Abstract
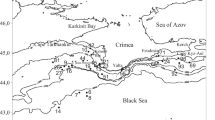
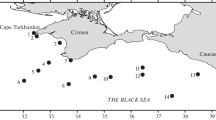
The causes and features of the variability of the bioluminescence intensity of the plankton community in the spring and autumn periods along the coast of Crimea are analyzed based on expedition and satellite data. It is noted that synoptic and mesoscale vortex processes exert a significant impact on the vertical profile of the bioluminescence intensity in hydrobionts and must be taken into account in the analysis of the seasonal variability of bioluminescence parameters. The concept of integral hydrobiont bioluminescence intensity (IHBI) is introduced; it allows one to estimate the total biomass of hydrobionts inhabiting the depth range under consideration. It is found that the average IHBI in the northern part of the Black Sea in the autumn period is higher than in spring by more than ten times. It is noted that mesoscale vortex formations exert the greatest effect on the IHBI in the region of the continental slope.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. S. Konstantinov, General Hydrobiology (Vysshaya shkola, Moscow, 1986) [in Russian].
V. V. Zavoruev, E. N. Zavorueva, and S. P. Krum, Plankton Distribution in Frontal Zones of Water Ecosystems (Siberian Federal University, Krasnoyarsk, 2012) [in Russian].
Yu. I. Sorokin, The Black Sea: Nature and Resources (Nauka, Moscow, 1982) [in Russian].
O. A. Cherepanov, L. A. Levin, and R. N. Utyushev, “Correlation of bioluminescence with biomass and number of luminous and total plankton. 1. Black Sea,” Mor. Ekol. Zh. 6 (3), 84–89 (2007).
E. P. Bityukov and L. M. Khlystova, “Bioluminescence in the neritic zone of the Black Sea and its correlation with plankton parameters,” in Marine Biology (Naukova dumka, Kiev, 1975), is. 34, p. 100–109 [in Russian].
I. I. Gitel’zon, R. I. Chumakova, V. S. Filimonov, L. A. Levin, V. I. Degtyarev, R. N. Utyushev, and A. P. Shevyrnogov, Bioluminescence in Sea (Nauka, Moscow, 1969) [in Russian].
Ye. B. Mel’nikova, “Evaluation of parameters of plankton communities biological rythms under natural environment of the Black Sea using Fourier transform,” Luminescence 32 (3), 321–326 (2017).
V. V. Zavoruev, “The distribution of plankton bioluminescence and fluorescence caused by physicochemical properties of aqueous medium in the water area of the Peruvian upwelling,” Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 16 (1), 72–76 (2003).
Ye. B. Melnikova, “The spatial variability of the intensity of the bioluminescence field in coastal waters of the Crimean Peninsula in the spring period,” Inland Water Biol. 9 (2), 135–141 (2016).
Yu. N. Tokarev, Foundations of Biophysical Ecology of Hydrobionts (EKOSI-Gidrofizika, Sevastopol, 2006) [in Russian].
A. B. Polonsky, E. B. Mel’nikova, A. N. Serebrennikov, and Yu. N. Tokarev, “Regional peculiarities of hydrobiont bioluminescence intensity and chlorophyll a concentration in Black Sea waters,” Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 31 (4), 365–371 (2018).
Ye. B. Melnikova, “Interannual variability in bioluminescence field intensity in nearshore waters of the Black Sea,” Inland Water Biol. 11 (2), 147–153 (2018).
M. I. Senicheva, “Biodiversity, seasonal and interannual variability of microalgae in plankton near coasts of the Crimea,” in Microalgae of the Black Sea: Problems of Maintenance of the Biodiversity and Bioengineering Use (EKOSI-Gidrofizika, Sevastopol, 2008), p. 5–17 [in Russian].
D. M. Filippov, Black Sea Water Circulation and Structure (Nauka, Moscow, 1968) [in Russian].
A. B. Polonskii and G. F. Dzhiganshin, “Structure and mesoscale variability of the Black Sea rim current near the Coast of the Crime,” Dokl. Natsional’noi Akademii Nauk Ukrainy. No. 6, 107–112 (2010).
V. S. Tuzhilkin, “Thermochaline structure of the sea. The Black Sea environment,” in The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry (Springer, Berlin; Heidelberg, 2008).
S. Miladinova, A. Stips, E. Garcia-Gorriz, and Moy D. Macias, “Black Sea thermohaline properties: Long-term trends and variations,” J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans 122 (7), 5624–5644 (2017).
T. Oguz, “Role of physical processes controlling oxycline and suboxic layer structures in the Black Sea,” Global Biogeochem. Cycles 16 (2), 3–13 (2002).
W. E. Fischer and A. B. Green, Upwelling: Mechanisms, Ecological Effects and Threats to Biodiversity (Nova Science Publishers, New York, USA, 2013), p. 59–76.
A. B. Polonskii and E. A. Lovenkova, “Long-term tendencies in the variability of characteristics of the Black Sea pycnocline,” Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 42 (3), 386–396 (2006).
E. V. Stanev, “Understanding Black-Sea dynamics,” Oceanography 18 (2), 56–75 (2005).
T. Oguz and P. Malanotte-Rizzoli, “Seasonal variability of wind and thermohaline-driven circulation in the Black Sea: Modeling studies,” J. Geophys. Res. 101 (7), 16,551 (1996).
E. Ozsoy and A. Mikaelyan, Sensitivity to Change: Black Sea, Baltic Sea, North Sea (Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht, 1997).
A. B. Polonskii and N. S. Drobosyuk, “On an abrupt sea surface temperature (SST) decrease in the Black Sea using data of long-term satellite observations,” Sistemy Kontrolya Okruzhayushchei Sredy. No. 13 (33), 42–49 (2018).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to the reviewer for comments received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by A. Nikol’skii
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polonsky, A.B., Mel’nikova, E.B. & Serebrennikov, A.N. Features of the Variability of the Bioluminescence Intensity of the Plankton Community in the Nearshore Zone of the Black Sea in the Spring and Autumn Periods. Atmos Ocean Opt 33, 146–153 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1024856020020062
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1024856020020062