Abstract
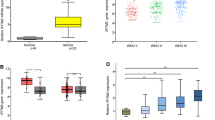
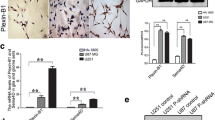
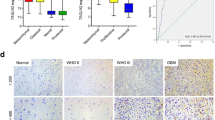
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most aggressive type of brain tumor and it is associated with poor survival. Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is a serine/threonine protein pseudo-kinase that binds to the cytoplasmic domains of β1 and β3 integrins and has been previously shown to promote invasion and metastasis in many cancer types, including GBM. However, little is known regarding the exact molecular mechanism implicating ILK in GBM aggressiveness. In this study, we used two brain cell lines, the non-invasive neuroglioma H4 cells, and the highly invasive glioblastoma A172 cells, which express ILK in much higher levels than H4. We studied the effect of ILK silencing on the metastatic behavior of glioblastoma cells in vitro and elucidate the underlying molecular mechanism. We showed that siRNA-mediated silencing of ILK inhibits cell migration and invasion of the highly invasive A172 cells while it does not affect the migratory and invasive capacity of H4 cells. These data were also supported by respective changes in the expression of Rho-associated kinase 1 (ROCK1), fascin actin-bundling protein 1 (FSCN1), and matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13), which are known to regulate cell migration and invasion. Our findings were further corroborated by analyzing the Cancer Genome Atlas Glioblastoma Multiforme (TCGA-GBM) dataset. We conclude that ILK promotes glioblastoma cell invasion through activation of ROCK1 and FSCN1 in vitro, providing a more exact molecular mechanism for its action.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kleihues P, Sobin LH (2000) World Health Organization classification of tumors. Cancer 88(12):2887
Buckner JC, Brown PD, O'Neill BP, Meyer FB, Wetmore CJ, Uhm JH (2007) Central nervous system tumors. Mayo Clin Proc 82(10):1271–1286. https://doi.org/10.4065/82.10.1271
Porter KR, McCarthy BJ, Berbaum ML, Davis FG (2011) Conditional survival of all primary brain tumor patients by age, behavior, and histology. Neuroepidemiology 36(4):230–239. https://doi.org/10.1159/000327752
Ma YS, Wu ZJ, Bai RZ, Dong H, Xie BX, Wu XH, Hang XS, Liu AN, Jiang XH, Wang GR, Jiang JJ, Xu WH, Chen XP, Tan GH, Fu D, Liu JB, Liu Q (2018) DRR1 promotes glioblastoma cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via regulating AKT activation. Cancer Lett 423:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.03.015
Ivaska J, Heino J (2000) Adhesion receptors and cell invasion: mechanisms of integrin-guided degradation of extracellular matrix. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 57(1):16–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050496
Bellail AC, Hunter SB, Brat DJ, Tan C, Van Meir EG (2004) Microregional extracellular matrix heterogeneity in brain modulates glioma cell invasion. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(6):1046–1069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2004.01.013
Kai F, Drain AP, Weaver VM (2019) The extracellular matrix modulates the metastatic journey. Dev Cell 49(3):332–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.03.026
Agrez M, Chen A, Cone RI, Pytela R, Sheppard D (1994) The alpha v beta 6 integrin promotes proliferation of colon carcinoma cells through a unique region of the beta 6 cytoplasmic domain. J Cell Biol 127(2):547–556. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.127.2.547
Cruet-Hennequart S, Maubant S, Luis J, Gauduchon P, Staedel C, Dedhar S (2003) alpha(v) integrins regulate cell proliferation through integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene 22(11):1688–1702. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206347
Chin YT, He ZR, Chen CL, Chu HC, Ho Y, Su PY, Yang YSH, Wang K, Shih YJ, Chen YR, Pedersen JZ, Incerpi S, Nana AW, Tang HY, Lin HY, Mousa SA, Davis PJ, Whang-Peng J (2019) Tetrac and NDAT induce anti-proliferation via integrin alphavbeta3 in colorectal cancers with different K-RAS status. Front Endocrinol 10:130. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00130
Li R, Shi Y, Zhao S, Shi T, Zhang G (2019) NF-kappaB signaling and integrin-beta1 inhibition attenuates osteosarcoma metastasis via increased cell apoptosis. Int J Biol Macromol 123:1035–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.003
Zaidel-Bar R, Itzkovitz S, Ma'ayan A, Iyengar R, Geiger B (2007) Functional atlas of the integrin adhesome. Nat Cell Biol 9(8):858–867. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0807-858
