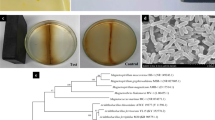
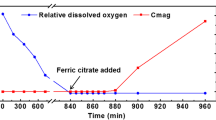
Abstract
Ferroplasma thermophilum, a sort of extreme acidophilic archaea, which can synthesize intracellular cobalt ferrite nanocrystals, is investigated in this study. The nanocrystals were analyzed with ultrathin sections and transmission electron microscope, with the size of 20–60 nm, the number of more than 30 in each cell at average, which indicated that F. thermophilum can synthesize intracellular nanocrystals and also belongs to high-yield nanocrystals-producing strain. Intriguingly, the nanocrystals contain ferrite and cobalt characterized by EDS X-ray analysis, suggesting that both cobalt and ferrite are potentially contributed to the formation of nanocrystals. Moreover, under the different energy source culture conditions of FeSO4 and CuFeS2, the size and the morphology of the nanocrystals are different. It was also found that the higher initial Fe availability leads to an induced synthesis of larger nanocrystals and the lower oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) leads to an induced effect on the synthesis of nanocrystals with abnormal unhomogeneous size, which suggested that the higher initial Fe availability and the lower oxidation-reduction potential lead to a higher uptake efficiency of iron ions of F. thermophilum by iron and ORP gradient culture.
摘要
本文研究一种极端嗜酸古菌 Ferroplasma thermophilum 合成胞内含铁钴的纳米颗粒. 通过冷冻切片和透射电镜发现纳米颗粒的大小在 20~60 nm, 其数目在每个细胞中平均超过 30 个, 这表明 Ferroplasma thermophilum 不仅可以合成胞内纳米颗粒, 还是一种高产菌. 更有趣的是, 通过 EDS X-ray 分析表明, 纳米颗粒的元素组成包含铁与钴, 这表明铁与钴都参与了纳米颗粒的合成. 更重要的是, 在不同能源物质由硫酸亚铁与黄铜矿的培养下, 发现 Ferroplasma thermophilum 所合成的纳米颗粒大小与形态不同. 进一步研究表明, 这一现象与培养基中最初铁离子浓度和电位有关, 在高初始铁离子 浓度培养下, Ferroplasma thermophilum 所合成的纳米颗粒较大, 低电位导致纳米颗粒形态不均一, 原因在于高初始铁离子浓度与低电位促进了 Ferroplasma thermophilum 铁离子的吸收. 我们的研究丰富了磁性细菌的趋磁种类, 增加了微生物合成胞内纳米颗粒的多样性, 尤其是钴的参与.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
QIN Wen-qing, YANG Cong-ren, LAI Shao-shi, WANG Jun, LIU Kai, ZHANG Bo. Bioleaching of chalcopyrite by moderately thermophilic microorganisms [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 129: 200–208. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.11.050.
ZHAO Hong-bo, WANG Jun, YANG Cong-ren, HU Ming-hao, GAN Xiao-wen, TAO Lang, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Effect of redox potential on bioleaching of chalcopyrite by moderately thermophilic bacteria: An emphasis on solution compositions [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2015, 151: 141–150. DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.11.009.
ZHAO Hong-bo, WANG Jun, HU Ming-hao, QIN Wen-qing, ZHANG Yan-sheng, QIU Guan-zhou. Synergistic bioleaching of chalcopyrite and bornite in the presence of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 149:71–76. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.09.035.
ZHAO Hong-bo, WANG Jun, GAN Xiao-wen, HU Ming-hao, ZHANG Er-xing, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Cooperative bioleaching of chalcopyrite and silver-bearing tailing by mixed moderately thermophilic culture: An emphasis on the chalcopyrite dissolution with XPS and electrochemical analysis [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 81: 29–39. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2015.07.015.
WU Shi-fa, YANG Cong-ren, QIN Wen-qing, JIAO Fen, WANG Jun, ZHANG Yan-sheng. Sulfur composition on surface of chalcopyrite during its bioleaching at 50 °C [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(25): 12–4110. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)64062-6.
