Abstract
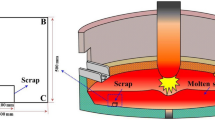
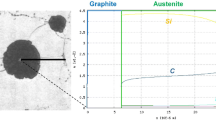
To clarify the effects of Si concentration, temperature, and time on melting of the silicon steel, three silicon steels with different Si concentrations were used to conduct an experimental investigation of the melting of scrap cylinders under natural convection. Thermodynamics and kinetics of scrap cylinder melting were revealed and analyzed based on the experimental results. Carbon diffusion between the cylinders and hot metal during melting was modeled using Thermo-Calc 2017b software to evaluate the mass-transfer coefficients. Results showed that a higher Si concentration and lower melting temperature led to slower melting of the silicon steel scrap cylinder. The mass-transfer coefficient of C during the melting decreased with an increase of Si concentration. At 1623 K (1350 °C), the mass-transfer coefficients were 1.322 × 10−4, 0.436 × 10−4, and 0.142 × 10−4 m s−1 for low (0.30 mass pct), medium (1.58 mass pct), and high (3.21 mass pct) Si concentrations in the scrap cylinders, respectively; at a melting temperature of 1723 K (1450 °C), the values of the respective mass-transfer coefficients were 1.370 × 10−4, 0.613 × 10−4, and 0.289 × 10−4 m s−1.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Pauliuk, R. L. Milford, D. B. Muller, and J. M. Allwood: Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, vol. 47, pp. 3448–54.
J. Johnson, B. K. Reck, T. Wang, and T. E. Graedel: Energy Policy, 2008, vol. 36, pp. 181–92.
J. Oda, K. Akimoto, and T. Tomoda: Resour. Conserv. Recycl., 2013, vol. 81, pp. 81–91.
K. Bellmann and A. Khare: Technovation, 2000, vol. 20, pp. 677–90.
B. Lee and I. Sohn: JOM, 2014, vol. 66, pp. 1581–94.
M. Kosaka and S. Minowa: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1967, vol. 53, pp. 983–97.
Y. U. Kim and R. Pehlke: Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 2527–32.
Y. K. Wu and M. Lacroix: Int. Comm. Heat Mass Transfer, 1995, vol. 22, pp. 517–25.
K. Mori and T. Sakuraya: Transactions ISIJ, 1982, vol. 22, pp. 984–90.
J. K. Wright: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1989, vol. 20B, pp. 363–74.
J. Szekely, Y. K. Chuang, and J. W. Hlinka: Metall. Trans, 1972, vol. 3, pp. 2825–33.
R. Boom and R. Steffen: Steel Res., 2001, vol. 72, pp. 91–6.
N. Arzpeyma, O. Widlund, M. Ersson, and P. Jönsson: ISIJ Int, 2013, vol. 53, pp. 48–55.
F. M. Penz, J. Schenk, R. Ammer, G. Klösch, and K. Pastucha: Metals, 2018, vol. 8, pp. 1078.
Y. U. Kim and R. D. Pehlke: Metall. Trans. B, 1975, vol. 6, pp. 585–91.
R. I. L. Guthrie and P. Stubbs: Can. Metall. Quart., 1973, vol. 12, pp. 465–73.
K. Isobe, H. Maede, K. Ozawa, K. Umezawa, and C. Saito: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1990, vol. 76, pp. 2033–40.
M. Kawakami, K. Takatani, and L.C. Brabie: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1999, vol. 85, pp. 658–65.
J. H. Li, G. Brooks, and N. Provatas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2005, vol. 36B, pp. 293–302.
J. H. Li and N. Provatas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 268–79.
A. K. Shukla, B. Deo, and D. G. C. Robertson: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44B, pp. 1407–27.
A. Kruskopf: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 1195–206.
A. Kruskopf and L. Holappa: Metall. Res. Technol., 2018, vol. 115, pp. 201.
M. Gao, S. F. Yang, and Y. L. Zhang: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2009, https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2019.1659003.
L. C. Brabie and M. Kawakami: High Temp. Mater. Process, 2000, vol. 19, pp. 241–56.
É.M. Goldfarb and B.I. Sherstov: J. Eng. Phys. Therm., 1970, vol. 18, pp. 342–7.
F. M. Penz and J. Schenk: Steel Res. Int., 2019, vol. 90, pp. 1900124.
M. Kosaka and S. Minowa: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1967, vol. 53, pp. 1467–77.
M. Hino and K. Ito: ‘Thermodynamic Data for Steelmaking’, 1st edn, 1–8; 2010, Sendai, Tohoku University Press.
C. Bodsworth, I. M. Davidson, and D. Atkinson: Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME, 1968, vol. 242, pp. 1135–43.
A. M. Krishtal, Y. S. Sokolov, and A. A. Zhukov: Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A, 1971, vol. 45, pp. 1187.
C. Wagner: Thermodynamics of Alloys, 1st edn. Addison-Wesley, Boston, pp. 28–33, 1952
Y.H. Pei, Q.A. Chen, G.B. Tang, and Y. Peng: Iron and Steel, 2010, vol. 45, pp. 67–71.
F. Neumann and B. Person: Hart. Technol. Mitt., 1968, vol. 23, pp. 296–310.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 51604201 and 51774217 and the International Postdoctoral Exchange Fellowship Program (2017) by the China Postdoctoral Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted November 29, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Zhang, H., Fang, Q. et al. Effect of Silicon Concentration on Melting Behavior of Scraps in Hot Metal. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 1668–1678 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01871-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01871-3