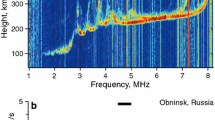
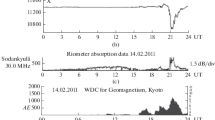
Abstract—
A new method has been developed for determining the characteristics of internal atmospheric waves based on the use of inclined sporadic E-layers of Earth’s ionosphere as a detector. The method is based on the fact that an internal wave propagating through an initially horizontal sporadic E-layercauses rotation of the plasma density gradient in the direction of the wave vecto which leads to the establishment of a layer ionization plane parallel to the phase wave front. The developed method allows us to study the relationship between small-scale internal waves and sporadic E-layers in Earth’s ionosphere and significantly expands the capabilities of traditional radio occultation monitoring of the atmosphere. It was found that the studied internal atmospheric waves have periods from 35 to 46 min and vertical phase velocities from 1.2 to 2.0 m/s which is in good agreement with the results of independent experiments and modeling data for sporadic E-structures at an altitude of ~100 km in Earth’s polar cap.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Wu, D.L., Ao, C.O., Hajj, G.A., de la Torre Juarez, M., et al., Sporadic E morphology from GPS-CHAMP radio occultations, J. Geophys. Res., 2005, vol. 110, A01306. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JA010701
Arras, C., Wickert, J., Beyerle, G., et al., A global climatology of ionospheric irregularities derived from GPS radio occultation, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2008, vol. 35, L14809. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL03415
Haldoupis, C.A., Tutorial review on sporadic E layers, in Aeronomy of the Earth’s Atmosphere and Ionosphere, Abdu, M.A., Pancheva, D., and Bhattacharyya, A., Eds., Berlin: Springer, 2011, pp. 381–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-0326-1-2
Whitehead, J.D., Recent work on midlatitude and equatorial sporadic E, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 1989, vol. 51, pp. 401–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9169(89)90122-0
Kirkwood, S. and Nilsson, H., High-latitude sporadic-E and other thin layers—the role of magnetospheric electric fields, Space Sci. Rev., 2000, vol. 91, pp. 579–613.
Haldoupis, C., Midlatitude sporadic E layers. A typical paradigm of atmosphere–ionosphere coupling, Space Sci. Rev., 2012, vol. 168, pp. 441–461.
Roddy, P.A., Earle, G.D., Swenson, C.M., et al., Relative concentrations of molecular and metallic ions in midlatitude intermediate and sporadic-E layers, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2004, vol. 31, L19807. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL020604
Maruyama, T., Kato, H., and Nakamura, M., Ionospheric effects of the Leonid meteor shower in November 2001 as observed by rapid run ionosondes, J. Geophys. Res., 2003, vol. 108, no. A8, 1324. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JA009831
Maruyama, T., Kato, H., and Nakamura, M., Meteor-induced transient sporadic E as inferred from rapid-run ionosonde observations at midlatitudes, J. Geophys. Res., 2008, vol. 113, A09308. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JA013362
Malhotra, A., Mathews, J.D., and Urbina, J., Effect of meteor ionization on sporadic-E observed at Jicamarca, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2008, vol. 35, L15106. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL034661
Hysell, D.L., Yamamoto, M., and Fukao, S., Imaging radar observations and theory of type I and type II quasi-periodic echoes, J. Geophys. Res., 2002, vol. 107, no. A11, 1360. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JA009292
Hysell, D.L., Larsen, M.F., and Zhou, Q.H., Common volume coherent and incoherent scatter radar observations of mid-latitude sporadic E-layers and QP echoes, Ann. Geophys., 2004, vol. 22, pp. 3277–3290. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-22-3277-2004
Larsen, M.F., Hysell, D.L., Zhou, Q.H., et al., Imaging coherent scatter radar, incoherent scatter radar, and optical observations of quasiperiodic structures associated with sporadic E layers, J. Geophys. Res., 2007, vol. 112, A06321. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JA012051
Cosgrove, R.B. and Tsunoda, R.T., A direction-dependent instability of sporadic-E layers in the nighttime midlatitude ionosphere, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2002, vol. 29, no. 18, 1864. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002GL014669
Cosgrove, R.B. and Tsunoda, R.T., Instability of the E–F coupled nighttime midlatitude ionosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 2004, vol. 109, A04305. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JA010243
Yokoyama, T., Hysell, D.L., Otsuka, Y., and Yamamoto, M., Three-dimensional simulation of the coupled Perkins and ES-layer instabilities in the nighttime midlatitude ionosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 2009, vol. 114, A03308. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JA013789
Woodman, R.F., Yamamoto, M., and Fukao, S., Gravity wave modulation of gradient drift instabilities in mid-latitude sporadic E irregularities, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1991, vol. 18, pp. 1197–1200. https://doi.org/10.1029/91GL01159
Didebulidze, G.G. and Lomidze, L.N., Double atmospheric gravity wave frequency oscillations of sporadic E formed in a horizontal shear flow, Phys. Lett. A, 2010, vol. 374, no. 7, pp. 952–969.