YANG Bao-jun, ZHAO Chun-xiao, LUO Wen, LIAO Rui, GAN Min, WANG Jun, LIU Xue-duan, QIU Guan-zhou. Catalytic effect of silver on copper release from chalcopyrite mediated by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 392: 122290. DOI: 10.1016/ j.jhazmat.2020.122290.
CHANG Ke-xin, ZHANG Yan-sheng, ZHANG Jia-ming, LI Teng-fei, WANG Jun, QIN Wen-qing. Effect of temperature-induced phase transitions on bioleaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(29): 10–2183. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65124-1.
WU Ai-xiang, HU Kai-jian, WANG Hong-jiang, ZHANG Ai-qing, YANG Ying. Effect of ultraviolet mutagenesis on heterotrophic strain mutation and bioleaching of low grade copper ore [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(24): 10–2245. DOI: 10.1007/s1l771-017-3634-2.
ZHAO Hong-bo, WANG Jun, QIN Wen-qing, HU Ming-hao, ZHU Shan, QIU Guan-zhou. Electrochemical dissolution process of chalcopyrite in the presence of mesophilic microorganisms [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 71: 159–169. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2014.10.025.
ZHAO Hong-bo, WANG Jun, QIN Wen-qing, ZHENG Xi-hua, TAO Lang, GAN Xiao-wen, QIU Guan-zhou. Surface species of chalcopyrite during bioleaching by moderately thermophilic bacteria [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(25): 8–2725. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63897-3.
ZHAO Hong-bo, HU Ming-hao, LI Yi-ni, ZHU Shan, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou, WANG Jun. Comparison of electrochemical dissolution of chalcopyrite and bornite in acid culture medium [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(25): 1–303.
NANCUCHEO I, JOHNSON D B. Production of glycolic acid by Chemolithotrophic iron- and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and its role in delineating and sustaining acidophilic sulfide mineral-oxidizing consortia [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(76): 2–461. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01832-09.
WANG Xing-xing, LIAO Rui, ZHAO Hong-bo, HONG Mao-xing, HUANG Xiao-tao, PENG Hong, WEN Wen, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou, HUANG Cao-ming, WANG Jun. Synergetic effect of pyrite on strengthening bornite bioleaching by Leptospirillum ferriphilum [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2018, 176: 9–16. DOI: 10.1016/ j.hydromet.2017.12.003.
LIU Sheng, XIE Lei, LIU Jun, LIU Guang-yi, ZHONG Hong, WANG Yi-xiang, ZENG Hong-bo. Probing the interactions of hydroxamic acid and mineral surfaces: Molecular mechanism underlying the selective separation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 374: 123–132. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.152.
ZHAO Hong-bo, HUANG Xiao-tao, WANG Jun, LI Yi-ni, LIAO Rui, WANG Xing-xing, QIU Xiao, XIONG Yu-ming, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Comparison of bioleaching and dissolution process of p-type and n-type chalcopyrite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2017, 109: 153–161. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2017.03.013.
YANG Bao-jun, LIN Mo, FANG Jing-hua, ZHANG Rui-yong, LUO Wen, WANG Xing-xing, LIAO Rui, WU Bai-qiang, WANG Jun, GAN Min, LIU Bin, ZHANG Yi, LIU Xue-duan, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Combined effects of jarosite and visible light on chalcopyrite dissolution mediated by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 698: 134175. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134175.
QIN Wen-qing, LIU Kai, DIAO Meng-xue, WANG Jun, ZHANG Yan-sheng, YANG Cong-ren, JIAO Fen. Oxidation of arsenite (As(III)) by ferric iron in the presence of pyrite and a mixed moderately thermophilic culture [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 137: 53–59. DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.05.011.
LEFEVRE C T, BAZYLINSKI D A. Ecology, diversity, and evolution of magnetotactic bacteria [J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2013, 77(77): 3–497. DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00021-13.
UEBE R, SCHUELER D. Magnetosome biogenesis in magnetotactic bacteria [J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(10): 621–637. DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00021-13.
FAIVRE D, MENGUY N, POSFAI M, SCHUELER D. Environmental parameters affect the physical properties of fast-growing magnetosomes [J]. American Mineralogist, 2008, 93(2, 3): 463–469. DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.99.
