Abstract
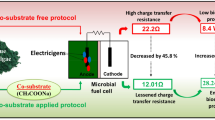
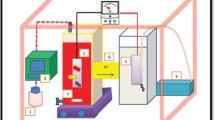
In recent years, microbial fuel cell (MFC) has been regarded as a promising technology for dye wastewater treatment. Compared with traditional anaerobic reactors, MFC has better decolorization effect while producing electricity simultaneously. In this paper, a double-chamber MFC with the sponge anode modified by polyaniline and chitosan-NCNTs was employed for simultaneous azo dye decolorization and bioelectricity generation. The influence of dye concentration, co-substrate concentration, and operating temperature on the performance of MFC with the modified anodes were studied. The results showed that a high decolorization efficiency (98.41%) and maximum power density (2816.67 mW m−3) of MFC equipped with modified bioanodes were achieved due to the biocompatibility and bioelectrocatalysis of modified material. And the biomass on the modified anode’s surface was increased by 1.47 times. Additionally, microbial community analysis revealed that the modification of polyaniline and chitosan-NCNTs improved the selective enrichment of specific communities and the main microorganism was the electroactive and decolorizing bacteria Enterobacter (62.84%). Therefore, the composite anode is capable of fully utilizing the synergistic role of various materials, leading to superior performance of dye decolorization in MFCs. This work provided a strategy for the research on the recovery of biomass energy and decolorization in wastewater treatment.

Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saratale, R. G., Saratale, G. D., Chang, J. S., & Govindwar, S. P. (2011). Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: a review. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 42(1), 138–157.
Zhang, Y., Liu, M. M., Zhou, M. H., Yang, H. J., Liang, L., & Gu, T. Y. (2019). Microbial fuel cell hybrid systems for wastewater treatment and bioenergy production: synergistic effects, mechanisms and challenges. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 103, 13–29.
Kumar, S. S., Kumar, V., Malyan, S. K., Sharma, J., Mathimani, T., Maskarenj, M. S., Ghosh, P. C., & Pugazhendhi, A. (2019). Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for bioelectrochemical treatment of different wastewater streams. Fuel, 254(15), 115526.
Nidheesh, P. V., Zhou, M. H., & Oturan, M. A. (2018). An overview on the removal of synthetic dyes from water by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere, 197, 210–227.
Guo, X., Zhan, Y. L., Chen, C. M., Cai, B., Wang, Y., & Guo, S. H. (2016). Influence of packing material characteristics on the performance of microbial fuel cells using petroleum refinery wastewater as fuel. Renewable Energy, 87(1), 437–444.
Fang, Z., Song, H. L., Cang, N., & Li, X. N. (2015). Electricity production from azo dye wastewater using a microbial fuel cell coupled constructed wetland operating under different operating conditions. Biosens Bioelectron, 68(15), 135–141.
Fang, Z., Song, H. L., Yu, R., & Li, X. N. (2016). A microbial fuel cell-coupled constructed wetland promotes degradation of azo dye decolorization products. Ecological Engineering, 94, 455–463.
Wen, Q., Kong, F. Y., Zheng, H. T., Yin, J. L., Cao, D. X., Ren, Y. M., & Wang, G. L. (2011). Simultaneous processes of electricity generation and ceftriaxone sodium degradation in an air-cathode single chamber microbial fuel cell. Journal of Power Sources, 196(5), 2567–2572.
Kim, K. Y., Yang, W. L., & Logan, B. E. (2015). Impact of electrode configurations on retention time and domestic wastewater treatment efficiency using microbial fuel cells. Water Research, 80(1), 41–46.
Li, Z. J., Zhang, X. W., Lin, J., Han, S., & Lei, L. C. (2010). Azo dye treatment with simultaneous electricity production in an anaerobic-aerobic sequential reactor and microbial fuel cell coupled system. Bioresource Technology, 101(12), 4440–4445.
Cao, Y. Q., Hu, Y. Y., Sun, J. A., & Hou, B. (2010). Explore various co-substrates for simultaneous electricity generation and Congo red degradation in air-cathode single-chamber microbial fuel cell. Bioelectrochemistry, 79(1), 71–76.
Zhang, X., Li, X., Zhao, X., & Li, Y. (2019). Factors affecting the efficiency of a bioelectrochemical system: a review. RSC Advances, 9, 19748–19761.
Santoro, C., Arbizzani, C., Erable, B., & Ieropoulos, I. (2017). Microbial fuel cells: from fundamentals to applications. A review. Journal of Power Sources, 356(15), 225–244.
Valdivia, A., Gonzalez-Martinez, S., & Wilderer, P. A. (2007). Biological nitrogen removal with three different SBBR. Water Science and Technology, 55(7), 245–254.
Deng, L. J., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W. S., Wang, J., & Zhang, H. W. (2018). Evaluation of a new sponge addition-microbial fuel cell system for removing nutrient from low C/N ratio wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 338(15), 166–175.