Chu, Y.-H., Brahmanandam, P.S., Wang, C.-Y., et al., Coordinated sporadic E layer observations made with Chung-Li 30 MHz radar, ionosonde and FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC satellites, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2011, vol. 73, pp. 883–894.
Larsen, M.F., A shear instability seeding mechanism for quasiperiodic radar echoes, J. Geophys. Res., 2000, vol. 105, no. A11, pp. 24931–24940. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999JA000290
Bernhardt, P.A., The modulation of sporadic-E layers by Kelvin–Helmholtz billows in the neutral atmosphere, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2002, vol. 64, pp. 1487–1504.
Hysell, D.L., Nossa, E., Larsen, M.F., et al., Sporadic E layer observations over Arecibo using coherent and incoherent scatter radar: Assessing dynamic stability in the lower thermosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 2009, vol. 114, A12303. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JA014403
Tsunoda, R.T., Fukao, S., and Yamamoto, M., On the origin of quasiperiodic radar backscatter from midlatitude sporadic E, Radio Sci., 1994, vol. 29, pp. 349–366.
Yamamoto, M., Fukao, S., Woodman, R.F., et al., Mid-latitude e region field-aligned irregularities observed with the MU radar, J. Geophys. Res.: Space, 1991, vol. 96, pp. 15943–15949.
Yamamoto, M., Fukao, S., Ogawa, T., et al., A morphological study of mid-latitude E-region field-aligned irregularities observed with the MU radar, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 1992, vol. 54, pp. 769–777.
Bernhardt, P.A., Selcher, C.A., Siefring, C., et al., Radio tomographic imaging of sporadic-E layers during SEEK-2, Ann. Geophys., 2005, vol. 23, pp. 2357–2368. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-23-2357-2005
Yamamoto, M., Fukao, S., Tsunoda, R.T., et al., SEEK-2 (Sporadic-E Experiment over Kyushu 2)—project outline, and significance, Ann. Geophys., 2005, vol. 23, pp. 2295–2305. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-23-2295-2005
Larsen, M.F., Fukao, S., Yamamoto, M., et al., The SEEK chemical release experiment: Observed neutral wind profile in a region of sporadic-E, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1998, vol. 25, pp. 1789–1792.
Larsen, M.F., Yamamoto, M., Fukao, S., and Tsunoda, R.T., SEEK 2: Observations of neutral winds, wind shears, and wave structure during a sporadic E/QP event, Ann. Geophys., 2005, vol. 23, pp. 2369–2375.
Yokoyama, T., Yamamoto, M., Fukao, S., et al., Numerical simulation of mid-latitude ionospheric E-region based on SEEK and SEEK-2 observations, Ann. Geophys., 2005, vol. 23, no. 7, pp. 2377–2384.
Saito, S., Yamamoto, M., Hashiguchi, H., and Maegawa, A., Observation of three-dimensional structures of quasi-periodic echoes associated with mid-latitude sporadic-E layers by MU radar ultra-multi-channel system, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2006, vol. 33, L14109. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL025526
Maruyama, T., Fukao, S., and Yamamoto, M., A possible mechanism for echo striation generation of radar backscatter from midlatitude sporadic E, Radio Sci., 2000, vol. 35, pp. 1155–1164.
Ogawa, T., Takahashi, O., Otsuka, Y., et al., Simultaneous middle and upper atmosphere radar and ionospheric sounder observations of midlatitude E region irregularities and sporadic E layer, J. Geophys. Res., 2002, vol. 107, no. A10, 1275. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JA900176
Yokoyama, T., Yamamoto, M., Fukao, S., and Cosgrove, R.B., Three-dimensional simulation on generation of polarization electric field in the midlatitude E‑region ionosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 2004, vol. 109, A01309. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JA010238
Kelley, M.C., The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics, San Diego, Calif.: Academic Press, 2009.
