Abstract
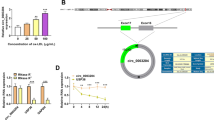
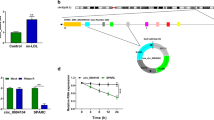
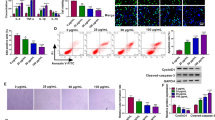
The modulatory roles of numerous circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been exposited in atherosclerosis (AS). Our study paid attention to the function of circRNA_ 0124644 (circ_0124644) in AS development, as well as its functional mechanism. The AS cell model was established by the treatment of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) to human vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs). Cell proliferation and cycle were severally measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and cell cycle detection kit. The examination of apoptosis rate was executed through flow cytometry. Western blot was exploited for detecting the associated proteins. The expression levels of circ_0124644 and microRNA-149-5p (miR-149-5p) and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) were assayed using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. The combination of targets was validated via the dual-luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP), and RNA pull-down assay. Clonal capacity was analyzed using colony formation assay. Ox-LDL restrained HUVECs proliferation and cycle, but facilitated apoptosis. Circ_0124644 expression was increased, while miR-149-5p was downregulated in ox-LDL-treated HUVECs. Besides, circ_0124644 served as a molecular sponge of miR-149-5p and intensified the ox-LDL-induced HUVECs injury by sponging miR-149-5p. PAPP-A was a target of miR-149-5p and miR-149-5p could mitigate the HUVECs injury caused by ox-LDL through inhibiting PAPP-A. Moreover, PAPP-A was positively regulated by circ_0124644 via the miR-149-5p. In this report, we concluded the promoted role of circ_0124644 in the ox-LDL-induced endothelial injury of HUVECs via the miR-149-5p/PAPP-A axis with an emphasis on its diagnostic and therapeutic values in AS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lusis AJ (2000) Atherosclerosis. Nature 407:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1038/35025203
Li CY, Ma L, Yu B (2017) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0003575 regulates oxLDL induced vascular endothelial cells proliferation and angiogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother 95:1514–1519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.064
Mannarino E, Pirro M (2008) Endothelial injury and repair: a novel theory for atherosclerosis. Angiology 59:69S–72S. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003319708320761
Paone S, Baxter AA, Hulett MD, Poon IKH (2019) Endothelial cell apoptosis and the role of endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles in the progression of atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 76:1093–1106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2983-9
Fasolo F, Di Gregoli K, Maegdefessel L, Johnson JL (2019) Non-coding RNAs in cardiovascular cell biology and atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 115:1732–1756. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvz203
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J (2017) Insights into circular RNA biology. RNA Biol 14:1035–1045. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1271524
Pan RY, Zhao CH, Yuan JX, Zhang YJ, Jin JL, Gu MF, Mao ZY, Sun HJ, Jia QW, Ji MY, Zhang J, Wang LS, Ma WZ, Ma WQ, Ding JD, Jia EZ (2019) Circular RNA profile in coronary artery disease. Am J Transl Res 11:7115–7125
Holdt LM, Stahringer A, Sass K, Pichler G, Kulak NA, Wilfert W, Kohlmaier A, Herbst A, Northoff BH, Nicolaou A, Gabel G, Beutner F, Scholz M, Thiery J, Musunuru K, Krohn K, Mann M, Teupser D (2016) Circular non-coding RNA ANRIL modulates ribosomal RNA maturation and atherosclerosis in humans. Nat Commun 7:12429. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12429
Zhao Z, Li X, Gao C, Jian D, Hao P, Rao L, Li M (2017) Peripheral blood circular RNA hsa_circ_0124644 can be used as a diagnostic biomarker of coronary artery disease. Sci Rep 7:39918. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39918
Schober A, Weber C (2016) Mechanisms of MicroRNAs in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Pathol 11:583–616. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-012615-044135
Qun L, Wenda X, Weihong S, Jianyang M, Wei C, Fangzhou L, Zhenyao X, Pingjin G (2016) miRNA-27b modulates endothelial cell angiogenesis by directly targeting Naa15 in atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis 254:184–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.10.007
Zhang X, Wang Z, Li W, Huang R, Zheng D, Bi G (2019) MicroRNA-217-5p ameliorates endothelial cell apoptosis induced by ox-LDL by targeting CLIC4. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2019.09.027
