Abstract
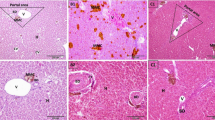
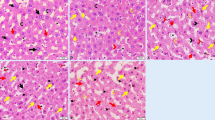
Melanization is the major deterioration in organoleptic quality of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei during cold storage and leads to dramatical reduction of commercial value. So far, the biochemical cascade mechanism triggering and accelerating melanosis progression remains unclear. Herein, this investigation aimed to monitor the melanosis development in L. vannamei during 5 days’ cold storage at 4 °C and to explore the role of serine protease (SP) in zymogen activation of polyphenol oxidase (PPO) by application of low field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and immunohistochemistry (IHC). The results showed that melanosis development was positively associated with the increase of PPO and SP activities, and the utmost melanization was observed at cephalothorax segment, following with the telson and abdomen. Besides, LF-NMR relaxometry revealed both a dramatical reduction in trapped water component T22 and a significant increase in free water component T23. Meanwhile, the histopathological findings of hepatopancreas tissue demonstrated the progressive disruption in cytoarchitecture. Along with the increase of T23 and cytoarchitecture disruption, SP and Ca2+ were arbitrarily disseminated in hepatopancreas tissue. In addition, a heat map analysis revealed that there was a highly positive relationship between melanosis development and the aberrant elevation of PPO and SP activities, ratio of T22 components, cytoarchitecture disruption level, and dissemination status of SP and Ca2+. Altogether, the biochemical cascade events for melanosis development of L. vannamei during cold storage could be sketched out; i.e., the cytoarchitecture disruption, in combination with the driving force of free water molecule migration, was greatly favorable for aggregation of SP, Ca2+, and PPO zymogen, following with aberrant activation of PPO zymogen and initiation of melanization. These data provide new insights into the biochemical cascade mechanism of melanosis development in L. vannamei during cold storage and pave new ways for target controlling of melanization at initial stage.

Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, C. W., Lee, M. J., & Jeung, E. B. (2017). Expression and localization of equine tissue-specific divalent ion-transporting channel proteins. Journal of Equine Veterinary Science, 59, 14–25.
Alparslan, Y., & Baygar, T. (2017). Effect of chitosan film coating combined with orange peel essential oil on the shelf life of deepwater pink shrimp. Food Bioprocess Technology, 10, 842–853.
Amparyup, P., Jitvaropas, R., Pulsook, N., & Tassanakajon, A. (2007). Molecular cloning, characterization and expression of a masquerade-like serine proteinase homologue from black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 22, 535–546.
Arancibia, M. Y., Lopez-Caballero, M. E., Gomez-Guill, M. C., & Montero, P. (2015). Chitosan coatings enriched with active shrimp waste for shrimp preservation. Food Control, 54, 259–266.
Benjakul, S., Visessanguan, W., & Tanaka, M. (2005). Properties of phenoloxidase isolated from the cephalothorex of kuruma prawn (Penaeus japonicus). Journal of Food Biochemistry, 29, 470–485.
Bradford, M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive for the quantitation of microgram quantitites of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Buda, S., Elizabeth, S., & Thomas, H. (2005). Expression of a serine proteinase homolog prophenoloxidase-activating factor from the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. part: B, 140, 521–531.
Chiu, C. H., Gu, Y. K., Liu, C. H., Pan, T. M., & Cheng, W. (2007). Immune responses and gene expression in Pacific white shrimps, Litopenaeus vannamei, induced by Lactobacillus plantarum. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 23, 364–377.
Dai, X. Y., Zhang, M. X., Wei, X. Y., Hider, R. C., & Zhou, T. (2016). Novel multifunctional hydroxypyridinone derivatives as potential shrimp preservatives. Food Bioprocess Technology, 9, 1079–1088.
Encarnacion, A. B., Orapint, F. F., Wanchai, J., Ikuo, W., & Toshiaki, H. O. (2012). Application of ergothioneine-rich extract from an edible mushroom Flammulina velutipes for melanosis prevention in shrimp, Penaeus monodon and Litopenaeus vannamei. Food Research International, 45, 232–237.
Erikson, U., Veliyulin, E., Singstad, T. E., & Aursand, M. (2004). Salting and desalting of fresh and frozen-thawed cod (Gadus morhua) fillets: a comparative study using 23 Na NMR, 23Na MRI, low-field 1H NMR, and physicochemical analytical methods. Journal of Food Science, 69, 107–114.
Geng, S., Wang, H., Wang, X., Ma, X., Xiao, S., Wang, & Tan, J. M. (2015). A non-invasive NMR and MRI method to analyze the rehydration of dried sea cucumber. Analytical Methods, 7, 2413–2419.
Gokoglu, N., & Yerlikaya, P. (2008). Inhibition effects of grape seed extracts on melanosis formation in shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris). International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 43, 1004–1008.
