Abstract
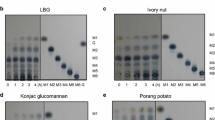
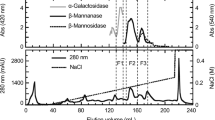
Endo-1,4-β-mannosidases catalyze the cleavage of the β-d-1,4-mannopyranosyl linkage in mannan and have potential biotechnological applications in biofuel production, manno-oligosaccharide production, cleansing, and food and feed industries. In this study, an endo-1,4-β-mannosidase gene (TaMan3A) from wheat (Triticum aestivum) was successfully expressed in Pichia pastoris, and the antifungal effectiveness and manno-oligosaccharide production of the enzyme were evaluated. The purified TaMan3A exhibited a molecular weight of approximately 43 kDa, and its highest enzyme activity at pH 4.0 and 40 °C. Comparisons with other β-mannanases showed that TaMan3A had a conserved mannan-binding V-shaped groove, catalytic acid/base residue (E179), and nucleophilic residue (E297). Antifungal assays for TaMan3A against seven fungi commonly associated with wheat kernels showed that this enzyme had higher inhibitory effects on hyphal growth of the field fungi Fusarium graminearum and Alternaria sp. in comparison with that of storage fungi. TaMan3A could hydrolyze mannan polymers of galactomannan and Konjac glucomannan to mannobiose, mannotriose, and mannotetraose as the main products. Overall, these results showed the potential of TaMan3A for enhancing host resistance against fungal pathogens in wheat and manno-oligosaccharide production in the feed and food industries.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TaMan3A:
-
endo-1,4-β-mannosidase gene in Triticum aestivum chromosome 3A
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- YPD:
-
yeast extract peptone dextrose medium
- TLC:
-
thin-layer chromatography
References
Ali S, Ganai BA, Kamili AN, Bhat AA, Mir ZA, Bhat JA, Tyagi A, Islam ST, Mushtaq M, Yadav P, Rawat S, Grover A (2018) Pathogenesis-related proteins and peptides as promising tools for engineering plants with multiple stress tolerance. Microbiol Res 212–213:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2018.04.008
Anguelova-Merhar VS, Westhuizen AJV, Pretorius ZA (2001) β-1,3-Glucanase and chitinase activities and the resistance response of wheat to leaf rust. J Phytopathol 149(7–8):381–384. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0434.2001.tb03866.x
Arlorio M, Ludwig A, Boiler T, Bonfante P (1992) Inhibition of fungal growth by plant chitinases and beta-1,3-glucanases: a morphological study. Protoplasma 171(1–2):34–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01379278
Balasubramanian V, Vashisht D, Cletus J, Sakthivel N (2012) Plant β-1,3-glucanases: their biological functionsand transgenic expression against phytopathogenic fungi. Biotechnol Lett 34:1983–1990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1012-6
Barbosa IP, Kemmelmeier C (1993) Chemical composition of the hyphal wall from Fusarium graminearum. Exp Mycol 17(4):274–283. https://doi.org/10.1006/emyc.1993.1026
Behera SS, Ray RC (2016) Konjac glucomannan, a promising polysaccharide of Amorphophallus konjac K. Koch in health care. Int J Biol Macromol 92:942–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.098
Bien-Cuong D, Thi-Thu D, Berrin J-G, Haltrich D, Kim-Anh T, Sigoillot J-C, Yamabhai M (2009) Cloning, expression in Pichia pastoris, and characterization of a thermostable GH5 mannan endo-1,4- β -mannosidase from Aspergillus niger BK01. Microb Cell Fact 8(1):59. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-8-59
Bourgault R, Oakley AJ, Bewley JD, Wilce MCJ (2005) Three-dimensional structure of (1,4)-β-D-mannan mannanohydrolase from tomato fruit. Protein Sci 14:1233–1241. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.041260905
Brummell DA, Cin VD, Crisosto CH, Labavitch JM (2004) Cell wall metabolism during maturation, ripening and senescence of peach fruit. J Exp Bot 55(405):2029–2039. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh227
Bush DA, Horisberger M (1973) Mannan of yeast bud scars. J Biol Chem 248(4):1318–1320
Chauhan PS, Puri N, Sharma P, Gupta N (2012) Mannanases: microbial sources, production, properties and potential biotechnological applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:1817–1830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-3887-5
Chauhan P, George N, Sondhi S, Puri N, Gupta N (2014) An overview of purification strategies for microbial mannanases. Int J Pharma Bio Sci 5(1):176–192
