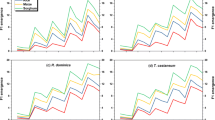
Abstract
Studies on residual efficacy of insecticides with reduced risk are necessary for strategies on their use and application frequency. Within these insecticides, insect growth regulators, such as pyriproxyfen, have been successfully used to control stored grain pests. The objective of this study was to evaluate the residual efficacy of pyriproxyfen in larvae of the stored grain pests Oryzaephilus surinamensis, Tribolium castaneum and Trogoderma granarium. Grains of wheat, maize, rice, and oats were exposed to pyriproxyfen at concentrations of 1, 2 or 4 mg kg−1. Six bioassays were performed by releasing the insects on treated grains after different post treatment periods (0, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 16 weeks). Adult emergence of the three insect species was reduced at tested concentrations in all treated grains. For all bioassays the residual efficacy of pyriproxyfen decreased with increase in the post treatment period. At 4 mg kg−1, the adult emergence did not exceed 16% at week 0 and it was <40% at week 12 in all tested insect species on all grains, but it increased at week 16. The residual effect of pyriproxyfen was more effective in wheat followed by oats, maize and rice for T. castaneum and T. granarium, whereas against O. surinamensis pyriproxyfen was more effective in oats followed by wheat, maize and rice. Results show that pyriproxyfen has potential for residual control of O. surinamensis, T. castaneum and T. granarium, and may be used for replacement of conventional neurotoxic insecticides for managing the insect pests of stored commodities.
Zusammenfassung
Studien zur Residualwirkung von Insektiziden mit reduziertem Risiko sind notwendig für Strategien zu deren Einsatz und Anwendungshäufigkeit. Innerhalb dieser Insektizide wurden Wachstumsregulatoren wie Pyriproxyfen erfolgreich zur Bekämpfung von Vorratsschädlingen eingesetzt. Ziel dieser Studie war es, die Residualwirkung von Pyriproxyfen in Larven der Vorratsschädlinge Oryzaephilus surinamensis, Tribolium castaneum und Trogoderma granarium zu bewerten. Weizen‑, Mais‑, Reis- und Haferkörner wurden mit Pyriproxyfen in Konzentrationen von 1, 2 oder 4 mg kg−1 behandelt. Sechs Bioassays wurden durchgeführt, indem die Insekten nach verschiedenen Behandlungszeiträumen (0, 2, 4, 8, 12 und 16 Wochen) auf die behandelten Körner freigesetzt wurden. Die Entwicklung der Adulten der drei Insektenarten wurde bei den getesteten Konzentrationen in allen behandelten Körnern reduziert. Bei allen Bioassays nahm die Residualwirkung von Pyriproxyfen entsprechend der Behandlungszeit ab. Bei 4 mg kg−1 betrug die Entwicklung von Adulten in Woche 0 nicht mehr als 16 % und lag in Woche 12 bei allen getesteten Insektenarten auf allen Körnern bei <40 %, stieg aber in Woche 16 an. Die Residualwirkung von Pyriproxyfen war bei T. castaneum und T. granarium bei Weizen wirksamer, gefolgt von Hafer, Mais und Reis, während Pyriproxyfen gegen O. surinamensis bei Hafer wirksamer war, gefolgt von Weizen, Mais und Reis. Die Ergebnisse zeigen, dass Pyriproxyfen Potenzial zur Kontrolle von O. surinamensis, T. castaneum und T. granarium besitzt und als Ersatz für herkömmliche neurotoxische Insektizide zur Bekämpfung von Schadinsekten in gelagerten Waren eingesetzt werden kann.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali Q, Hasan M, Sagheer M, Saleem S, Faisal M et al (2017) Screening of seven insect growth regulators for their anti-insect activity against the larvae of Trogoderma granarium (Everts) and Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). Pak J Agric Sci 54:589–595
Ali Q, Hasan M, Shakir HU, Anjum NA, Saleem S et al (2018) Transgenerational effect of insect growth regulators on the Trogoderma granarium (Everts) (Coleoptera: Dermestidae) under different abiotic factors. Pak J Agric Sci 55:897–903
Arbogast RT (1991) Beetles: coleoptera. In: Gorham JR (ed) Ecology and management of food-industry pests. Association of Official Analytical chemists, Arlington, pp 131–150
Arthur FH (1996) Grain protectants: current status and prospects for the future. J Stored Prod Res 32:293–302
Arthur FH (2019) Efficacy of combinations of methoprene and deltamethrin as long-term commodity protectants. Insects 10:50
Arthur FH, Hartzer KL (2018) Susceptibility of selected stored product insects to a combination treatment of pyriproxyfen and novaluron. J Pest Sci 91:699–705
Arthur FH, Liu S, Zhao B, Phillips TW (2009) Residual efficacy of pyriproxifen and hydroprene applied to wood, metal and concrete for control of stored-product insects. Pest Manag Sci 65:791–797
Arthur FH, Ghimire MN, Myers SW, Phillips TW (2018) Evaluation of pyrethroid insecticides and insect growth regulators applied to different surfaces for control of Trogoderma granarium (Coleoptera: Dermestidae) the khapra beetle. J Econ Entomol 111:612–619