Wang, H. C., Liu, X. P., Zhang, B. C., Yang, J. B., Zhang, Z. J., Yue, R. R., & Wang, Z. W. (2019). Highly compressible supercapacitor based on carbon nanotubes-reinforced sponge electrode. Journal of Alloys And Compounds, 786(25), 995–1004.
Ma, C. Y., & Hou, C. H. (2019). Enhancing the water desalination and electricity generation of a microbial desalination cell with a three-dimensional macroporous carbon nanotube-chitosan sponge anode. Sci Total Environ, 675(20), 41–50.
Quan, X. C., Xu, H. D., Sun, B., & Xiao, Z. T. (2018). Anode modification with palladium nanoparticles enhanced Evans Blue removal and power generation in microbial fuel cells. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 132, 94–101.
Mohamed, H. O., Obaid, M., Poo, K. M., Abdelkareem, M. A., Talas, S. A., Fadali, O. A., Kim, H. Y., & Chae, K. J. (2018). Fe/Fe2O3 nanoparticles as anode catalyst for exclusive power generation and degradation of organic compounds using microbial fuel cell. Chemical Engineering Journal, 349(1), 800–807.
Zhong, D. J., Liu, Y. Q., Liao, X. R., Zhong, N. B., & Xu, Y. L. (2018). Facile preparation of binder-free NiO/MnO2-carbon felt anode to enhance electricity generation and dye wastewater degradation performances of microbial fuel cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 43(51), 23014–23026.
Liu, X., Zhao, X. H., Yu, Y. Y., Wang, Y. Z., Shi, Y. T., Cheng, Q. W., Z., F., & Yong, Y. C. (2017). Facile fabrication of conductive polyaniline nanoflower modified electrode and its application for microbial energy harvesting. Electrochimica Acta., 255(20), 41–47.
Zhong, D. J., Liao, X. R., Liu, Y. Q., Zhong, N. B., & Xu, Y. L. (2018). Enhanced electricity generation performance and dye wastewater degradation of microbial fuel cell by using a petaline NiO@ polyaniline-carbon felt anode. Bioresource Technology, 258, 125–134.
Yellappa, M., Sravan, J. S., Sarkar, O., Reddy, Y., & Mohan, S. V. (2019). Modified conductive polyaniline-carbon nanotube composite electrodes for bioelectricity generation and waste remediation. Bioresource Technology, 284, 148–154.
Lv, Z. S., Chen, Y. F., Wei, H. C., Li, F. S., Hu, Y., Wei, C. H., & Feng, C. H. (2013). One-step electrosynthesis of polypyrrole/graphene oxide composites for microbial fuel cell application. Electrochimica Acta, 111, 366–373.
Wang, W., You, S. J., Gong, X. B., Qi, D. P., Chandran, B. K., Bi, L. P., Cui, F. Y., & Chen, X. D. (2016). Bioinspired nanosucker array for enhancing bioelectricity generation in microbial fuel cells. Advanced Materials, 28(2), 270–275.
Sun, J., Cai, B. H., Xu, X. J., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y. P., Peng, Y. P., Chang, K. L., Kuo, J. H., Chen, K. F., Ning, X. N., Liu, G. H., Wang, Y. J., Yang, Z. Y., & Liu, J. Y. (2017). Enhanced bioelectricity generation and azo dye treatment in a reversible photo-bioelectrochemical cell by using novel anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS)/MnOx-doped polypyrrole film electrodes. Bioresource Technology, 225, 40–47.
Chen, T. W., Vasantha, A. S., Chen, S. M., Farraj, D. A., Elshikh, M. S., Alkufeidy, R. M., & Al Khulaifi, M. M. (2019). Sonochemical synthesis and fabrication of honeycomb like zirconium dioxide with chitosan modified electrode for sensitive electrochemical determination of anti-tuberculosis (TB) drug. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 59, 104718.
Zhao, X. B., Wei, Z. H., Zhao, Z. P., Miao, Y. L., Qiu, Y. D., Yang, W. J., Jia, X., Liu, Z. Y., & Hou, H. W. (2018). Design and development of graphene oxide nanoparticle/chitosan hybrids showing pH-sensitive surface charge-reversible ability for efficient intracellular doxorubicin delivery. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10(7), 6608–6617.
Saldias, C., Diaz, D. D., Bonardd, S., Soto-Marfull, C., Cordoba, A., Saldias, S., Quezada, C., Radic, D., & Leiva, Á. (2018). In situ preparation of film and hydrogel bio-nanocomposites of chitosan/ fluorescein-copper with catalytic activity. Carbohydrate Polymers, 180(15), 200–208.
Xu, H. T., Wu, J. S., Qi, L. J., Chen, Y., Wen, Q., Duan, T. G., & Wang, Y. Y. (2018). Preparation and microbial fuel cell application of sponge-structured hierarchical polyaniline-texture bioanode with an integration of electricity generation and energy storage. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 48(11), 1285–1295.
Wang, Y. Y., Wen, Q., Chen, Y., & Qi, L. J. (2017). A novel polyaniline interlayer manganese dioxide composite anode for high-performance microbial fuel cell, A review. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 75, 112–118.