Han, M. Y., Wang, P., Xu, X. L., & Zhou, G. H. (2014). Low-field NMR study of heat-induced gelation of pork myofibrillar proteins and its relationship with microstructural characteristics. Food Research International, 62, 1175–1182.
Hu, Y., Ji, R., Jiang, H., Zhang, J., Chen, J., & Ye, X. (2012). Participation of cathepsin L in modori phenomenon in carp (Cyprinus carpio) surimi gel. Food Chemistry, 134, 2014–2020.
Jiang, H. B., Wang, Y., Yu, X. Q., Zhu, Y. F., & Kanost, M. (2003). Prophenoloxidase-activating proteinase-3 (PAP-3) from Manduca sexta hemolymph: a clip-domain serine proteinase regulated by serpin-1J and serine proteinase homologs. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 33, 1049–1060.
José-Pablo, Z., Martínez-Álvarez, O., Montero, P., & del Gómez-Guillén, C. M. (2009). Characterisation and tissue distribution of polyphenol oxidase of deepwater pink shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris). Food Chemistry, 112, 104–111.
Kaur, B. P., Kaushik, N., Rao, P. S., & Chauhan, O. P. (2013). Effect of high-pressure processing on physical, biochemical, and microbiological characteristics of black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Food Bioprocess Technology, 6, 1390–1400.
Li, E. C., Chen, L. Q., Zeng, C. N., Yu, Z. Q., Xiong, Chen, X. F., & Qin, J. G. (2008). Comparison of digestive and antioxidant enzymes activities, haemolymph oxyhemocyanin contents and hepatopancreas histology of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, at various salinities. Aquaculture, 274, 80–86.
Li, C. B., Liu, D. Y., Zhou, G. H., Xu, X. L., Qi, J., Shi, P. L., & Xia, T. L. (2012). Meat quality and cooking attributes of thawed pork with different low field NMR T21. Meat Science, 92, 79–83.
Li, M., Li, B., & Zhang, W. J. (2018). Rapid and non-invasive detection and imaging of the hydrocolloid-injected prawns with low-field NMR and MRI. Food Chemistry, 242, 16–21.
Liu, Y. J., Hou, F. J., Wang, X. Z., & Liu, X. L. (2015a). Recombinant expression and characterization of a serine protease inhibitor (Lvserpin 7) from the Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 42, 256–263.
Liu, P. F., Liu, Q. H., Wu, Y., & Jie, H. (2015b). A pilot metabolic profiling study in hepatopancreas of Litopenaeus vannamei with white spot syndrome virus based on 1H- NMR spectroscopy. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 124, 51–56.
Liu, Y. J., Liu, T., Hou, F. J., Wang, X. Z., & Liu, X. L. (2016). Lvserpin 3 is involved in shrimp innate immunity via the inhibition of bacterial proteases and proteases involved in prophenoloxidase system. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 48, 128–135.
Liu, Y. J., Sun, Y. H., Wang, Q., Hou, F. J., & Liu, X. L. (2017). Identification and functional characterizations of serpin 8, a potential prophenoloxidase-activating protease inhibitor in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 60, 492–501.
Lopez-Caballero, M., Martínez-Alvarez, O., Gomez-Guillen, M., & Montero, P. (2007). Quality of thawed deepwater pink shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris) treated with melanosis-inhibiting formulations during chilled storage. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 42, 1029–1038.
Luna-Acosta, A., Thomas-Guyon, H., Amari, M., Rosenfeld, E., Bustamante, P., & Fruitier-Arnaudin, I. (2011). Differential tissue distribution and specificity of phenoloxidases from the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part: B, 159, 220–226.
Manheem, K., Benjakul, S., Kijroongrojana, K., & Visessanguan, W. (2012). The effect of heating conditions on polyphenol oxidase, proteases and melanosis in pre-cooked Pacific white shrimp during refrigerated storage. Food Chemistry, 131, 1370–1375.
Montero, P., Lopez-Caballero, M. E., & Perez-Mateos, M. (2001). The effect of inhibitors and high-pressure treatment to prevent melanosis and microbial growth on chilled prawns (Penaeus japonicus). Journal of Food Science, 66, 1201–1206.
Nirmal, N. P., & Benjaku, S. (2009). Effect of ferulic acid on inhibition of polyphenoloxidase and quality changes of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) during iced storage. Food Chemistry, 116, 323–331.
Nunes, E. T., Braga, A. A., & Camargo-Mathias, M. I. (2014). Histochemical study of the hepatopancreas in adult females of the pink-shrimp Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis Latreille, 1817. Acta Histochemistry, 116, 243–251.
Perazzolo, M. L., & Barracco, A. M. (1997). The prophenoloxidase activating system of the shrimp Penaeus paulensi and associated factors. Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 21, 385–395.
