Abstract
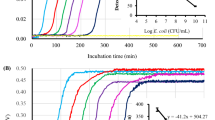
Salmonella, one of the most common foodborne pathogens, poses a serious threat to human health. In recent years, the antibiotic resistance of Salmonella has become serious as well, which has strengthened the harm of Salmonella to human health. In this paper, a simple and effective electrochemical approach was developed to obtain profile of the antimicrobial susceptibility. Screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCEs) were used to detect various concentrations of target bacteria at the same time, which have good stability, low cost, and easy mass production. The electroactive redox, resazurin, was used to monitor levels of metabolically active bacteria. As a demonstration, the antibacterial effect of ofloxacin and penicillin on Salmonella gallinarum (S. gallinarum) isolates was evaluated, and the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was measured as well. In the real sample measurement, the MIC obtained was similar to that obtained by conventional antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST). In this assay, bacterial activity was quantified sensitively and accurately, and the detection time was greatly reduced compared with conventional AST (16–20 h), which means that metabolic capacity of live bacteria could be observed after 1 h of incubation. We were able to clearly detect bacteria above 102 CFU/m. This method aims to nonspecific and can be widely applied to the detection of a variety of drug-resistant bacteria, providing an experimental basis for the rational use of antibiotics and bacterial resistance mechanisms.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carvalho FC, Sousa OV, Carvalho EM, Hofer E, Vieira RH (2013) Antibiotic Resistance of Salmonella spp. Isolated from Shrimp Farming Freshwater Environment in Northeast Region of Brazil. J Pathogens 4:1–5
Peek SE, Hartmann FA, Thomas CB, Nordlund KV (2004) Isolation of Salmonella spp from the environment of dairies without any history of clinical salmonellosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc 225(4):574–577
Hurd HS, Mckean JD, Wesley IV, Karriker LA (2001) The effect of lairage on Salmonella isolation from market swine. J Food Prot 64(7):939–944
Braden CR (2006) Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis and eggs: a national epidemic in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 43(4):512–517
Feldsine PT, Lienau AH, Leung SC, Mui LA, Humbert F, Bohnert M, Mooijman K, Schulten S, Pi V, Rollier P (2003) Detection of Salmonella in fresh cheese, poultry products, and dried egg products by the ISO 6579 Salmonella culture procedure and the AOAC official method: collaborative study. J AOAC Int 86(2):275–295
Sokolov DM, Sokolov MS (2013) Rapid methods for the genus Salmonella bacteria detection in food and raw materials. Vopr Pitan 82(1):33–40
Velasquez CG, Macklin KS, Kumar S, Bailey M, Ebner PE, Oliver HF, Martin-Gonzalez FS, Singh M (2018) Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Salmonella isolated from poultry farms in southeastern United States. Poult Sci 97(6)
Cuypers WL, Jacobs J, Wong V, Klemm EJ, Deborggraeve S, Van PS (2018) Fluoroquinolone resistance in Salmonella: insights by whole-genome sequencing. Microbial Genomics 4(7)
Jorgensen J, Ferraro M (1998) Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: general principles and contemporary practices. Clin Infect Dis 26(4):973–980
Mach KE, Wong PK, Liao JC (2011) Biosensor diagnosis of urinary tract infections: a path to better treatment? Trends Pharmacol Sci 32(6):330–336
Geyer CN, Hanson ND (2013) Rapid PCR amplification protocols decrease the turn-around time for detection of antibiotic resistance genes in gram-negative pathogens. Diag Micr Infec Dis 77(2):113–117
Strauss C, Endimiani A, Perreten V (2015) A novel universal DNA labeling and amplification system for rapid microarray-based detection of 117 antibiotic resistance genes in gram-positive bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 108:25–30
Hombach M, Jetter M, Blöchliger N, Kolesnik-Goldmann N, Böttger EC (2017) Fully automated disc diffusion for rapid antibiotic susceptibility test results: a proof-of-principle study. J Antimicrob Chemother 72(6):1659–1668
Bing L, Yong Q, Andrew G, David MI, Qian L, Jon C, Han-Chang S, Huabing Y (2014) Gradient microfluidics enables rapid bacterial growth inhibition testing. Anal Chem 86(6):3131–3137
Malmberg C, Yuen P, Spaak J, Cars O, Tängdén T, Lagerbäck P (2016) A novel microfluidic assay for rapid phenotypic antibiotic susceptibility testing of bacteria detected in clinical blood cultures. PLoS One 11(12):3131–3137
Kumar K, Giribhattanavar P, Sagar C, Patil S (2017) A rapid and simple resazurin assay to detect minimum inhibitory concentration for first-line drugs of mycobacterium tuberculosis isolated from cerebrospinal fluid. J Glob Antimicrob Re 12:157–161
Kaushik AM, Hsieh K, Chen L, Shin DJ, Liao JC, Wang TH (2017) Accelerating bacterial growth detection and antimicrobial susceptibility assessment in integrated picoliter droplet platform. Biosens Bioelectron 97:260–266
Keays MC, O'Brien M, Hussain A, Kiely PA, Dalton T (2016) Rapid identification of antibiotic resistance using droplet microfluidics. Bioengineered Bugs 7(2):79–87
Leonard H, Heuer C, Weizman D, Massad-Ivanir N, Halachmi S, Colodner R, Segal E (2019) Rapid diagnostic susceptibility testing of bacteria and fungi from clinical samples using silicon gratings. Front Biol Detect 10895:1089504
Kamonnaree C, Wipa S, Albert S (2014) Advanced amperometric respiration assay for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Anal Chem 86(20):10315–10322