Nygren, T., Jalonen, L., Oksman, J., and Turunen, T., The role of electric field and neutral wind direction in the formation of sporadic E-layers, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 1984, vol. 46, pp. 373–381.
Turunen, T., Nygren, T., and Huuskonen, A., Nocturnal high-latitude E-region in winter during extremely quiet conditions, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 1993, vol. 55, pp. 783–795.
Bristow, W.A. and Watkins, B.J., Numerical simulation of the formation of thin ionization layers at high latitudes, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1991, vol. 18, pp. 404–407.
Bristow, W.A. and Watkins, B.J., Incoherent scatter observations of thin ionization layers at Sondrestrom, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 1993, vol. 55, pp. 873–894.
Kirkwood, S. and von Zahn, U., On the role of auroral electric fields in the formation of low altitude sporadic-E and sudden sodium layers, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 1991, vol. 53, pp. 389–407.
Kirkwood, S. and von Zahn, U., Formation mechanisms for lowaltitude Es and their relationship with neutral Fe layers: Results from the metal campaign, J. Geophys. Res., 1993, vol. 98, pp. 21549–21561.
Lehmacher, G.A., Larsen, M.F., and Croskey, C.L., Observation of electron biteout regions below sporadic E layers at polar latitudes, Ann. Geophys., 2015, vol. 33, pp. 371–380. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-33-371-2015
Cox, R.M. and Plane, J.M.C., An ion–molecule mechanism for the formation of neutral sporadic Na layers, J. Geophys. Res., 1998, vol. 103, no. D6, pp. 6349–6359.
Hunten, D.M., Turco, R.P., and Toon, O.B., Smoke and dust particles of meteoric origin in the mesosphere and stratosphere, J. Atmos. Sci., 1980, vol. 37, pp. 1342–1357.
Heinselman, C.J., Thayer, J.P., and Watkins, B.J., A high-latitude observation of sporadic sodium and sporadic E-layer formation, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1998, vol. 25, pp. 3059–3062.
Igarashi, K., Pavelyev, A.G., Hocke, K., et al., Observation of wave structures in the upper atmosphere by means of radio holographic analysis of the RO data, Adv. Space Res., 2001, vol. 27, pp. 1321–1327.
Pavelyev, A.G., Liou, Y.A., Wickert, J., et al., New applications and advances of the GPS radio occultation technology as recovered by analysis of the FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC and CHAMP data-base, in New Horizons in Occultation Research: Studies in Atmosphere and Climate, Steiner, A., Pirscher, B., Foelsche, U., and Kirchengast, G., Eds., Berlin–Heidelberg: Springer, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00321_9
Pavelyev, A.G., Liou, Y.A., Zhang, K., et al., Identification and localization of layers in the ionosphere using the eikonal and amplitude of radio occultation signals, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 2012, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 1–16. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-5-1-2012
Pavelyev, A.G., Liou, Y.A., Matyugov, S.S., et al., Application of the locality principle to radio occultation studies of the Earth’s atmosphere and ionosphere, Atm-os. Meas. Tech., 2015, vol. 8, no. 7, pp. 2885–2899. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-8-2885-2015
Gubenko, V.N., Pavelyev, A.G., Kirillovich, I.A., and Liou, Y.-A., Case study of inclined sporadic E layers in the Earth’s ionosphere observed by CHAMP/GPS radio occultations: Coupling between the tilted plasma layers and internal waves, Adv. Space Res., 2018, vol. 61, no. 7, pp. 1702–1716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.10.001
Yue, X., Schreiner, W.S., Zeng, Z., et al., Case study on complex sporadic E layers observed by GPS radio occultations, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 2015, vol. 8, pp. 225–236. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-8-225-2015
Zeng, Z. and Sokolovskiy, S., Effect of sporadic E cloud on GPS radio occultation signal, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2010, vol. 37, L18817. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL044561
Mathews, J.D., Sporadic E: Current views and recent progress, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 1998, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 413–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-6826(97)00043-6
Hines, C.O., Internal atmospheric gravity waves at ionospheric heights, Can. J. Phys., 1960, vol. 38, pp. 1441–1481.
