Abstract
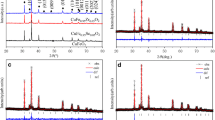
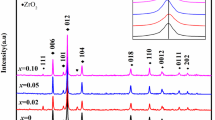
The polycrystalline CuFeO2 (CFO) and CuFe1-xMxO2 (M = Ti, Hf, Zr, M-CFO) samples are synthesized by solid-state reaction method. The doping effect of tetravalent nonmagnetic transition metal M4+ ions on the microstructure, defect evolution, and magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of the CFO system are comparatively investigated. The substitution of M4+ for Fe3+ increases lattice parameters, changes the bond length of Fe/Cu-O and bond angle of Fe-O-Fe, and improves the microstructure to some extent. Positron annihilation spectroscopy results indicate that M4+ doping induces the agglomeration of small-sized vacancy defects manifested as the increase in vacancy-type defect size and the suppression of inherent defect concentration. Magnetic measurements show that the antiferromagnetic stability of CFO system is clearly affected by M4+ doping, and Ti4+ doping has a more noticeable impact than Hf4+ and Zr4+ doping. Meanwhile, the coexistence of weak ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism is detected in all doped samples, while Ti-doped system exhibits extraordinary magnetic properties. Especially for Ti-CFO2 (x = 0.03) sample, the maximum magnetization reaches as high as 11.81 emu/g at 0.5 T, which enhanced one order of magnitude than that of undoped CFO. Isothermal M-H data at different temperatures show that entropy change (ΔSM) and refrigerant capacity (RC) for CFO and M-CFO2 samples are significantly weakening with M4+ substitution in bulk CFO. The maximum ΔSM = 4.79 J·kg−1 K−1 and RC = 12.79 J·kg−1 for undoped CFO are obtained near the transition temperature TN2 = 12 K, with the applied fields up to 6 T. The possible reasons for the above observations are discussed in detail.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kimura, T., Goto, T., Shintani, H., Ishizaka, K., Arima, T., Tokura, Y.: Magnetic control of ferroelectric polarization. Nature. 426, 55–58 (2003)
Ramirez, A.P.: Strongly geometrically frustrated magnets. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 24, 453–480 (2003)
Bonville, P., Hodges, J.A., Ocio, M., Sanchez, J.P., Vulliet, P., Sosin, S., Braithwaite, D.: Low temperature magnetic properties of geometrically frustrated Gd2Sn2O7 and Gd2Ti2O7. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 15, 7777–7787 (2003)
Yaouanc, A., Dalmas de Réotier, P., Glazkov, V., et al.: Magnetic Density of States at Low Energy in Geometrically Frustrated Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 047203–1–047203-4 (2005)
Mugnier, E., Barnabé, A., Tailhades, P.: Synthesis and characterization of CuFeO2+δ delafossite powders. Solid State Ionics. 177, 607–612 (2006)
Shannon, R.D., Rogers, D.B., Prewitt, C.T.: Chemistry of noble metal oxides I. Syntheses and properties of ABO2 delafossite compounds. Inorg. Chem. 10, 713–718 (1971)
Sobolev, A., Rusakov, V., Moskvin, A., et al.: 57Fe Mössbauer study of unusual magnetic structure of multiferroic 3R-AgFeO2. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 29, 275803 (2017)
Albaalbaky, A., Kvashnin, Y., Ledue, D., Patte, R., Frésard, R.: Magnetoelectric properties of multiferroic CuCrO2 studied by means of ab initio calculations and Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Rev. B. 96, 064431–1–064431-6 (2017)
Whangbo, M.H., Dai, D., Lee, K.S., Kremer, R.K.: On the conflicting pictures of magnetism for the frustrated triangular lattice antiferromagnet CuFeO2. Chem. Mater. 18, 1268–1274 (2006)
Apostolov, A.T., Apostolova, I.N., Wesselinowa, J.M.: Ferroelectricity in the multiferroic delafossite CuFeO2 induced by ion doping or magnetic field. Solid State Commun. 292, 11–16 (2019)
Hayashi, K., Fukatsu, R., Nozaki, T., Miyazaki, Y., Kajitani, T.: Structural, magnetic, and ferroelectric properties of CuFe1−xMnxO2. Phys. Rev. B. 87, 064418–1–064418-5 (2013)
Elkhoun, T., Amami, M., Hlil, E.K., Ben Salah, A.: Effect of spin dilution on the magnetic state of delafossite CuFeO2 with an S=5/2 antiferromagnetic triangular sublattice. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28, 1439–1447 (2015)
Wang, J.Y., Deng, Q.L., Li, M.J., Jiang, K., Zhang, J.Z., Hu, Z.G.: Copper ferrites@reduced graphene oxide anode materials for advanced lithium storage applications. Sci. Rep. 7, 8903 (2017)
Gupta, R.K., Cavas, M., Al-Ghamdi, A.A., Gafer, Z.H., El-Tantawy, F., Yakuphanoglu, F.: Electrical and photoresponse properties of Al/p-CuFeO2/p-Si/Al MTCOS photodiode. Sol. Energy. 92, 1–6 (2013)