POSFAI M, LEFEVRE T., TRUBITSYN D, BAZYLINSKI A, FRANKEL B. Phylogenetic significance of composition and crystal morphology of magnetosome minerals [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2013, 4: 344. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00344.
LEAO P, TEIXEIRA S, CYPRIANO J, FARINA M, ABREU F, BAZYLINSKI A, LINS U. North-seeking magnetotactic gammaproteobacteria in the southern hemisphere [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2016, 82(82): 18–5595. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01545-16.
JI Bo-yang, ZHANG Sheng-da, ZHANG Wei-jia, ROUY Z, ALBERTO F, SANTINI C, MANGENOT S, GAGNOT S, PHILIPPE N, PRADEL N, ZHANG Li-chen, TEMPEL S, LI Ying, MEDIGUE C, HENRISSAT B, COUTINHO P M, BARBE V, TALLA E, WU Long-fei. The chimeric nature of the genomes of marine magnetotactic coccoid-ovoid bacteria defines a novel group of Proteobacteria [J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 19(19): 3–1103. DOI: 10.1111/1462-2920.13637.
HUIZAR-FELIX A M, MUNOZ D, ORUE I, MAGEN C, IBARRA A, BARANDIARAN J M, MUELA A, FDEZ-GUBIEDA M L. Assemblies of magnetite nanoparticles extracted from magnetotactic bacteria: A magnetic study [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 108(6): 0631096. DOI: 10.1063/ 1.4941835.
BAZYLINSKI D A, FRANKEL R B, HEYWOOD B R, MANN S, KING J W, DONAGHAY P L, HANSON A K. Controlled biomineralization of magnetite (Fe304) and greigite (Fe3S4) in a magnetotactic bacterium [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1995, 61(61): 9–3232. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.61.9.3232-3239.1995.
LEFEVRE CHRISTOPHER T, MENGUY N, ABREU F, LINS U, POSFAI M, PROZOROV T, PIGNOL D, FRANKEL R B, BAZYLINSKI D A. A cultured greigite-producing magnetotactic bacterium in a novel group of sulfate-reducing bacteria [J]. Science, 2011, 334(334): 6063–1720. DOI: 10.1126/science.1212596.
BARBER-ZUCKER S, ZARIVACH R. A look into the biochemistry of magnetosome biosynthesis in magnetotactic bacteria [J]. ACS Chemical Biology, 2017, 12(12): 1–13. DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.6b01000.
PROZOROV T, PALO P, WANG Li-jun, NILSEN-HAMILTON M, JONES D, ORR D, MALLAPRAGADA S K, NARASIMHAN B, CANFIELD P C, PROZOROV R. Cobalt ferrite nanocrystals: Out-performing magnetotactic bacteria [J]. ACSNano, 2007, 1(1): 3–228. DOI: 10.1021/ nn700194h.
STANILAND S, WILLIAMS W, TELLING N, van der LAAN G, HARRISON A, WARD B. Controlled cobalt doping of magnetosomes in vivo [J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2008, 3(3): 158–162. DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2008.35.
COKER V S, TELLING N D, van der LAAN G, PATTRICK RAD, PEARCE C I, ARENHOLZ El, TUNA F, WINPENNY RICHARD P, LLOYD JONATHAN R. Harnessing the extracellular bacterial production of nanoscale cobalt ferrite with exploitable magnetic properties [J]. ACS Nano, 2009, 3(3): 7–1922. DOI: 10.1021/nn900293d.
FANG Jing-hua, LIU Yong, HE Wan-li, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou, WANG Jun. Transformation of iron in pure culture process of extremely acidophilic microorganisms [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(27): 5–1150. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60134-1.
YAN Lei, LI Pei-ye, ZHAO Xiao-peng, JI Rong, ZHAO Li-juan. Physiological and metabolic responses of maize (Zea mays) plants to Fe3O4 nanoparticles [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 718: 137400. DOI: 10.1016/ j.scitotenv.2020.137400.
WU Ling-bo, YANG Bao-jun, WANG Xing-xing, WU Bai-qiang, HE Wan-li, GAN Min, QIU Guan-zhou, WANG Jun. Effects of single and mixed energy sources on intracellular nanoparticles synthesized by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(3): 163. DOI: 10.3390/min9030163.