Gossard, E.E. and Hooke, W.H., Waves in the Atmosphere, Amsterdam–Oxford–New York: Elsevier, 1975.
Otsuka, Y., Shiokawa, K., Ogawa, T., et al., Spatial relationship of nighttime medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances and f region field-aligned irregularities observed with two spaced all-sky airglow imagers and the middle and upper atmosphere radar, J. Geophys. Res., 2009, vol. 114, A05302. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JA013902
Tsunoda, R.T. and Cosgrove, R.B., Coupled electrodynamics in the nighttime midlatitude ionosphere, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2001, vol. 8, pp. 4171–4174.
Kato, S., Reddy, C.A., and Matsushita, S., Possible hydromagnetic coupling between the perturbations of the neutral and ionized atmosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 1970, vol. 75, pp. 2540–2550.
Chimonas, G. and Axford, W.I., Vertical movement of temperate-zone sporadic E layers, J. Geophys. Res., 1968, vol. 73, pp. 111–117.
Chimonas, G., Enhancement of sporadic E by horizontal transport within the layer, J. Geophys. Res., 1971, vol. 76, pp. 4578–4586.
Whitehead, J.D., Ionization disturbances caused by gravity waves in the presence of an electrostatic field and background wind, J. Geophys. Res., 1971, vol. 76, pp. 238–241.
Gubenko, V.N., Pavelyev, A.G., and Andreev, V.E., Determination of the intrinsic frequency and other wave parameters from a single vertical temperature or density profile measurement, J. Geophys. Res., 2008, vol. 113, D08109. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD008920
Gubenko, V.N., Pavelyev, A.G., Salimzyanov, R.R., and Pavelyev, A.A., Reconstruction of internal gravity wave parameters from radio occultation retrievals of vertical temperature profiles in the Earth’s atmosphere, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 2011, vol. 4, no. 10, pp. 2153–2162. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-4-2153-2011
Gubenko, V.N., Pavelyev, A.G., Salimzyanov, R.R., and Andreev, V.E., A method for determination of internal gravity wave parameters from a vertical temperature or density profile measurement in the Earth’s atmosphere, Cosmic Res., 2012, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 21–31.
Gubenko, V.N., Kirillovich, I.A., and Pavelyev A.G. Characteristics of internal waves in the Martian atmosphere obtained on the basis of an analysis of vertical temperature profiles of the Mars Global Surveyor mission, Cosmic Res., 2015, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 133–142. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952515020021
Gubenko, V.N. and Kirillovich, I.A., Diagnostics of internal atmospheric wave saturation and determination of their characteristics in Earth’s stratosphere from radiosonde measurements, Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2018, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 41–48. https://doi.org/10.12737/stp-42201807
Gubenko, V.N., Kirillovich, I.A., Pavelyev, A.G., and Andreev, V.E., Detection of saturated internal gravity waves in the Martian atmosphere and reconstruction of their characteristics, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Fiz., 2016, vol. 59, no. 12-2, pp. 46–49.
Gubenko, V.N., Kirillovich, I.A., Liou, I.-A., and Pavelyev, A.G., Monitoring of the activity of internal gravity waves in the atmosphere of the Arctic and Antarctic, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Fiz., 2016, vol. 59, no. 12-3, pp. 80–85.
MacDougall, J.W., Jayachandran, P.T., and Plane, J.M.C., Polar cap sporadic-E: Part 1. Observations, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2000, vol. 62, pp. 1155–1167.
MacDougall, J.W., Plane, J.M.C., and Jayachandran, P.T., Polar cap sporadic-E: Part 2. Modeling, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2000, vol. 62, pp. 1169–1176.
Kirkwood, S. and Collis, P.N., Gravity wave generation of simultaneous auroral sporadic-E layers and sudden neutral sodium layers, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 1989, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 259–269.
Funding
This study was supported by a state task and was partially supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (RFBR project no. 19-02-00083 A) and program no. 12 of the Presidium of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by N. Topchiev
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gubenko, V.N., Kirillovich, I.A. Association of Inclined Sporadic E-Layers and Small-Scale Atmospheric Waves in Earth’s Ionosphere. Cosmic Res 58, 139–149 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952520030028
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952520030028