Yu, B.F., Gao, Q., Zhang, B., Meng, X.Z., Chen, Z.: Review on research of room temperature magnetic refrigeration. Int. J. Refrig. 26, 622–636 (2003)
Katsura, H., Nagaosa, N., Balatsky, A.V.: Spin current and magneto-electric effect in non-collinear magnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 057205–1–057205-4 (2005)
Terada, N., Mitsuda, S., Suzuki, S., Kawasaki, T., Fukuda, M., Nagao, T., Katori, H.A.: Disappearance of quasi-Ising character in triangular lattice antiferromagnet CuFeO2 by a small amount of substitution. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 73, 1442–1445 (2004)
Terada, N., Mitsuda, S., Gukasov, A.: Impurity-induced orthogonal double sinusoidal magnetic structure in the triangular lattice antiferromagnet CuFe1-xAlxO2. Phys. Rev. B. 73, 014419–1–014419-8 (2006)
Seki, S., Yamasaki, Y., Shiomi, Y., Iguchi, S., Onose, Y., Tokura, Y.: Impurity-doping-induced ferroelectricity in the frustrated antiferromagnet. Phys. Rev. B. 75, 100403–1–100403-4 (2007)
Terada, N., Nakajima, T., Mitsuda, S., Kitazawa, H., Kaneko, K., Metoki, N.: Ga-substitution-induced single ferroelectric phase in multiferroic CuFeO2. Phys. Rev. B. 78, 014101–1–014101-6 (2008)
Naka-in, L., Kamwanna, T., Srepusharawoot, P., Pinitsoontorn, S., Amornkitbamrung, V.: Effects of Ge substitution on the structural and physical properties of CuFeO2 delafossite oxide. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 54, 04DH10–1–04DH10–5 (2015)
Zhang, L., Goodman, B.A., Xiong, D.K., Deng, W.: Evolution of microstructure, optical, and magnetic properties in multiferroic CuFe1-xSnxO2 (x=0–0.05). Ceram. Int. 45, 3007–3012 (2019)
Dai, H.Y., Gu, L.T., Li, T., Liu, D.W., Chen, Z.P., Cao, X.Z., Wang, B.Y.: Investigations of Ti-substituted CuFeO2 ceramics on the structure, defects, the local electron density and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 484, 279–285 (2019)
Sedivy, L., Cizek, J., Belas, E., Grill, R., Melikhova, O.: Positron annihilation spectroscopy of vacancy-related defects in CdTe:cl and CdZnTe:Ge at different stoichiometry deviations. Sci. Rep. 6, 20641 (2016)
Ishibashit, S., Suenagatll, K., Yamamotot, R., Doyama, M., Matsumoto, T.: Positron annihilation studies of the iron-substituted oxide superconductor YBa2(Cu1-xFex)3O7-y. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2, 3691–3696 (1990)
Dai, H.Y., Xie, X.Y., Chen, Z.P., Ye, F.J., Li, T., Yang, Y.: Microstructure evolution and magnetic properties of Eu doped CuFeO2 multiferroic ceramics studied by positron annihilation. Ceram. Int. 44, 13894–13900 (2018)
Nisiro, D., Fabbri, G., Celotti, G.C., Bellosi, A.: Influence of the additives and processing conditions on the characteristics of dense SnO2-based ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 38, 2727–2742 (2003)
Dai, H.Y., Li, T., Chen, Z.P., Liu, D.W., Xue, R.Z., Zhao, C.Z., Liu, H.Z., Huang, N.K.: Studies on the structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Ce-doped BiFeO3 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 672, 182–189 (2016)
Terada, N., Nakajima, T., Mitsuda, S., Kitazawa, H.: Magnetic phase diagram of multiferroic delafossite CuFe1−yGayO2. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 145, 012071 (2009)
Zhang, L., Goodman, B.A., Xiong, D.K., Deng, W.: Magnetic transitions in delafossite CuFeO2: a magnetocaloric effect study. Phys. Lett. A. 383, 125834 (2019)
Oliveira, G.N.P., Machado, P., Pires, A.L., Pereira, A.M., Araújo, J.P., Lopes, A.M.L.: Magnetocaloric effect and refrigerant capacity in polycrystalline YCrO3. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 91, 182–188 (2016)
Das, K.: Magnetocaloric effect at low temperature in robust charge ordered Sm1-xCaxMnO3 compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 458, 52–56 (2018)
Shi, J.H., Yin, S.Q., Seehra, M.S., Jain, M.: Enhancement in magnetocaloric properties of ErCrO3 via A-site Gd substitution. J. Appl. Phys. 123, 193901–1–193901-9 (2018)
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 11675149, 11775192).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Dai, H., Li, T. et al. Effect of Transition Metal Ion Doping on the Microstructure, Defect Evolution, and Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Properties of CuFeO2 Ceramics. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 2881–2890 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05550-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05550-x