Abstract
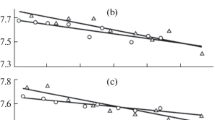
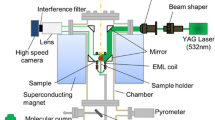
The article presents original experimental data on surface tension of the Fe100 –xMnx (x = 4–13 wt %) melts. Surface tension and density of the melt were measured by the sessile drop method at heating from the liquidus temperature to 1780°C and subsequent sample cooling in the atmosphere of high-purity helium. Temperature and concentration dependences of surface tension and density of Fe–Mn melts were plotted. Manganese is a surface-active substance in iron melt. The value of surface tension coefficient of Fe–Mn melts decreases as Mn content increases. Experimental data on the surface tension of Fe–Mn melts is consistent with the theoretical dependences (the Pavlov–Popel’ equation and the Shishkovsky equation). During the investigation of Fe–Mn melt microheterogenity, correlation between the values of kinematic viscosity, surface tension, and density is revealed. Fluidity dependence of Fe–Mn melts on their density in the cooling mode has a linear character which indicates satisfaction of the Bachinskii law. Discrepancy in the melt viscosity ratios to the surface tension coefficient obtained from the experimental data and from the empirical formula is discovered. Using the experimental data on viscosity and surface tension of Fe–Mn melts, the entropy change in the melt’s bulk and the change in the melt’s surface entropy, respectively, are studied. The surface entropy and the bulk entropy in the melt decrease in their absolute value with its increasing Mn content. From the study results, it is concluded that there is no destruction of the microheterogeneous structure of Fe100 –xMnx (x = 4–13 wt %) melts when heated up to 1780°C.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Vlasov, V.I. and Komolova, E.F., Litaya vysokomargantsevaya stal’ G13L. Svoistva i proizvodstvo (Casted High Manganese Steel G13L: Properties and Production), Moscow: Mashgiz, 1963.
Grässel, O. and Frommeyer, G., Effect of martensitic phase transformation and deformation twinning on mechanical properties of Fe–Mn–Si–AI steels, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1998, vol. 14, no. 12, pp. 1213–1217.
Frommeyer, G., Brux, U., and Neumann, P., Supra-ductile and high-strength manganese-TRIP/TWIP steels for high energy absorption purposes, ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 438–446.
Grässel, O., Krüger, L., Frommeyer, G., and Meyer, L.W., High strength Fe–Mn–(Al, Si) TRIP/TWIP steels development–properties–application, Int. J. Plast., 2000, vol. 16, nos. 11–12, pp. 1391–1409.
Idrissi, H., Renard, K., Ryelandt, L., Schryvers, D., and Jacques, P.J., On the mechanism of twin formation in Fe–Mn–C TWIP steels, Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 2464–2476.
Zhuang C., Liu J., Mi Z., Jiang H., Tang D., and Wang G., Non-metallic inclusions in TWIP steel, Steel Res. Int., 2014, vol. 85, no. 10, pp. 1432–1439.
So, K.H., Kim, J.S., Chun, Y.S., Park, K.-T., Lee, Y.-K., and Lee, C.S., Hydrogen delayed fracture properties and internal hydrogen behavior of a Fe–18Mn–1.5Al–0.6C TWIP steel, ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49, no. 12, pp. 1952–1959.
Lee, J., Hoai, L.T., and Shin, M., Density and surface tension of liquid Fe–Mn alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42, no. 3, pp. 546–549.
Hoai, L.T. and Lee, J., Density of liquid Fe–Mn–C alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42, no. 5, pp. 925–927.
Hoai, L.T. and Lee, J., Effect of surface adsorption of carbon on the surface tension of liquid Fe–Mn–C alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 2012, vol. 47, no. 24, pp. 8303–8307.
Dubberstein, T., Heller, H.-P., Klostermann, J., et al., Surface tension and density data for Fe–Cr–Mo, Fe–Cr–Ni, and Fe–Cr–Mn–Ni steels, J. Mater. Sci., 2015, vol. 50, no. 22, pp. 7227–7237.
Adolf, Z., Plura, J, and Parma, V., Effect of carbon on surface tension in Fe–Mn–C, Fe–Si–C, Fe–P–C, and Fe–S–C melts, Hutnicke Listy, 1987, vol. 42, no. 8, pp. 537–544.
Popel’, S.I., Tsarevskii, B.V., and Dzhemilev, N.K., Isotherms of density and surface tension of Fe–Mn melts, Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 1964, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 158–160.
Van Ts.-T., Karasev, R.A., and Samarin, A.M., Surface tension of Fe–Mn and Fe–S melts, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Otd. Tekh. Nauk,Metall. Topl., 1960, vol. 2, pp. 49–52.
Nakamoto, M. and Tanaka, T., Estimation of activity coefficient of solute in infinite dilute liquid iron based on surface tension of binary liquid Fe alloys, J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 2019, vol. 105, no. 3, pp. 53–57.
Wang, J., Bian, M., and Ma, L., Composition in surface of liquid Fe–Mn and Fe–S systems, Acta Metall. Sin., 1986, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. a270–a274.
Keene, B.J., Review of data for the surface tension of iron and its binary alloys, Int. Mater. Rev., 1988, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 1–37.
Gedgagova, M.V., Guketlov, Kh.M., Kumykov, V.K., Manukyants, A.R., Sergeev, I.N., and Sozaev, V.A., High-temperature measurements of surface tension of metals in vacuum, Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci.: Phys., 2007, vol. 71, no. 5, pp. 608–610.
Direktor, L.B., Zaichenko, V.M., and Maikov, I.L., An improved method of sessile drop for determining the surface tension of liquids, High Temp., 2010, vol. 48, no. 2, pp. 176–180.
Ostrovskii, O.I., Grigoryan, V.A., and Vishkarev, A.F., Svoistva metallicheskikh rasplavov (Properties of Metallic Melts), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1988.
Chikova, O., Sinitsin, N., Vyukhin, V., and Chezganov, D., Microheterogeneity and crystallization conditions of Fe-Mn melts, J. Cryst. Growth, 2019, vol. 527, art. ID 125239.
Popel’, S.I., Poverkhnostnye yavleniya v rasplavakh (Surface Phenomena in Melts), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1994.
Semenchenko, V.K., Poverkhnostnye yavleniya v metallakh i splavakh (Surface Phenomena in Metals and Alloys), Moscow: Gostekhizdat, 1957.
Eremenko, V.N., Ivanov, M.I., Lukashenko, G.M., et al., Fizicheskaya khimiya neorganicheskikh materialov (Physical Chemistry of Inorganic Materials), Eremenko, V.N., Ed., Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1988, vol. 2.
Korol’kov, A.M., Surface tension of aluminum and its alloys, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Tekh. Nauki, 1956, no. 2, pp. 35–42.
Nizhenko, V.I. and Eremenko, V.N., Surface-active additions in liquid metals, Sov. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 1964, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 98–103.
Fomenko, V.S., Emissionnye svoistva khimicheskikh elementov i ikh soedinenii. Spravochnik (Emission Properties of Chemical Elements and Their Compounds: Handbook), Samsonov, G.V., Ed., Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1964.
Summ, B.D., New correlations of surface tension with volume properties of liquids, Vestn. Mosk. Univ., Ser. 2:Khim., 1999, vol. 40, no. 6, pp. 400–405.
Funding
The reported study was funded by Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 19-33-90198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by E. Oborin
About this article
Cite this article
Sinitsin, N.I., Chikova, O.A. & V’yukhin, V.V. Surface Tension and Density of Fe–Mn Melts. Steel Transl. 50, 16–21 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091220010118
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091220010118