Abstract
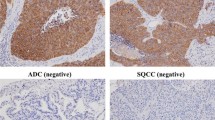
High-grade neuroendocrine tumors (HGNET) have distinctive tumor biology/behaviour. Newer modalities of treatment (immunotherapy) for them have been included in recent NCCN guidelines. Detection of programmed death receptor-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression by immunohistochemistry have made easy identification of patients eligible for immunotherapy. We aimed to ascertain expression of PD-L1 on small cell and large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas of lung and review existing literature. Eighty-five cases of HGNET lung (primary/metastatic), were retrieved and reviewed. Immunostaining for PD-L1 using clone SP263 was done. Any amount/intensity of membranous staining of > = 1% tumor cells was cut-off for positivity. Previously published studies using Google and/Pubmed search engines were reviewed. Of 85 cases, 70 were small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), 11 large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) and 4 combined SCLC. Median age was 46.5 years with male preponderance. No PD-L1 expression was seen in 91.6% cases. The 7 positive cases were 4 LCNEC, 2 SCLC and 1 combined SCLC. The percentage positivity varied from 1–100%; lower percentage positivity was seen in SCLC. PD-L1 expression on immune cells was seen in 31.3% cases. Sixteen studies evaluating 1992 NET were found; E1L3N PD-L1 clone was commonly used clone. PD-L1 positivity was associated with better prognosis in most studies. There are only a few studies available in literature related to PDL1 expression in high grade neuroendocrine carcinomas of lung. In general, PD-L1 positivity is highly variable and seen in lower percentage of these tumors. With the recent approval of immunotherapy, biomarkers other than PD-L1 should also be investigated in these tumors.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable
References
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG, Yatabe Y, Austin JH, Beasley MB, Chirieac LR, Dacic S, Duhig E, Flieder DB, Geisinger K The 2015 World health organization classification of lung tumors: impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol 2015:1243–1260
Horn L, Reck M, Spigel DR. The future of immunotherapy in the treatment of small cell lung cancer. Oncologist 2016:910–921
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Small cell Lung cancer (Version 1.2019) https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/sclc.pdf. (Accessed 22 Apr 2019)
Tang J, Yu JX, Hubbard-Lucey VM, Neftelinov ST, Hodge JP, Lin Y. Trial watch: the clinical trial landscape for PD1/PDL1 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2018:854–855
Ventana Medical Systems (2016) VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) Assay staining of non-small cell lung cancer. [interpretation manual] 1:1–42
Inamura K. Update on immunohistochemistry for the diagnosis of lung cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2018:1–15
Tsao MS, Kerr KM, Dacic S, Yatabe Y, Hirsch FR (2017) IASLC atlas of PD-L1 immunohistochemistry testing in lung cancer. Editorial Rx Press, North Fort Myers
Schultheis AM, Scheel AH, Ozretić L, George J, Thomas RK, Hagemann T, Zander T, Wolf J, Buettner R. PD-L1 expression in small cell neuroendocrine carcinomas. Eur J Cancer 2015:421–426
George J, Fernandez-Cuesta L, Walter V, Hayes N. Comparative analysis of small cell lung cancer and other pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the 107th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research; 2016 Apr 16–20; New Orleans, LA. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res 2016;76(14 Suppl):Abstract nr 122
Takada K, Toyokawa G, Okamoto T, Akamine T, Takamori S, Katsura M, Fujishita T, Shoji F, Oda Y, Maehara Y. An immunohistochemical analysis of PD-L1 protein expression in surgically resected small cell lung cancer using different antibodies and criteria. Anticancer Res 2016:3409–3412
Inamura K, Yokouchi Y, Kobayashi M, Ninomiya H, Sakakibara R, Nishio M, Okumura S, Ishikawa Y. Relationship of tumor PD-L1 (CD274) expression with lower mortality in lung high-grade neuroendocrine tumor. Cancer Med 2017:2347–2356
Tsuruoka K, Horinouchi H, Goto Y, Kanda S, Fujiwara Y, Nokihara H, Yamamoto N, Asakura K, Nakagawa K, Sakurai H, Watanabe SI. PD-L1 expression in neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Lung Cancer 2017:115–120
Ohtaki Y, Kaira K, Atsumi J, Nagashima T, Kawashima O, Ibe T, Kamiyoshihara M, Onozato R, Fujita A, Yazawa T, Sugano M. Prognostic significance of PD-L1 expression and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of lung. Am J Transl Res 2018:3243–3253
George J, Saito M, Tsuta K, Iwakawa R, Shiraishi K, Scheel AH, Uchida S, Watanabe SI, Nishikawa R, Noguchi M, Peifer M. Genomic amplification of CD274 (PD-L1) in small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2017:1220–1226