Athanassiou CG, Arthur FH, Throne JE (2011) Efficacy of layer treatment with methoprene for control of Rhyzopertha dominica (Coleoptera: Bostrychidae) on wheat, rice and maize. Pest Manag Sci 67:380–384
Athanassiou CG, Phillips TW, Wakil W (2019) Biology and control of the khapra beetle, Trogoderma granarium, a major quarantine threat to global food security. Annu Rev Entomol 64:131–148
Athanassiou CG, Phillips TW, Arthur FH, Aikins MJ, Agrafioti P et al (2020) Efficacy of phosphine fumigation for different life stages of Trogoderma inclusum and Dermestes maculatus (Coleoptera: Dermestidae). J Stored Prod Res 86:101556
Bowditch TG, Madden JL (1997) Infestation of chocolate-based products: Insects responsible and origins of contamination. Austral J Entomol 36:263–267
Boyer S, Zhang H, Lempérière G (2012) A review of control methods and resistance mechanisms in stored-product insects. Bull Entomol Res 102:213–229
Carpaneto B, Bartosik R, Cardoso L, Manetti P (2016) Pest control treatments with phosphine and controlled atmospheres in silo bags with different airtightness conditions. J Stored Prod Res 69:143–151
Castro AA, Lacerda MC, Zanuncio TV, Ramalho FS, Polanczyk RA et al (2012) Effect of the insect growth regulator diflubenzuron on the predator Podisus nigrispinus (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Ecotoxicology 21:96–103
Chanbang Y, Arthur FH, Wilde GE, Throne JE, Subramanyam B (2008) Susceptibility of eggs and adult fecundity of the lesser grain borer, Rhyzopertha dominica, exposed to methoprene. J Insect Sci 8:1–5
Fiaz M, Ali A, Ahmad F, Hasan M, Sagheer M et al (2018) Comparative potential of chitin synthesis inhibitors against Trogoderma granarium (Coleoptera: Dermestidae) for stored wheat management in Pakistan. Pak J Agric Sci 55(4):949–954
Fiaz M, Martínez LC, Plata-Rueda A, Gonçalves WG, de Souza DLL et al (2019) Pyriproxyfen, a juvenile hormone analog, damages midgut cells and interferes with behaviors of Aedes aegypti larvae. PeerJ 7:e7489. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7489
Fields PG (1992) The control of stored-product insects and mites with extreme temperatures. J Stored Prod Res 28:89–118
Ghimire MN, Arthur FH, Myers SM, Phillips TW (2016) Residual efficacy of deltamethrin and b‑cyfluthrin against Trogoderma variabile and Trogoderma inclusum (Coleoptera: Dermestidae). J Stored Prod Res 66:6–11
Hagstrum DW, Subramanyam B (2006) Fundamentals of stored-product entomology. AACC International,, St. Paul, pp 57–76
Hashem MY, Ahmed SS, El-Mohandes MA, Gharib MA (2012) Susceptibility of different life stages of saw-toothed grain beetle Oryzaephilus surinamensis (L.) (Coleoptera: Silvanidae) to modified atmospheres enriched with carbon dioxide. J Stored Prod Res 48:46–51
Hubert J, Stejskal V, Athanassiou CG, Throne JE (2018) Health hazards associated with arthropod infestation of stored products. Annu Rev Entomol 63:553–573
Kavallieratos NG, Athanassiou CG, Vayias BJ, Mihail SB, Tomanovic Z (2009) Insecticidal efficacy of abamectin against three stored-product insect pests: influence of dose rate, temperature, commodity, and exposure interval. J Econ Entomol 102:1352–1359
Kavallieratos NG, Athanassiou CG, Vayias BJ, Tomanovic Z (2012) Efficacy of insect growth regulators as grain protectants against two stored-product pests in wheat and maize. J Food Prot 75:942–950
Kavallieratos NG, Athanassiou CG, Korunic Z, Mikeli NH (2015) Evaluation of three novel diatomaceous earths against three stored-grain beetle species on wheat and maize. Crop Prot 75:132–138
Koeppe JK, Fuchs M, Chen TT, Hunt LM, Kovalick GE et al (1985) The role of juvenile hormone in reproduction. In: Kerkut LI, Gilbert GA (eds) Comprehensive insect physiology and pharmacology, vol 8. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 165–203
Korunic Z (1998) Diatomaceous earths, a group of natural insecticides. J Stored Prod Res 34:87–97
Kostyukovsky M, Chen B, Atsmi S, Shaaya E (2000) Biological activity of two juvenoids and two ecdysteroids against three stored product insects. Insect Biochem Molec Biol 30:891–897
Liu SS, Arthur FH, VanGundy D, Phillips TW (2016) Combination of methoprene and controlled aeration to manage insects in stored wheat. Insects 7:25
Mamatha DM, Kanji VK, Cohly HHP, Rao MR (2008) Juvenile hormone analogues, methoprene and fenoxycarb dose dependently enhance certain enzyme activities in the silkworm Bombyx mori (L.). Int J Environ Res Public Health 5:120–124
Martinez LC, Plata-Rueda A, Neves GS, Gonçalves WG, Zanuncio JC et al (2018) Permethrin induces histological and cytological changes in the midgut of the predatory bug, Podisus nigrispinus. Chemosphere 212:629–637
Martinez LC, Plata-Rueda A, Gonçalves WG, Aires Freire AFP, Zanuncio JC et al (2019) Toxicity and cytotoxicity of the insecticide imidacloprid in the midgut of the predatory bug, Podisus nigrispinus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 167:69–75