Elad N, Volberg T, Patla I, Hirschfeld-Warneken V, Grashoff C, Spatz JP, Fassler R, Geiger B, Medalia O (2013) The role of integrin-linked kinase in the molecular architecture of focal adhesions. J Cell Sci 126(Pt 18):4099–4107. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.120295
Winograd-Katz SE, Fassler R, Geiger B, Legate KR (2014) The integrin adhesome: from genes and proteins to human disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(4):273–288. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3769
Horton ER, Byron A, Askari JA, Ng DH, Millon-Frémillon A, Robertson J, Koper EJ, Paul NR, Warwood S, Knight D (2015) Definition of a consensus integrin adhesome and its dynamics during adhesion complex assembly and disassembly. Nat Cell Biol 17(12):1577
Hannigan GE, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Fitz-Gibbon L, Coppolino MG, Radeva G, Filmus J, Bell JC, Dedhar S (1996) Regulation of cell adhesion and anchorage-dependent growth by a new beta 1-integrin-linked protein kinase. Nature 379(6560):91–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/379091a0
Legate KR, Montanez E, Kudlacek O, Fassler R (2006) ILK, PINCH and parvin: the tIPP of integrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7(1):20–31
Gkretsi V, Mars WM, Bowen WC, Barua L, Yang Y, Guo L, St-Arnaud R, Dedhar S, Wu C, Michalopoulos GK (2007) Loss of integrin linked kinase from mouse hepatocytes in vitro and in vivo results in apoptosis and hepatitis. Hepatology 45(4):1025–1034. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21540
Liang F, Zhang S, Wang B, Qiu J, Wang Y (2014) Overexpression of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) promotes glioma cell invasion and migration and down-regulates E-cadherin via the NF-kappaB pathway. J Mol Histol 45(2):141–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-013-9540-5
Zheng CC, Hu HF, Hong P, Zhang QH, Xu WW, He QY, Li B (2019) Significance of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in tumorigenesis and its potential implication as a biomarker and therapeutic target for human cancer. Am J Cancer Res 9(1):186–197
Persad S, Attwell S, Gray V, Delcommenne M, Troussard A, Sanghera J, Dedhar S (2000) Inhibition of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) suppresses activation of protein kinase B/Akt and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of PTEN-mutant prostate cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(7):3207–3212. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.060579697
Wang SC, Makino K, Xia W, Kim JS, Im SA, Peng H, Mok SC, Singletary SE, Hung MC (2001) DOC-2/hDab-2 inhibits ILK activity and induces anoikis in breast cancer cells through an Akt-independent pathway. Oncogene 20(47):6960–6964. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204873
Bravou V, Klironomos G, Papadaki E, Taraviras S, Varakis J (2006) ILK over-expression in human colon cancer progression correlates with activation of beta-catenin, down-regulation of E-cadherin and activation of the Akt-FKHR pathway. J Pathol 208(1):91–99. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1860
Wang M, Li C, Nie H, Lv X, Qu Y, Yu B, Su L, Li J, Chen X, Ju J, Yu Y, Yan M, Gu Q, Zhu Z, Liu B (2012) Down-regulated miR-625 suppresses invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting ILK. FEBS Lett 586(16):2382–2388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.050
Zheng K, Wang G, Li C, Shan X, Liu H (2015) Knockdown of ILK inhibits glioma development via upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of cyclin D1. Oncol Rep 34(1):272–278. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.3983
Hall A, Nobes CD (2000) Rho GTPases: molecular switches that control the organization and dynamics of the actin cytoskeleton. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 355(1399):965–970. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2000.0632
Worthylake RA, Lemoine S, Watson JM, Burridge K (2001) RhoA is required for monocyte tail retraction during transendothelial migration. J Cell Biol 154(1):147–160. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200103048
Zervas CG, Gregory SL, Brown NH (2001) Drosophila integrin-linked kinase is required at sites of integrin adhesion to link the cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 152(5):1007–1018. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.152.5.1007