Cletus J, Balasubramanian V, Vashisht D, Sakthivel N (2013) Transgenic expression of plant chitinases to enhance disease resistance. Biotechnol Lett 35:1719–1732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1269-4
Dhawan S, Kaur J (2007) Microbial mannanases: an overview of production and applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 27:197–216. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388550701775919
Fan Q, Tian S, Liu H, Xu Y (2002) Production of β-1,3-glucanase and chitinase of two biocontrol agents and their possible modes of action. Chin Sci Bull 47(4):292–296. https://doi.org/10.1360/02tb9070
Free SJ (2013) Fungal cell wall organization and biosynthesis. Adv Genet 81:33–82
Gong X-m, Yan R-w, Xu H-y, Li C, Guang S-y, Fang M (2002) Study of the extraction methods and properties of konjak glucomannan. Chin Fine Chem 19(8):486–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-407677-8.00002-6
Grover A (2012) Plant chitinases: genetic diversity and physiological roles. Crit Rev Plant Sci 31:57–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2011.616043
Hector RF (1993) Compounds active against cell walls of medically important fungi. Clin Microbiol Rev 6(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.6.1.1
Hiller K, Grote A, Scheer M, Münch R, Jahn D (2004) PrediSi: prediction of signal peptides and their cleavage positions. Nucleic Acids Res 32:W375–W379. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh378
Hoshikawa K, Endo S, Mizuniwa S, Makabe S, Takahashi H, Nakamura I (2012) Transgenic tobacco plants expressing endo-β-mannanase gene from deep-sea Bacillus sp. JAMB-602 strain confer enhanced resistance against fungal pathogen (Fusarium oxysporum). Plant Biotechnol Rep 6:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-012-0219-2
Johnston IR (1965) The composition of the cell wall of Aspergillius niger. Biochem J 96(3):651–658. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj0960651
Katsuraya K, Okuyama K, Hatanaka K, Oshima R, Sato T, Matsuzaki K (2003) Constitution of konjac glucomannan: chemical analysis and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Carbohyd Polym 53:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(03)00039-0
Lim TK (2012) Triticum aestivum. Edible medicinal and non-medicinal plants 5(Fruits):385–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5653-3_20
Liu B, Lu Y, Xin Z, Zhang Z (2009) Identification and antifungal assay of a wheat β-1,3-glucanase. Biotechnol Lett 31:1005–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-9958-8
Lombard V, Ramulu HG, Drula E, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B (2014) The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D490–D495. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1178
Magan N, Hope R, Cairns V, Aldred D (2003) Post-harvest fungal ecology: Impact of fungal growth and mycotoxin accumulation in stored grain. Eur J Plant Pathol 109:723–730. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1026082425177
Martina Aulitto S, Fusco D, Limauro G, Fiorentino S, Bartolucci P (2019) Galactomannan degradation by thermophilic enzymes: a hot topic for biotechnological applications. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2591-3
Muthukrishnan S, Liang GH, Trick HN, Gill BS (2001) Pathogenesis-related proteins and their genes in cereals. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 64(2–3):93–114. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1010763506802
Nonogaki H, Gee OH, Bradford KJ (2000) A germination-specific endo-β-mannanase gene is expressed in the micropylar endosperm cap of tomato seeds. Plant Physiol 123:1235–1245. https://doi.org/10.2307/4279361
Oerkea E-C, Meiera A, Dehnea H-W, Sulyokb M, Krskab R, Steiner U (2010) Spatial variability of fusarium head blight pathogens and associated mycotoxins in wheat crops. Plant Pathol 59:671–682. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2010.02286.x
Petersen TN, Brunak S, Heijne Gv, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8:785–786. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1701
Rahmani N, Kashiwagi N, Lee J, Niimi-Nakamura S, Matsumoto H, Kahar P, Lisdiyanti P, Yopi, Prasetya B, Ogino C, Kondo A (2017) Mannan endo-1,4-β-mannosidase from Kitasatospora sp. isolated in Indonesia and its potential for production of mannooligosaccharides from mannan polymers. AMB Express 7(1):100. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-017-0401-6