Reis, C. V., Kelen, E. M. A., Farsky, S. H. P., Portaro, F. C. V., Sampaio, C. A. M., Fernandes, B. L. A. C., Camargo, M., & Chudzinski-Tavassi, A. M. A. (1999). Ca2+ activated serine protease (LOPAP) could be responsible for the hemorrhagic syndrome caused by the caterpillar Lonomia oblique. Lancet, 353, 1942.
Romano, N., Koh, C. B., & Ng, W. K. (2015). Dietary microencapsulated organic acids blend enhances growth, phosphorus utilization, immune response, hepatopancreatic integrity and resistance against Vibrio harveyi in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture, 435, 228–236.
Sánchez-Alonso, I., Martinez, I., Sánchez-Valencia, J., & Careche, M. (2012). Estimation of freezing storage time and quality changes in hake (Merluccius merluccius, L.) by low field NMR. Food Chemistry, 135, 1626–1634.
Sánchez-Alonso, I., Moreno, P., & Careche, M. (2014). Low field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR) relaxometry in hake (Merluccius merluccius, L.) muscle after different freezing and storage conditions. Food Chemistry, 153, 250–257.
Sánchez-Valencia, J., Sánchez-Alonso, I., Martínez, I., & Careche, M. (2014). Estimation of frozen storage time or temperature by kinetic modeling of the Kramer shear resistance and water holding capacity (WHC) of hake (Merluccius merluccius, L.) muscle. Journal of Food Engineering, 120, 37–43.
Shao, J. H., Deng, Y. M., Song, L., Batur, A., Jia, N., & Liu, D. Y. (2016). Investigation the effects of protein hydration states on the mobility water and fat in meat batters by LF-NMR technique. LWT-Food Science Technology, 66, 1–6.
Singh, A., & Benjakul, S. (2018). Proteolysis and its control using protease inhibitors in fish and fish products: a review. Comprehensive Review in Food Science and Food Safety, 17, 496–509.
Somprasong, N., Rimphanitchayakit, V., & Tassanakajon, A. (2006). A five-domain Kazal-type serine proteinase inhibitor from black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon and its inhibitory activities. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 30, 998–1008.
Visetnan, S., Donpudsa, S., & Supungul, P. A. (2009). Tassanakajon, V. Rimphanitchayakit, Kazal-type serine proteinase inhibitors from the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon and the inhibitory activities of SPIPm4 and 5. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 27, 266–274.
Wang, Y. B., Liu, L., Zhou, J. R., Ruan, X. M., Lin, J. D., & Fu, L. L. (2015a). Effect of chitosan nanoparticle coatings on the quality changes of postharvest white leg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, during storage at 4 °C. Food Bioprocess Technology, 8, 907–915.
Wang, M., Wang, J. J., Sun, X. H., Pan, Y. J., & Zhao, Y. (2015b). Preliminary mechanism of acidic electrolyzed water ice on improving the quality and safety of shrimp. Food Chemistry, 176, 333–341.
Wu, J. P., Chen, H. C., & Huang, D. J. (2008). Histopathological and biochemical evidence of hepatopancreatic toxicity caused by cadmium and zinc in the white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Chemosphere, 73, 1019–1026.
Xu, Z. H., Regenstein, J. M., Xie, D. D., Lu, W. J., Ren, X. C., Yuan, J. J., & Mao, L. C. (2018a). The oxidative stress and antioxidant responses of Litopenaeus vannamei to low temperature and air exposure. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 72, 564–571.
Xu, D. F., Sun, L. J., Li, C. H., Wang, Y. L., & Ye, R. Y. (2018b). Inhibitory effect of glucose oxidase from Bacillus sp. CAMT22370 on the quality deterioration of Pacific white shrimp during cold storage. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 92, 339–346.
Funding
The authors received financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 31201309, 31772048 and 31371777) and the Key Laboratory of Aquatic Products Processing, Ministry of Agriculture, South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute Key Laboratory of Fishery Products Processing, Ministry of Agriculture, People’s Republic of China (No. NYJG201404) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Ocean University (No. C16396).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Research Highlights
1. Biochemical cascade mechanism underlying melanosis development of L. vannamei during storage was investigated.
2. Melanosis development was highly associated with the elevation of PPO and SP activity in hepatopancreas tissue.
3. Gradual disintegration of cytoarchitecture in hepatopancreas tissue was observed using HC and TEM.
4. Both the significant decrease in T22 and increase in T23 components were determined by LF-NMR.
5. Cytoarchitecture disruption and free water molecule migration droved dissemination of sarcoplasmic reticulum SP and Ca2+.
6. Heat map analysis demonstrated the significant correlation between melanosis development and biochemical indicators.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Yang, X., Wang, Y. et al. Cascading Mechanism Triggering the Activation of Polyphenol Oxidase Zymogen in Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei After Postmortem and the Correlation with Melanosis Development. Food Bioprocess Technol 13, 1131–1145 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02435-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02435-8