Sakai T, Li S, Docheva D, Grashoff C, Sakai K, Kostka G, Braun A, Pfeifer A, Yurchenco PD, Fässler R (2003) Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is required for polarizing the epiblast, cell adhesion, and controlling actin accumulation. Genes Dev 17(7):926–940
Etienne-Manneville S (2006) In vitro assay of primary astrocyte migration as a tool to study Rho GTPase function in cell polarization. Methods Enzymol 406:565–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(06)06044-7
Deng L, Li G, Li R, Liu Q, He Q, Zhang J (2010) Rho-kinase inhibitor, fasudil, suppresses glioblastoma cell line progression in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther 9(11):875–884. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.9.11.11634
Rath N, Morton JP, Julian L, Helbig L, Kadir S, McGhee EJ, Anderson KI, Kalna G, Mullin M, Pinho AV, Rooman I, Samuel MS, Olson MF (2017) ROCK signaling promotes collagen remodeling to facilitate invasive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumor cell growth. EMBO Mol Med 9(2):198–218. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201606743
Li D, Wang H, Ding Y, Zhang Z, Zheng Z, Dong J, Kim H, Meng X, Zhou Q, Zhou J (2018) Targeting the NRF-2/RHOA/ROCK signaling pathway with a novel aziridonin, YD0514, to suppress breast cancer progression and lung metastasis. Cancer Lett 424:97–108
Gkretsi V, Louca M, Stylianou A, Minadakis G, Spyrou GM, Stylianopoulos T (2019) Inhibition of breast cancer cell invasion by Ras suppressor-1 (RSU-1) silencing is reversed by growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15). Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010163
Jayo A, Parsons M, Adams JC (2012) A novel Rho-dependent pathway that drives interaction of fascin-1 with p-Lin-11/Isl-1/Mec-3 kinase (LIMK) 1/2 to promote fascin-1/actin binding and filopodia stability. BMC Biol 10:72. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-10-72
Zhang H, Cong QX, Zhang SG, Zhai XW, Li HF, Li SQ (2018) High expression levels of fascin-1 protein in human gliomas and its clinical relevance. Open Med 13:544–550. https://doi.org/10.1515/med-2018-0080
Vignjevic D, Schoumacher M, Gavert N, Janssen KP, Jih G, Lae M, Louvard D, Ben-Ze'ev A, Robine S (2007) Fascin, a novel target of beta-catenin-TCF signaling, is expressed at the invasive front of human colon cancer. Cancer Res 67(14):6844–6853. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0929
Hashimoto Y, Skacel M, Adams JC (2005) Roles of fascin in human carcinoma motility and signaling: prospects for a novel biomarker? Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37(9):1787–1804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2005.05.004
Grothey A, Hashizume R, Ji H, Tubb BE, Patrick CW Jr, Yu D, Mooney EE, McCrea PD (2000) C-erbB-2/HER-2 upregulates fascin, an actin-bundling protein associated with cell motility, in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene 19(42):4864–4875. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203838
Louca M, Stylianou A, Minia A, Pliaka V, Alexopoulos LG, Gkretsi V, Stylianopoulos T (2019) Ras suppressor-1 (RSU-1) promotes cell invasion in aggressive glioma cells and inhibits it in non-aggressive cells through STAT6 phospho-regulation. Sci Rep 9(1):7782. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44200-8
Louca M, Gkretsi V, Stylianopoulos T (2019) Coordinated expression of Ras suppressor 1 (RSU-1) and growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) affects glioma cell invasion. Cancers 11:8. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081159
Sintupisut N, Liu PL, Yeang CH (2013) An integrative characterization of recurrent molecular aberrations in glioblastoma genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 41(19):8803–8821. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt656
Yizhak K, Aguet F, Kim J, Hess JM, Kubler K, Grimsby J, Frazer R, Zhang H, Haradhvala NJ, Rosebrock D, Livitz D, Li X, Arich-Landkof E, Shoresh N, Stewart C, Segre AV, Branton PA, Polak P, Ardlie KG, Getz G (2019) RNA sequence analysis reveals macroscopic somatic clonal expansion across normal tissues. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw0726
Roufas C, Chasiotis D, Makris A, Efstathiades C, Dimopoulos C, Zaravinos A (2018) The expression and prognostic impact of immune cytolytic activity-related markers in human malignancies: a comprehensive meta-analysis. Front Oncol 8:27. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00027