Ye ZM, Yang S, Xia YP, Hu RT, Chen S, Li BW, Chen SL, Luo XY, Mao L, Li Y, Jin H, Qin C, Hu B (2019) LncRNA MIAT sponges miR-149-5p to inhibit efferocytosis in advanced atherosclerosis through CD47 upregulation. Cell Death Dis 10:138. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1409-4
Lee S, Vasudevan S (2013) Post-transcriptional stimulation of gene expression by microRNAs. Adv Exp Med Biol 768:97–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_7
Dembic M, Hedley PL, Torp-Pedersen C, Kober L, Christiansen M (2017) Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) and the proform of the eosinophil major basic protein (ProMBP) are associated with increased risk of death in heart failure patients. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 77:352–357. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365513.2017.1325926
Yu XH, He LH, Gao JH, Zhang DW, Zheng XL, Tang CK (2018) Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A in atherosclerosis: molecular marker, mechanistic insight, and therapeutic target. Atherosclerosis 278:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.10.004
Lu J, Mitra S, Wang X, Khaidakov M, Mehta JL (2011) Oxidative stress and lectin-like ox-LDL-receptor LOX-1 in atherogenesis and tumorigenesis. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:2301–2333. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3792
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Panda AC (2018) Circular RNAs Act as miRNA Sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087:67–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_6
Ni WJ, Leng XM (2016) miRNA-dependent activation of mRNA translation. Microrna 5:83–86. https://doi.org/10.2174/2211536605666160825151201
Afonso-Grunz F, Muller S (2015) Principles of miRNA-mRNA interactions: beyond sequence complementarity. Cell Mol Life Sci 72:3127–3141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-1922-2
Charoenphol P, Mocherla S, Bouis D, Namdee K, Pinsky DJ, Eniola-Adefeso O (2011) Targeting therapeutics to the vascular wall in atherosclerosis–carrier size matters. Atherosclerosis 217:364–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.04.016
Fredman G, Tabas I (2017) Boosting inflammation resolution in atherosclerosis: the next frontier for therapy. Am J Pathol 187:1211–1221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.01.018
Wang C, Niimi M, Watanabe T, Wang Y, Liang J, Fan J (2018) Treatment of atherosclerosis by traditional Chinese medicine: questions and quandaries. Atherosclerosis 277:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.08.039
Kattoor AJ, Kanuri SH, Mehta JL (2019) Role of Ox-LDL and LOX-1 in atherogenesis. Curr Med Chem 26:1693–1700. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867325666180508100950
Cao Y, Yuan G, Zhang Y, Lu R (2018) High glucose-induced circHIPK3 downregulation mediates endothelial cell injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 507:362–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.041
Yuan J, Chen M, Xu Q, Liang J, Chen R, Xiao Y, Fang M, Chen L (2017) Effect of the diabetic environment on the expression of MiRNAs in endothelial cells: Mir-149-5p restoration ameliorates the high glucose-induced expression of TNF-alpha and ER stress markers. Cell Physiol Biochem 43:120–135. https://doi.org/10.1159/000480330
Tang SL, Zhao ZW, Liu SM, Wang G, Yu XH, Zou J, Wang SQ, Dai XY, Fu MG, Zheng XL, Zhang DW, Fu H, Tang CK (2019) Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A accelerates atherosclerosis by regulating reverse cholesterol transport and inflammation. Circ J 83:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-18-0700
Zhang F, Zhang R, Zhang X, Wu Y, Li X, Zhang S, Hou W, Ding Y, Tian J, Sun L, Kong X (2018) Comprehensive analysis of circRNA expression pattern and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in rabbits. Aging (Albany NY) 10:2266–2283. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101541
Li M, Duan L, Li Y, Liu B (2019) Long noncoding RNA/circular noncoding RNA-miRNA-mRNA axes in cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci 233:116440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.066
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2020_3764_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 1. Circ_0124644 promoted the ox-LDL-induced colony formation inhibition in HUVECs. The colony formation assay was administrated to analyze the function of si-circ_0124644 or circ_0124644 on colony formation capacity in ox-LDL-treated HUVECs. (TIF 811 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Li, Y., Liu, Z. et al. Circular RNA circ_0124644 exacerbates the ox-LDL-induced endothelial injury in human vascular endothelial cells through regulating PAPP-A by acting as a sponge of miR-149-5p. Mol Cell Biochem 471, 51–61 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03764-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03764-0