initio elastic properties and tensile strength of crystalline hydroxyapatite. Acta Biomater. 5(8), 3067–3075 (2009)
de Leeuw, N.H., Bowe, J.R., Rabone, J.A.L.: A computational investigation of stoichiometric and calcium-deficient oxy-and hydroxyapatites. Faraday Discuss. 134, 195–214 (2007)
Menéndez-Proupin, E., Cervantes-Rodríguez, S., Osorio-Pulgar, R., Franco-Cisterna, M., Camacho-Montes, H., Fuentes, M.E.: Computer simulation of elastic constants of hydroxyapatite and fluorapatite. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 4(7), 1011–1020 (2011)
Mostafa, N.Y., Brown, P.W.: Computer simulation of stoichiometric hydroxyapatite: structure and substitutions. J. Phys.Chem. Solids. 68(3), 431–437 (2007)
Snyders, R., Music, D., Sigumonrong, D., Schelnberger, B., Jensen, J., Schneider, J.M.: Experimental and ab initio study of the mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(19), 193902–193902 (2007)
Segall, M.D., Lindan, P.J.D., Probert, M.J., Pickard, C.J., Hasnip, P.J., Clark, S.J., Payne, M.C.: First-principles simulation: ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 14, 2717 (2002)
Perdew, J.P., Burke, K., Ernzerhof, M.: Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996)
Monkhorst, H.J., Pack, J.D.: Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B. 13, 5188 (1976)
Hu, W., Ma, J., Wang, J., et al.: Fine structure study on low concentration zinc substituted hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 32(8), 2404–2410 (2012)
Posner, A.S.: Hydrogen-bonding in calcium-deficient hydroxyapatites. Nature. 188, 486–487 (1960)
Zhu, W., Wu, P.: Surface energetics of hydroxyapatite: a DFT study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 396(1), 38–42 (2004)
Wang, R., Wang, S.F., Wu, X.Z., Yao, Y.: First-principles calculations on temperature-dependent elastic constant of rare-earth intermetallic compounds: YAg and YCu. Physica B. 406, 3951–3955 (2011)
Hill, R.: The elastic behavior of a crystalline aggregate. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. A. 65, 349 (1952)
Aryal, S., Matsunaga, K., Ching, W.Y.: Ab initio simulation of elastic and mechanical properties of Zn- and Mg-doped hydroxyapatite (HAP). J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 47, 135–146 (2014)
Pugh, S.F.: Relations between the elastic moduli and the plastic properties of polycrystalline pure metals. Philos. Mag. 45, 823 (1954)
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant #21471102, #20971088) and Shenzhen Government’s Plan of Science and Technology (grant #JCYJ20150525092941007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Q., Wan, L., Wu, J. et al. Investigation of the effect of doped Zn atom to the hydroxyapatite based on experimental method and first-principles calculations. J Aust Ceram Soc 56, 1413–1419 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00430-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00430-7