Mondal KAMSH, Parween S (2000) Insect growth regulators and their potential in the management of stored-product insect pests. Integr Pest Manag Rev 5:255–295
Myers SW, Hagstrum DW (2012) Quarantine. In: Hagstrum DW, Phillips TW, Cuperus G (eds) Stored product protection. Kansas State University, Manhattan, pp 297–304
Oberlander H, Silhacek D (2000) Insect growth regulators. In: Subramanyam B, Hagstrum DW (eds) Alternatives to pesticides in stored-product IPM. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp 147–163
Oberlander H, Silhacek DL, Shaaya E, Ishaaya I (1997) Current status and future perspectives of the use of insect growth regulators for the control of stored product pests. J Stored Prod Res 33:1–6
Oberlander H, Silhacek D, Leach CE (1998) Interactions of ecdysteroid and juvenoid agonists in Plodia interpunctella (Hubner). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 38:91–99
Parween S, Faruki SI, Begum M (2001) Impairment of reproduction in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) due to larval feeding on triflumuron-treated diet. J Appl Entomol 125:413–416
Phillips TW, Throne JE (2010) Biorational approaches to managing stored-product insects. Annu Rev Entomol 55:375–397
Pricket AJ, Muggleton J, Llewellin JA (1990) Insecticide resistance in populations of Oryzaephilus surinamensis and Cryptolestes ferrugineus from grain stores in England and Wales. Proc Brighton Crop Prot Conf Pests Dis 3:1189–1194
R Core Team (2013) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Sagheer M, Yasir M, Hasan M, Ashfaq M (2012) Impact of triflumuron on reproduction and development of red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Pak J Agric Sci 49:173–178
Santos-Junior VC, Martinez LC, Plata-Rueda A, Bozdogan H, Zanuncio JC et al (2019) Exposure to spinosad induces histopathological and cytotoxic effects on the salivary complex of the non-target predato Podisus nigrispinus. Chemosphere 225:688–695
Scheff DS, Subramanyam B, Arthur FH (2016) Effect of methoprene treated polymer packaging on fecundity, egg hatchability, and egg-to-adult emergence of Tribolium castaneum and Trogoderma variabile. J Stored Prod Res 69:227–234
Scheff DS, Subramanyam B, Arthur FH (2017) Susceptibility of Tribolium castaneum and Trogoderma variabile larvae and adults exposed to methoprene-treated woven packaging material. J Stored Prod Res 73:142–150
Segura DF, Caceres C, Vera MT, Wornoayporn V, Islam A et al (2009) Enhancing mating performance after juvenile hormone treatment in Anastrepha fraterculus: a different response in males and females acts as a physiological sexing system. Entomol Exper Applic 131:75–84
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research, 3rd edn. W.H. Freeman and Co, New York
Staal GB (1975) Insect growth regulators with juvenile hormone activity. Annu Rev Entomol 20:417–460
Trematerra P, Gentile P, Brunetti A, Collins LE, Chambers J (2007) Spatio-temporal analysis of trap catches of Tribolium confusum duVal in a semolina mill, with a comparison of female and male distributions. J Stored Prod Res 43:315–322
Trostanetsky A, Kostyukovsky M, Quinn E (2015) Transovarial effect of novaluron on Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) after termination of direct contact. J Insect Sci 15:125
Vayias BJ, Athanassiou CG, Milonas DN, Mavrotas C (2010) Persistence and efficacy of spinosad on wheat, maize and barley grains against four major stored product pests. Crop Prot 29:496–505
Wijayaratne LKW, Fields PG, Arthur FH (2012) Effect of methoprene on the progeny production of Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Pest Manag Sci 68:217–224
Yasir M, Sagheer M, Abbas SK, Hasan M, Ahmad S et al (2019a) Bioactivity of lufenuron against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Sains Malays 48:75–80
Yasir M, Hasan M, Sagheer M, Javed N (2019b) Residual efficacy of methoxyfenozide applied on different grain commodities for the control of three stored-product insect pests. Türk Entomol Derg 43:385–394
Zettler JL, Cuperus GW (1990) Pesticide resistance in Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) and Rhyzopertha dominica (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae) in wheat. J Econ Entomol 83:1677–1681
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
M. Yasir, M. ul Hasan, M. Sagheer, M. Fiaz and J.E. Serrão declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasir, M., ul Hasan, M., Sagheer, M. et al. Residual Efficacy of Pyriproxyfen on Grain Commodities Against Stored Product Insect Pests. Gesunde Pflanzen 72, 265–272 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-020-00509-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-020-00509-3
Keywords
- Insect growth regulator
- Grain commodities
- Juvenile hormone analog
- Stored grain insects
- Residual efficacy