Gkretsi V, Kalli M, Efstathiades C, Papageorgis P, Papanikolaou V, Zacharia LC, Tsezou A, Athanassiou E, Stylianopoulos T (2019) Depletion of Ras suppressor-1 (RSU-1) promotes cell invasion of breast cancer cells through a compensatory upregulation of a truncated isoform. Sci Rep 9(1):10050. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46575-0
Gkretsi V, Stylianou A, Louca M, Stylianopoulos T (2017) Identification of Ras suppressor-1 (RSU-1) as a potential breast cancer metastasis biomarker using a three-dimensional in vitro approach. Oncotarget 8(16):27364–27379. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16062
Dayal N, Mikek CG, Hernandez D, Naclerio GA, Yin Chu EF, Carter-Cooper BA, Lapidus RG, Sintim HO (2019) Potently inhibiting cancer cell migration with novel 3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline boronic acid ROCK inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 180:449–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.06.089
Peraud A, Mondal S, Hawkins C, Mastronardi M, Bailey K, Rutka JT (2003) Expression of fascin, an actin-bundling protein, in astrocytomas of varying grades. Brain Tumor Pathol 20(2):53–58
Roma AA, Prayson RA (2005) Fascin expression in 90 patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Ann Diagn Pathol 9(6):307–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2005.07.005
Senger D, Cairncross JG, Forsyth PA (2003) Long-term survivors of glioblastoma: statistical aberration or important unrecognized molecular subtype? Cancer J 9(3):214–221
Parsons M, Adams JC (2008) Rac regulates the interaction of fascin with protein kinase C in cell migration. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 17):2805–2813. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.022509
Tsai WC, Jin JS, Chang WK, Chan DC, Yeh MK, Cherng SC, Lin LF, Sheu LF, Chao YC (2007) Association of cortactin and fascin-1 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma: correlation with clinicopathological parameters. J Histochem Cytochem 55(9):955–962. https://doi.org/10.1369/jhc.7A7235.2007
Hayashi Y, Osanai M, Lee GH (2011) Fascin-1 expression correlates with repression of E-cadherin expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and augments their invasiveness in combination with matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Sci 102(6):1228–1235. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01910.x
Fan Y, Gan Y, Shen Y, Cai X, Song Y, Zhao F, Yao M, Gu J, Tu H (2015) Leptin signaling enhances cell invasion and promotes the metastasis of human pancreatic cancer via increasing MMP-13 production. Oncotarget 6(18):16120–16134. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3878
Zhang R, Zhu Z, Shen WZ, Li XR, Dhoomun DK, Tian Y (2019) Golgi membrane protein 1 (GOLM1) promotes growth and metastasis of breast cancer cells via regulating matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP13). Med Sci Monit 25:847–855. https://doi.org/10.12659/Msm.911667
Kumamoto K, Fujita K, Kurotani R, Saito M, Unoki M, Hagiwara N, Shiga H, Bowman ED, Yanaihara N, Okamura S, Nagashima M, Miyamoto K, Takenoshita S, Yokota J, Harris CC (2009) ING2 is upregulated in colon cancer and increases invasion by enhanced MMP13 expression. Int J Cancer 125(6):1306–1315. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24437
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the Molecular Medicine Research Center of the University of Cyprus for offering advice and access to specialized research infrastructure. M.L was supported by fellowship from the Cyprus Scholarship Foundation.
Funding
This work was funded by the European Research Council under the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013)/ERC Grant Agreement No. 336839-ReEngineeringCancer (to TS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ML designed the study, performed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; AZ extracted the TCGA data and performed the analysis of ILK expression in glioblastomas and the pairwise correlations of gene expression using the TCGA-GBM database, VG and TS participated in the conceptualization and study design, edited the manuscript and oversaw the project. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Non-financial conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Louca, M., Zaravinos, A., Stylianopoulos, T. et al. ILK silencing inhibits migration and invasion of more invasive glioblastoma cells by downregulating ROCK1 and Fascin-1. Mol Cell Biochem 471, 143–153 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03774-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03774-y