Rizza V, Kornfeld JM (1969) Components of conidial and hyphal walls of Penicillium chrysogenum. J Gen Microbiol 58(3):307–315. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-58-3-307
Schröder R, Atkinson RG, Redgwell RJ (2009) Re-interpreting the role of endo-β-mannanases as mannan endotransglycosylase/hydrolases in the plant cell wall. Ann Bot 104:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcp120
Srivastava PK, Kapoor M (2017) Production, properties, and applications of endo-β-mannanases. Biotechnol Adv 35:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.11.001
Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, Beer TAPd, Rempfer C, Bordoli L, Lepore R, Schwede T (2018) SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 46:W296–W303. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky427
Weeranuch Seesom P, Thongket T, Yamamoto S, Takenaka T, Sakamoto WS (2017) Purification, characterization, and overexpression of an endo-1,4-β-mannanase from thermotolerant Bacillus sp. SWU60. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2224-7
Yamabhai M, Sak-Ubol S, Srila W, Haltrich D (2014) Mannan biotechnology: from biofuels to health. Crit Rev Biotechnol 36(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2014.923372
Yan J, Yuan S-s, Jiang L-l, Ye X-j, Ng TB, Wu Z-j (2015) Plant antifungal proteins and their applications in agriculture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(12):4961–4981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6654-6
Yuan S, Chan HCS, Filipek S, Vogel H (2016) PyMOL and Inkscape Bridge the Data and the Data Visualization. Structure 24(12):2041–2042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2016.11.012
Zhang Z-G, Yi Z-L, Pei X-Q, Wu Z-L (2010) Improving the thermostability of Geobacillus stearothermophilus xylanase XT6 by directed evolution and site-directed mutagenesis. Biores Technol 101:9272–9278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.07.060
Zhang S-B, Zhang W-J, Zhai H-C, Lv Y-Y, Cai J-P, Jia F, Wang J-S, Hu Y-S (2019) Expression of a wheat β-1,3-glucanase in Pichia pastoris and its inhibitory effect on fungi commonly associated with wheat kernel. Protein Expr Purif 154:134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2018.10.011
Zhou Y-f, Zhang Y-s, Liang Z-y (1991) Structural determination of yeast Mannan and its NMR spectral analysis. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol 7(1):74–78
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project no. 31772023), the National Key Research and Development Plan (Project Nos.2017YFC1600900 and 2017YFD0401404), the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2019YFC1605400), and the Scientific Research foundation of Henan University of Technology (Project No. 2018RCJH14). SBZ and JPC designed the experiments, SBZ and WJZ executed the experiments. NL, HCZ, and YYL analyzed experiments results. SBZ and YSH wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
Alignment of amino acid sequences of endo-1,4-β-mannosidase from Triticum aestivum, Aegilops tauschii (AAC14399.1), Brachypodium distachyon (CAJ58510.1), with sequence identity of 98.00% and 83.66%, respectively. (PNG 483 kb)
Fig. S2
The ribbon diagram of structural model of endo-1,4-β-mannosidase constructed by the SWISS-MODEL visualized using PyMOL. The canonical (β/α)8 fold secondary structure elements are colored green (β-strands) and violet (α-helices). Additional secondary structure elements are colored cyan (β-strands) and orange (α-helices). The catalytic residues E179 is shown as stick structure in red color and the nucleophile residue E297 is shown as stick structure in yellow color. (PNG 5652 kb)
Fig. S3
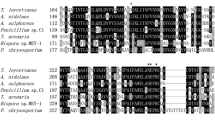
Identification of the catalytic acid/base residue (E179) and the nucleophilic residue (E297) by alignment of amino acid sequences of endo-1,4-β-mannosidase from Triticum aestivum and L. esculentum. The acid/base (Ê) and nucleophile (Ë) are highlighted. (PNG 483 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, SB., Zhang, WJ., Li, N. et al. Functional expression and characterization of an endo-1,4-β-mannosidase from Triticum aestivum in Pichia pastoris. Biologia 75, 2073–2081 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00525-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00525-8