Abstract
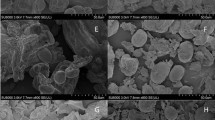
This study examined the effects of different doses of irradiation treatments on protein structure and digestion characteristic of seed-watermelon seed kernel protein. The results showed that, the molecular structure of seed-watermelon kernel protein was unfolded after the irradiation treatment, the content of β-sheet structure in the secondary structure was decreased, while the content of random coil structure increased. The average particle size of the protein increased, and the hydrophobic group buried in the β-sheet structure was exposed hence the surface hydrophobicity increased. Besides, the surface morphology of seed-watermelon protein changed from smooth and flat to coarse and concave, the specific surface area in contact with the aqueous medium increased and its solubility increased, the distribution of peptides in the digesta became wider, and the small molecular weight peptides gradually increased.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Bachir M. Some microbial, chemical and sensorial properties of gamma irradiated sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) seeds. Food Chem. 197: 191-197 (2016)
Chen N, Zhao, M, Sun, W, Ren J, Cui C. Effect of oxidation on the emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 52: 26-32 (2013)
Chen Y, Liu B, Yu HT, Barkley MD. The peptide bond quenches indole fluorescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118: 9271-9278 (1996)
Cho YS, Song KB. Effect of γ-irradiation on the molecular properties of bovine serum albumin and β-lactoglobulin. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 33: 133-137 (2000)
Du YX, Jiang Y, Zhu XM, Xiong H, Shi SH, Hu JW, Peng HL, Zhou Q, Sun WJ. Physicochemical and functional properties of the protein isolate and major fractions prepared from Akebia trifoliata var. australis seed. Food Chem. 133: 923-929 (2012)
El-Adawy TA, Taha KM. Characteristics and composition of different seed oils and flours. Food Chem. 74: 47-54 (2001)
Jin Y, Liang R, Liu J, Lin S, Yu Y, Cheng S. Effect of structure changes on hydrolysis degree, moisture state, and thermal denaturation of egg white protein treated by electron beam irradiation. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 77: 134-141 (2016)
Karthika K, Arun A, Melo J, Mittal K, Kumar M, Rekha P. Hydrolysis of acid and alkali presoaked lignocellulosic biomass exposed to electron beam irradiation. Bioresour. Technol. 129: 646-649 (2013)
Kato A, Nakai S. Hydrophobicity determined by a fluorescence probe method and its correlation with surface properties of proteins. BBA-Biomembranes 624: 13-20 (1980)
Koppelman SJ, Nieuwenhuizen WF, Gaspari M, Knippels LMJ, Penninks AH, Knol EF, Hefle SL, Jongh HHJ. Reversible denaturation of Brazil nut 2S albumin (Ber e1) and implication of structural destabilization on digestion by pepsin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53: 123-131 (2005).
Kristo E, Hazizaj A, Corredig M. Structural changes imposed on whey proteins by UV irradiation in a continuous UV light reactor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 60: 6204-6209 (2012)
Lassé M, Deb CS, Haines S, Larsen N, Gerrard JA, Dyer JM. The impact of pH, salt concentration and heat on digestibility and amino acid modification in egg white protein. J. Food Compos. Anal. 38: 42-48 (2015)
Li Zh, Zhou B, Li XT, Li, SG. Effect of alkaline electrolyzed water on physicochemical and structural properties of apricot protein isolate. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 28: 15-23 (2019)
Lin S, Wang K, Liu J. Improving effect of enzyme hydrolysis of corn gluten meal by assistant of electron beam irradiation. TCSAE 30: 300-308 (2014)
Lu X, Zhang H, Zhang H, Deng Z, Wang L, Qian H, Qi X. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of black seed-watermelon seeds protein and the in vitro antioxidant activity of the antioxidant peptides. Food Technol. Chicago 40: 73-78 (2015)
Lv L, Chi Y, Chen C, Xu W. Structural and functional properties of ovalbumin glycated by dry-heating in the presence of maltodextrin. Int. J. Food Prop. 18: 1326-1333 (2015)
Lv M, Mei K, Zhang H, Xu D, Yang W. Effects of electron beam irradiation on the biochemical properties and structure of myofibrillar protein from Tegillarca granosa meat. Food Chem. 254: 64-69 (2018)
Malik MA, Sharma HK, Saini CS. Effect of gamma irradiation on structural, molecular, thermal and rheological properties of sunflower protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 72: 312-322 (2017)
Menge H, Richardson GV. The influence of a linoleic-acid-deficient maternal diet on growth of progeny. Poult. Sci. 47: 542-547 (1968)
Moon S, Song KB. Effect of γ-irradiation on the molecular properties of ovalbumin and ovomucoid and protection by ascorbic acid. Food Chem. 74: 479-483 (2001)
Nielsen PM, Petersen D, Dambmann C, Nielsen PM, Petersen D, Improved method for determining food protein degree of hydrolysis. J. Food Sci. 66: 642-646 (2001)
Pal RN, Mahadevan V. Chemical composition and nutritive value of Bijada cake (Citrulus vulgaris). Indian Vet. J. 45: 433 (1968)
Plancken IVD, Loey AV, Hendrickx ME. Foaming properties of egg white proteins affected by heat or high pressure treatment. J. Food Eng. 78: 1410-1426 (2007)
Robertson JA, Eastwood MA. An examination of factors which may affect the water holding capacity of dietary fibre. Br. J. Nutr. 45: 83-88 (1981)
Shah WH. Tannin contents and protein digestibility of black grams (Vigna mungo) after soaking and cooking. Plant Food Hum. Nutr. 56: 265-273 (2001)
Shawrang P, Nikkhah A, Zare SA, Sadeghi AA, Raisali G, Moradi SM. Effects of gamma irradiation on chemical composition and ruminal protein degradation of canola meal. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 77: 918-922 (2008)
Wang J, Chi Y, Cheng Y, Zhao Y. Physicochemical properties, in vitro digestibility and antioxidant activity of dry-heated egg white protein. Food Chem. 246: 18-25 (2018)
Wang L, Zhang X, Liu F, Ding Y, Wang R, Luo X, Li Y, Chen Z. Study of the functional properties and anti-oxidant activity of pea protein irradiated by electron beam. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 41: 124-129 (2017)
Wu L, Zhao W, Yang R, Yan W, Sun Q. Aggregation of egg white proteins with pulsed electric fields and thermal processes. J. Sci. Food Agr. 96: 3334-3341 (2016)
Xue P, Zhao Y, Wen C, Cheng S, Lin S. Effects of electron beam irradiation on physicochemical properties of corn flour and improvement of the gelatinization inhibition. Food Chem. 233: 467-475 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the following foundations: Comprehensive utilization of horticultural crop product processing by-products (No. 20150314208). Construction project of Youth Science and technology innovation leader in Corps (No. 2016BC001). Key technologies for quality control of seed snack foods and pilot demonstrations (No. 2019420113000018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Chu, S., Wang, P. et al. Effects of irradiation treatment on protein structure and digestion characteristics of seed-watermelon (Citrullus lanatus var.) kernel protein. Food Sci Biotechnol 29, 1201–1211 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-020-00777-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-020-00777-9