XU Hang, TAN Ling, CUI Hao, XU Mei-ying, XIAO Yong, WU Hai-yan, DONG Hai-gang, LIU Xin-xing, QIU Guan-zhou, XIE Jian-ping. Characterization of Pd(II) biosorption in aqueous solution by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 255: 333–340. DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.01.168.
ZHOU H, ZHANG R, HU P, ZENG W, XIE Y, WU C, QIU G. Isolation and characterization of Ferroplasma thermophilum sp nov., a novel extremely acidophilic, moderately thermophilic archaeon and its role in bioleaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2008, 105(105): 2–591. DOI: 10.HH/j.1365-2672.2008.03807.x.
ZHAO Hong-bo, WANG Jun, GAN Xiao-wen, HU Ming-hao, TAO Lang, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Role of pyrite in sulfuric acid leaching of chalcopyrite: An elimination of poly sulfide by controlling redox potential [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2016, 164: 159–165. DOI: 10.1016/ j.hydromet.2016.04.013.
WANG Jun, GAN Xiao-wen, ZHAO Hong-bo, HU Ming-hao, LI Kai-yun, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Dissolution and passivation mechanisms of chalcopyrite during bioleaching: DFT calculation, XPS and electrochemistry analysis [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016, 98: 264–278. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2016.06.006. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2016.09.008.
WANG Jun, TAO Lang, ZHAO Hong-bo, HU Ming-hao, ZHENG Xi-hua, PENG Hong, GAN Xiao-wen, XIAO Wei, CAO Pan, QIN Wen-qin, QIU Guan-zhou, WANG Dian-zuo. Cooperative effect of chalcopyrite and bornite interactions during bioleaching by mixed moderately thermophilic culture [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016, 95: 116–123. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2016.06.006.
FAIVRE D, SCHUELER D. Magnetotactic Bacteria and Magnetosomes [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2008, 108(108): 11–4875. DOI: 10.1021/cr078258w.
WANG Jun, HU Ming-hao, ZHAO Hong-bo, GAN Min, bGAN Xiao-wen, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Well-controlled column bioleaching of a low-grade copper ore by a novel equipment [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22: 3318–3325. DOI: 10.1007/s1l771-015-2872-4.
BAZYLINSKI D A, LEFEVRE C T. Magnetotactic bacteria from extreme environments [J]. Life-Basel, 2013, 3(2, Sp. Iss. SI): 295–307. DOI: 10.3390/life3020295.
ZHAO Hong-bo, GAN Xiao-wen, WANG Jun, TAO Lang, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Stepwise bioleaching of Cu-Zn mixed ores with comprehensive utilization of silver-bearing solid waste through a new technique process [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2017, 171: 374–386. DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2017.06.002.
FENG Ya-li, WANG Hong-jun, LI Hao-ran, CHEN Xi-pei, DU Zhu-wei, KANG Jin-xing. Effect of iron transformation on Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans bio-leaching of clay vanadium residue [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(4): 796–805. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-019-4049-z.
HONG Mao-xin, WANG Xing-xing, WU Ling-bo, FANG Chao-jun, HUANG Xiao-tao, LIAO Rui, ZHAO Hong-bo, QIU Guan-zhou, WANG Jun. Intermediates transformation of bornite bioleaching by Leptospirillum ferriphilum and Acidithiobacillus caldus [J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(3): 159. DOI: 10.3390/min9030159.
KOMEILI A. Molecular mechanisms of compartmentalization and biomineralization in magnetotactic bacteria [J]. Fems Microbiology Reviews, 2012, 36(36): 1–232. DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00315.x.
LIN Wei, BAZYLINSKI D A, XIAO Tian, WU Long-fei, PAN Yong-xin. Life with compass: Diversity and biogeography of magnetotactic bacteria [J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 16(9SI): 2646–2658. DOI: 10.1111/1462-2920.12313.
SCHEFFEL A, GRUSKA M, FAIVRE D, LINAROUDIS A, GRAUMANN P L, PLITZKO J M, SCHULER D. An acidic protein aligns magnetosomes along a filamentous structure in magnetotactic bacteria (vol 440, pg 110, 2006) [J]. Nature, 2006, 441(7090): 248. DOI: 10.1038/nature04382.