Yasuda Y, Ozasa H, Kim YH. PD-L1 Expression in Small Cell Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2018:e40–e41
Kasajima A, Ishikawa Y, Iwata A, Steiger K, Oka N, Ishida H, Sakurada A, Suzuki H, Kameya T, Konukiewitz B, Klöppel G. Inflammation and PD-L1 expression in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Endocr Relat Cancer 2018:339–350
Yoshimura A, Yamada T, Miyagawa-Hayashino A, Sonobe Y, Imabayashi T, Yamada T, Okada S, Shimamoto T, Chihara Y, Iwasaku M, Kaneko Y. Comparing three different anti-PD-L1 antibodies for immunohistochemical evaluation of small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2019:108–112
Yu H, Batenchuk C, Badzio A, Boyle TA, Czapiewski P, Chan DC, Lu X, Gao D, Ellison K, Kowalewski AA, Rivard CJ. PD-L1 Expression by two complementary diagnostic assays and mRNA in situ hybridization in small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2017:110–120
Fan Y, Ma K, Wang C, Ning J, Hu Y, Dong D, Dong X, Geng Q, Li E, Wu Y. Prognostic value of PD-L1 and PD-1 expression in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Onco Targets Ther 2016:6075–6082
Kim HS, Lee JH, Nam SJ, Ock CY, Moon JW, Yoo CW, Lee GK, Han JY. Association of PD-L1 Expression with tumor-infiltrating immune cells and mutation burden in high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. J Thorac Oncol 2018:636–648
Eichhorn F, Harms A, Warth A, Muley T, Winter H, Eichhorn ME. PD-L1 expression in large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 2018:76–82
Wang H, Li Z, Dong B, Sun W, Yang X, Liu R, Zhou L, Huang X, Jia L, Lin D. Prognostic significance of PD-L1 expression and CD8 + T cell infiltration in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Diagn Pathol 2018:30
Ishii H, Azuma K, Kawahara A, Yamada K, Imamura Y, Tokito T, Kinoshita T, Kage M, Hoshino T. Significance of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression and its association with survival in patients with small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2015:426–430
Miao L, Lu Y, Xu Y, Zhang G, Huang Z, Gong L, Fan Y. PD-L1 and c-MET expression and survival in patients with small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017:53978–53988
Hendifar AE, Marchevsky AM, Tuli R. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung: current challenges and advances in the diagnosis and management of well-differentiated disease. J Thorac Oncol 2017:425–436
Menon S, Shin S, Dy G. Advances in cancer immunotherapy in solid tumors. Cancers (Basel) 2016:1–21
Wang M, Zhao J, Zhang L, Wei F, Lian Y, Wu Y, Gong Z, Zhang S, Zhou J, Cao K, Li X. Role of tumor microenvironment in tumorigenesis. J Cancer 2017:761–773
Teixidó C, Vilariño N, Reyes R, Reguart N. PD-L1 expression testing in non-small cell lung cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol 2018:175883591876349
Derks JL, Leblay N, Lantuejoul S, Dingemans AMC, Speel EJM, Fernandez-Cuesta L. New insights into the molecular characteristics of pulmonary carcinoids and large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas, and the impact on their clinical management. J Thorac Oncol 2018:752–766
Maddison P, Newsom-Davis J, Mills KR, Souhami RL. Favourable prognosis in Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome and small-cell lung carcinoma. Lancet 1999:117–118
Wang W, Hodkinson P, McLaren F, Mackean MJ, Williams L, Howie SE, Wallace WA, Sethi T. Histologic assessment of tumor-associated CD45 + cell numbers is an independent predictor of prognosis in small cell lung cancer. Chest 2013:146–151
Scorer P, Scott M, Lawson N, Ratcliffe MJ, Barker C, Rebelatto MC, Walker J. Consistency of tumor and immune cell programmed cell death ligand-1 expression within and between tumor blocks using the VENTANA SP263 assay. Diagn Pathol 2018:47
Durvalumab (Imfinzi). https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/durvalumab-imfinzi. Accessed 04 Feb 2020
Williams GH, Nicholson AG, Snead DR, Thunnissen E, Lantuejoul S, Cane P, Kerr KM, Loddo M, Scott ML, Scorer PW, Barker C. Inter-observer Reliability of Programmed Cell Death Ligand-1 Scoring Using the VENTANA PD-L1 (SP263) Assay in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2020:550–555
Zhao X, Kallakury B, Chahine JJ, Hartmann D, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Zhang H, Zhang B, Wang C, Giaccone G. Surgical resection of SCLC: prognostic factors and the tumor microenvironment. J Thorac Oncol 2019:914–923
Ye Y, Zhou L, Xie X, Jiang G, Xie H, Zheng S. Interaction of B7-H1 on intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells with PD-1 on tumor-infiltrating T cells as a mechanism of immune evasion. J Surg Oncol 2009:500–504
Antonia SJ, López-Martin JA, Bendell J, Ott PA, Taylor M, Eder JP, Jäger D, Pietanza MC, Le DT, de Braud F, Morse MA, Ascierto PA, Horn L, Amin A, Pillai RN, Evans J, Chau I, Bono P, Atmaca A, Sharma P, Harbison CT, Lin CS, Christensen O, Calvo E. Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol 2016:883–895