Kumru, M., Eren, H., Catal, T., Bermek, H., & Akarsubasi, A. T. (2012). Study of azo dye decolorization and determination of cathode microorganism profile in air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Environmental Technology, 33(18), 2167–2175.
Solis, M., Solis, A., Perez, H. I., Manjarrez, N., & Flores, M. (2012). Microbial decolouration of azo dyes: a review. Process Biochemistry, 47(12), 1723–1748.
Zhang, B. G., Zhao, H. Z., Zhou, S. G., Shi, C. H., Wang, C., & Ni, J. R. (2009). A novel UASB-MFC-BAF integrated system for high strength molasses wastewater treatment and bioelectricity generation. Bioresource Technology, 100(23), 5687–5693.
Huang, L. P., Cheng, S. A., & Chen, G. H. (2011). Bioelectrochemical systems for efficient recalcitrant wastes treatment. Journal of Chemical Technology And Biotechnology., 86(4), 481–491.
Guo, W., Feng, J. L., Song, H., & Sun, J. H. (2014). Simultaneous bioelectricity generation and decolorization of methyl orange in a two-chambered microbial fuel cell and bacterial diversity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(9), 11531–11540.
Morris, J. M., Jin, S., Crimi, B., & Pruden, A. (2009). Microbial fuel cell in enhancing anaerobic biodegradation of diesel. Chemical Engineering Journal, 146(2), 161–167.
Sun, J., Hu, Y. Y., & Hou, B. (2011). Electrochemical characteriztion of the bioanode during simultaneous azo dye decolorization and bioelectricity generation in an air-cathode single chambered microbial fuel cell. Electrochimica Acta, 56(19), 6874–6879.
Fang, Z., Cao, X., Li, X. X., Wang, H., & Li, X. N. (2017). Electrode and azo dye decolorization performance in microbial-fuel-cell-coupled constructed wetlands with different electrode size during long-term wastewater treatment. Bioresource Technology, 238, 450–460.
Wang, J. F., Song, X. S., Wang, Y. H., Abayneh, B., Ding, Y., Yan, D. H., & Bai, J. H. (2016). Microbial community structure of different electrode materials in constructed wetland incorporating microbial fuel cell. Bioresource Technology, 221, 697–702.
Sun, R., Zhou, A. J., Jia, J. N., Liang, Q., Liu, Q., Xing, D. F., & Ren, N. Q. (2015). Characterization of methane production and microbial community shifts during waste activated sludge degradation in microbial electrolysis cells. Bioresource Technology, 175, 68–74.
Miran, W., Nawaz, M., Kadam, A., Shin, S., Heo, J., Jang, J., & Lee, D. S. (2015). Microbial community structure in a dual chamber microbial fuel cell fed with brewery waste for azo dye degradation and electricity generation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(17), 13477–13485.
Kong, F. Y., Ren, H. Y., Pavlostathis, S. G., Wang, A. J., Nan, J., & Ren, N. Q. (2018). Enhanced azo dye decolorization and microbial community analysis in a stacked bioelectrochemical system. Chemical Engineering Journal, 354(15), 351–362.
Li, T. T., Fang, Z., Yu, R., Cao, X., Song, H. L., & Li, X. N. (2016). The performance of the microbial fuel cell-coupled constructed wetland system and the influence of the anode bacterial community. Environmental Technology, 37(13), 1683–1692.
Toczylowska-Maminska, R., Szymona, K., Madej, H., Wong, W. Z., Bala, A., Brutkowski, W., Krajewski, K., H’ng, P. S., & Mamiński, M. (2015). Cellulolytic and electrogenic activity of Enterobacter cloacae in mediatorless microbial fuel cell. Applied Energy, 160(15), 88–93.
Logan, B. E., Rossi, R., Ragab, A., & Saikaly, P. E. (2019). Electroactive microorganisms in bioelectrochemical systems. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 17(5), 307–319.
Cui, M. H., Cui, D., Gao, L., Cheng, H. Y., & Wang, A. J. (2016). Analysis of electrode microbial communities in an up-flow bioelectrochemical system treating azo dye wastewater. Electrochimica Acta, 220(1), 252–257.
Chen, G., Huang, M. H., Chen, L., & Chen, D. H. (2011). A batch decolorization and kinetic study of Reactive Black 5 by a bacterial strain Enterobacter sp GY-1. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 65(6), 790–796.
Holkar, C. R., Pandit, A. B., & Pinjari, D. V. (2014). Kinetics of biological decolorisation of anthraquinone based Reactive Blue 19 using an isolated strain of Enterobacter sp. F NCIM 5545. Bioresource Technology, 173, 342–351.
Funding
The project was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21878060 and 21476053), Research Fund of State Key Laboratory for Marine Corrosion and Protection of Luoyang Ship Material Research Institute under the contract no. 6142901180401, China Scholarship Council (201806685019), and Research Project Fund of Harbin University of Commerce (2019DS082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Wang, L., Lin, C. et al. Improved Simultaneous Decolorization and Power Generation in a Microbial Fuel Cell with the Sponge Anode Modified by Polyaniline and Chitosan. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 192, 698–718 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03346-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03346-2