WANG Jun, LIAO Rui, TAO Lang, ZHAO Hong-bo, ZHAI Rui, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. A comprehensive utilization of silver-bearing solid wastes in chalcopyrite bioleaching [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2017, 169: 152–157. DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2017.01.006.
YAN Lei, YUE Xiao-xuan, ZHANG Shuang, CHEN Peng, XU Zhi-liang, LI Yang, LI Hong-yu. Biocompatibility evaluation of magnetosomes formed by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications, 2012, 32(32): 7–1802. DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2012.04.062.
YAN Lei, ZHANG Shuang, CHEN Peng, WANG Wei-dong, WANG Yan-jie, LI Hong-yu. Magnetic properties of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications, 2013, 33(33): 7–4026. DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2013.05.046.
GAN Min, LI Jia-yu, SUN Sheng-jie, CAO Yuan-yan, ZHENG Zhi-he, ZHU Jian-yu, LIU Xin-xing, WANG Jun, QIU Guan-zhou. The enhanced effect of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans on pyrite based Cr(VI) reduction [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 341: 27–36. DOI: 10.1016/ j.cej.2018.02.014.
MOISESCU C, ARDELEAN 11, BENNING L G. The effect and role of environmental conditions on magnetosome synthesis [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2014, 5(49). DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00049.
FUKUDA Y, OKAMURA Y, TAKEYAMA H, MATSUNAGA T. Dynamic analysis of a genomic island in Magnetospirillum sp strain AMB-1 reveals how magnetosome synthesis developed [J]. Febs Letters, 2006, 580(580): 3–801. DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.01.003.
ULLRICH S, KUBE M, SCHUBBE S, REINHARDT R, SCHULER D. A hypervariable 130-kilobase genomic region of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense comprises a magnetosome island which undergoes frequent rearrangements during stationary growth [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2005, 187(187): 21–7176. DOI: 10.1128/ JB.187.21.7176-7184.2005.
JOGLER C, WANNER G, KOLINKO S, NIEBLER M, AMANN R, PETERSEN N, KUBE M, REINHARDT R, SCHUELER D. Conservation of proteobacterial magnetosome genes and structures in an uncultivated member of the deep-branching nitrospira phylum [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(108): 3–1134. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1012694108.
WANG Jun, ZHAO Hong-bo, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Bioleaching of complex polymetallic sulfide ores by mixed culture [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(21): 7–2633. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-014-2223-x.
WANG Jun, ZHU Shan ZHANG Yan-sheng, ZHAO Hong-bo, HU Ming-hao, YANG Cong-ren, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Bioleaching of low-grade copper sulfide ores by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21: 728–734. DOI:10.1007/s1l771-014-1995-3.
ZHAO Hong-bo, ZHANG Yi-sheng, ZHANG Xian, QIAN Lu, SUN Meng-lin, YAN Yu, ZHANG Yan-sheng, WANG Jun, KIM Hyunjung, QIU Guan-zhou. The dissolution and passivation mechanism of chalcopyrite in bioleaching: An overview [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 136: 140–154. DOI:/10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.05.002.
WANG Jun, ZHAO Hong-bo, ZHUANG Tian, QIN Wen-qing, ZHU Shan, QIU Guan-zhou. Bioleaching of Pb-Zn-Sn chalcopyrite concentrate in tank bioreactor and microbial community succession analysis [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(23): 12–3758. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62926-X
ZHAO Hong-bo, HUANG Xiao-tao, HU Ming-hao, ZHANG Chen-yang, WANG Jun QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Insights into the surface transformation and electrochemical dissolution process of bornite in bioleaching [J]. Minerals, 2018,8: 173. DOI: 10.3390/min8040173.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2018JJ1041) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan, China; Projects(51774332, 51934009, U1932129) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Bq., He, Wl., Yang, Bj. et al. Synthesis of intracellular cobalt ferrite nanocrystals by extreme acidophilic archaea Ferroplasma thermophilum. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 1443–1452 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4380-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4380-4
Keywords
- Ferroplasma thermophilum
- cobalt ferrite nanocrystals
- biomineralization
- bioleaching
- extreme acidophilic microorganism