da Silva A, Bowden M, Zhang S, Masugi Y, Thorner AR, Herbert ZT, Zhou CW, Brais L, Chan JA, Hodi FS, Rodig S, Ogino S, Kulke MH. Characterization of the neuroendocrine tumor immune microenvironment. Pancreas 2018:1123–1129
Schats KA, Van Vré EA, Boeckx C, De Bie M, Schrijvers DM, Neyns B, De Meester I, Kockx MM. Optimal evaluation of programmed death ligand-1 on tumor cells versus immune cells requires different detection methods. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018:982–991
Ott PA, Elez E, Hiret S, Kim DW, Morosky A, Saraf S, Piperdi B, Mehnert JM. Pembrolizumab in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: results from the phase Ib KEYNOTE-028 study. J Clin Oncol 2017:3823–3829
Pacheco J, Bunn PA. Advancements in small-cell lung cancer: the changing landscape following IMpower-133. Clin Lung Cancer 2019:148–160
Yang S, Zhang Z, Wang Q. Emerging therapies for small cell lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol 2019:47
Verma V, Sharma G, Singh A. Immunotherapy in extensive small cell lung cancer. Exp Hematol Oncol 2019:5
Shah MH, Goldner WS, Halfdanarson TR, Bergsland E, Berlin JD, Halperin D, Chan J, Kulke MH, Benson AB, Blaszkowsky LS, Eads J. NCCN guidelines insights: neuroendocrine and adrenal tumors, version 2.2018. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2018:693–702
Pavan A, Attili I, Pasello G, Guarneri V, Conte PF, Bonanno L. Immunotherapy in small-cell lung cancer: from molecular promises to clinical challenges. J Immunother Cancer 2019:205
Tsao M, Kerr K, Yatabe Y, Hirsch FR. PD-L1 Immunohistochemistry comparability study in real-life, clinical samples: Results of Blueprint Phase 2 Project. J Thorac Oncol 2018:1302–1311
Hendry S, Byrne DJ, Wright GM, Young RJ, Sturrock S, Cooper WA, Fox SB. Comparison of four PD-L1 immunohistochemical assays in lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2018:367–376
Absenger G, Terzic J, Bezan A. ASCO update: lung cancer. Memo - Mag Eur Med Oncol 2017:224–227
Diggs LP, Hsueh EC. Utility of PD-L1 immunohistochemistry assays for predicting PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor response. Biomark Res 2017:12
Wang VE, Urisman A, Albacker L, Ali S, Miller V, Aggarwal R, Jablons D (2017) Checkpoint inhibitor is active against large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma with high tumor mutation burden. J Immunother Cancer 5:75
Zimmerman S, Das A, Wang S, Julian R, Gandhi L, Wolf J. 2017–2018 scientific advances in thoracic oncology: small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2019:768–783
Li Q, Yuan D, Ma C, Liu Y, Ma L, Lv T, Song Y. A new hope: the immunotherapy in small cell lung cancer. Neoplasma 2016:342–350
Eerola AK, Soini Y, Pääkkö P, Persson M, Bremnes RM, Busund L-T. A high number of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are associated with a small tumor size, low tumor stage, and a favorable prognosis in operated small cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2000:1875–1881
Vallonthaiel AG, Malik PS, Singh V, Kumar V, Kumar S, Sharma MC, Mathur S, Arava S, Guleria R, Jain D. Clinicopathologic correlation of programmed death ligand-1 expression in non-small cell lung carcinomas: a report from India. Ann Diagn Pathol 2017:56–61
Guleria P, Husain N, Shukla S, Kumar S, Parshad R, Jain D. PD-L1 immuno-expression assay in thymomas: study of 84 cases and review of literature. Ann Diagn Pathol 2018:135–141
Wang C, Hahn E, Slodkowska E, Eskander A, Enepekides D, Higgins K, Vesprini D, Liu SK, Downes MR, Xu B. Reproducibility of PD-L1 immunohistochemistry interpretation across various types of genitourinary and head/neck carcinomas, antibody clones, and tissue types. Hum Pathol 2018:131–139
Li C, Huang C, Mok TS, Zhuang W, Xu H, Miao Q, Fan X, Zhu W, Huang Y, Lin X, Jiang K. Comparison of 22C3 PD-L1 expression between surgically resected specimens and paired tissue microarrays in non–small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2017:1536–1543
Funding
The work is funded by DST-SERB CRG/2018/003722.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by [Prerna Guleria], [Sunil Kumar], Prabhat Singh Malik and [Deepali Jain]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [Prerna Guleria] and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
The work has the approval of the Institutional Ethics Committee.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was taken from all patients included in the study.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable
Code Availability
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guleria, P., Kumar, S., Malik, P.S. et al. PD-L1 Expression in Small Cell and Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinomas of Lung: an Immunohistochemical Study with Review of Literature. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 26, 2363–2370 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-020-00832-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-020-00832-0