Yaroslava C, Victoria S, Svetlana E, Alexander A (2012) Electrochemistry of Escherichia coli JM109: direct electron transfer and antibiotic resistance. Biosens Bioelectron 32(1):219–223
Villalba MI, Stupar P, Chomicki W, Bertacchi M, Dietler G, Arnal L, Vela ME, Yantorno O, Kasas S (2018) Nanomotion detection method for testing antibiotic resistance and susceptibility of slow-growing bacteria. Small 14(4)
Glatzel S, Hezwani M, Kitson PJ, Gromski PS, Schürer S, Cronin L (2016) A portable 3D printer system for the diagnosis and treatment of multidrug-resistant bacteria. Chem 1(3):494–504
Abeyrathne CD, Huynh DH, Mcintire TW, Nguyen TC, Nasr B, Zantomio D, Chana G, Abbott I, Choong P, Catton M (2016) Lab on a chip sensor for rapid detection and antibiotic resistance determination of Staphylococcus aureus. Analyst 141(6):1922–1929
Brosel-Oliu S, Mergel O, Uria N, Abramova N, van Rijn P, Bratov A (2019) 3D impedimetric sensors as a tool for monitoring bacterial response to antibiotics. Lab Chip 19(8):1436–1447
Mann TS, Mikkelsen SR (2008) Antibiotic susceptibility testing at a screen-printed carbon electrode array. Anal Chem 80(3):843–848
Hannah S, Addington E, Alcorn D, Shu W, Hoskisson PA, Corrigan DK (2019) Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing using low-cost, commercially available screen-printed electrodes. Biosens Bioelectron 145:111696
Castilho AL, Caleffi-Ferracioli KR, Canezin PH, Dias Siqueira VL, de Lima Scodro RB, Cardoso RF (2015) Detection of drug susceptibility in rapidly growing mycobacteria by resazurin broth microdilution assay. J Microbiol Methods 111:119–121
Yamanaka K, Vestergaard MC, Tamiya E (2016) Printable electrochemical biosensors: a focus on screen-printed electrodes and their application. Sensors 16(10):1761
Munteanu FD, Titoiu AM, Marty JL, Vasilescu A (2018) Detection of antibiotics and evaluation of antibacterial activity with screen-printed electrodes. Sensors 18 (3):901-
Shumyantseva V, Bulko T, Kuzikov A, Masamrekh R, Archakov A (2018) Analysis of l -tyrosine based on electrocatalytic oxidative reactions via screen-printed electrodes modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and nanosized titanium oxide (TiO 2 ). Amino Acids 50 (7):823–829
Ward AC, Hannah AJ, Kendrick SL, Tucker NP, Macgregor G, Connolly P (2018) Identification and characterisation of Staphylococcus aureus on low cost screen printed carbon electrodes using impedance spectroscopy. Biosens Bioelectron 91(3):166–172
Washe AP, Lozano P (2013) Facile and versatile approaches to enhancing electrochemical performance of screen printed electrodes. Electrochim Acta 91(3):166–172
Eguílaz M, Villalonga R, Rivas G (2018) Electrochemical biointerfaces based on carbon nanotubes-mesoporous silica hybrid material: bioelectrocatalysis of hemoglobin and biosensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron 111:144–151
Xia S, Zhu P, Pi F, Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang J, Sun X (2017) Development of a simple and convenient cell-based electrochemical biosensor for evaluating the individual and combined toxicity of DON, ZEN, and AFB1. Biosens Bioelectron 97:345–351
Laviron E (1979) General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J Electroanal Chem 101(1):19–28
Juan-Carlos P, Anandi M, Mirtha C, Humberto G, Jean S, Françoise P (2002) Resazurin microtiter assay plate: simple and inexpensive method for detection of drug resistance in mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46(8):2720–2722
Çakir S, Arslan EY (2010) Voltammetry of resazurin at a mercury electrode. Chem Pap 64(3):386–394
Khazalpour S, Nematollahi D (2014) Electrochemical study of Alamar Blue (resazurin) in aqueous solutions and room-temperature ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate at a glassy carbon electrode. RSC Adv 4(17):8431–8438
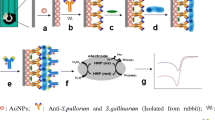
Hu C, Dou W, Zhao G (2014) Enzyme immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles electroposition and streptavidin-biotin system for detection of S. pullorum & S. gallinarum. Electrochim Acta 117(complete):239–245
Safavieh M, Pandya HJ, Venkataraman M, Thirumalaraju P, Kanakasabapathy MK, Singh A, Prabhakar D, Chug MK, Shafiee H (2017) Rapid real-time antimicrobial susceptibility testing with electrical sensing on plastic microchips with printed electrodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(14):12832
Kelley SO, Besant JD, Sargent EH (2015) Rapid electrochemical phenotypic profiling of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Lab Chip 15(13):2799–2807
Chalenko Y, Shumyantseva V, Ermolaeva S, Archakov A (2012) Electrochemistry of Escherichia coli JM109: direct electron transfer and antibiotic resistance. Biosens Bioelectron 32(1):219–223
Funding
This work has been supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFC1600102), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20190584), the Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Dairy Biotechnology (No. SKLDB2019-005), the National first-class discipline program of Food Science and Technology (JUFSTR20180303) and Collaborative Innovation Center for Food Safety and Quality Control.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3731 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Y., Ji, J., Sun, J. et al. Rapid detection of antibiotic resistance in Salmonella with screen printed carbon electrodes. J Solid State Electrochem 24, 1539–1549 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-020-04645-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-020-04645-8