Abstract
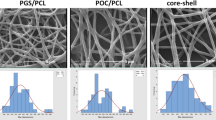
Delivery of retinal progenitor cells (RPCs) for restoring injured or diseased retinal tissue using biodegradable scaffolds is a promising treatment for retinal diseases. Blend of three polymers; poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL), poly(glycerol sebacate) (PGS), and poly(1,8-octanediol-co-citrate) (POC) was used to prepare a nanofibrous scaffold for retinal tissue engineering via electrospinning process. The PGS and POC were firstly synthesized through condensation polymerization. The combinations of PCL, PGS, and POC were then electrospun and optimized to prepare the nanofibrous scaffolds. Subsequently, hydrophilicity, degradability, and biocompatibility of the prepared scaffolds were evaluated. Morphological studies of the scaffolds showed nanofibers without any sings of beads. Tensile evaluations of the scaffolds confirmed that the prepared scaffolds could meet mechanical property requirements for retinal application. The incorporation of POC increased the hydrophilicity and degradation rate of the scaffolds. Also, in-vitro cell behavior assays revealed that human retinal pigment epithelium cells proliferated faster when the POC was added to the scaffold structure. The results suggest that the PGS/POC/PCL scaffold has the potential for retinal tissue engineering (TE) applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
E. Margalit and S. R. Sadda, Artif. Organs 27, 963(2003).
H. J. Klassen, T. F. Ng, Y. Kurimoto, I. Kirov, M. Shatos, P. Coffey, and M. J. Young, Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 45, 4167 (2004).
W. L. Neeley, S. Redenti, H. Klassen, S. Tao, T. Desai, M. J. Young, and R. Langer, Biomaterials 29, 418 (2008).
S. Khalili, S. Nouri Khorasani, N. Saadatkish, and K. Khoshakhlagh, Polym. Sci., Ser. A 58, 399 (2016).
M. R. Safran, H. Kim, and S. Zaffagnini, J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 16, 306 (2008).
S. Khalili, S. Nouri Khorasani, S. M. Razavi, B. Hashemibeni, and A. Tamayol, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 187, 1193 (2018).
S. Khalili, S. Nouri Khorasani, M. Razavi, B. Hashemibeni, F. Heydari, and A. Tamayol, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A 106, 370 (2018).
R. Vasita and D. S. Katti, Int. J. Nanomed. 1, 15 (2006).
Y. Zhang, B. Su, J. Venugopal, S. Ramakrishna, and C. T. Lim, Int. J. Nanomed. 2, 623 (2007).
S. Kumbar, R. James, S. P. Nukavarapu, and C. T. Laurencin, Biomed. Mater. 3, 034002 (2008).
E. Yuksel, J. Choo, M. Wettergreen, and M. Liebschner, Semin. Plast. Surg. 19, 261 (2005).
S. Karbasi, S. Nouri Khorasani, S. Ebrahimi, S. Khalili, F. Fekrat, and D. Sadeghi, Adv. Biomed. Res. 5, 177 (2016).
C. G. Jeong and S. J. Hollister, Biomaterials 31, 4304 (2010).
A. Nadim, S. Nouri Khorasani, M. Kharaziha, and S. M. Davoodi, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 78, 47 (2017).
M. Masoudi Rad, S. Nouri Khorasani, L. Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, M. P. Prabhakaran, M. R. Foroughi, M. Kharaziha, N. Saadatkish, and S. Ramakrishna, Mater. Sci. Eng., C 80, 75 (2017).
N. Masoumi, B. L. Larson, N. Annabi, M. Kharaziha, B. Zamanian, K. S. Shapero, A. T. Cubberley, G. Camci-Unal, K. B. Manning, J. E. Mayer, Jr., and A. Khademhosseini, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 3, 929 (2014).
S. Sant, D. Iyer, A. Gaharwar, A. Patel, and A. Khademhosseini, Acta Biomater. 9, 5963 (2013).
J. Yao, S. L. Tao, and M. J. Young, Polymers 3, 899 (2011).
A. Gaharwar, M. Nikkhah, S. Sant, and A. Khademhosseini, Biofabrication 7, 015001 (2015).
Y. Kang, J. Yang, S. Khan, L. Anissian, and G. A. Ameer, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A 77, 331 (2006).
Y. Wang, G. A. Ameer, B. J. Sheppard, and R. Langer, Nature Niotechnol. 20, 602 (2002).
C. L. Nijst, J. P. Bruggeman, J. M. Karp, L. Ferreira, A. Zumbuehl, C. J. Bettinger, and R. Langer, Biomacromolecules 8, 3067 (2007).
J. Yang, A. R. Webb, S. J. Pickerill, G. Hageman, and G. A. Ameer, Biomaterials 27, 1889 (2006).
Y. Guo, K. Liang, and Y. Ji, Eur. Polym. J. 110, 337 (2019).
L. Vogt, L. R. Rivera, L. Liverani, A. Piegat, and M. El Fray, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 103, 109712 (2019).
J. Yang, A. R. Webb, and G. A. Ameer, Adv. Mater. 16, 511 (2004).
Y. Wang, Y. M. Kim, and R. Langer, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A 66, 192 (2003).
R. Ravichandran, J. R. Venugopal, S. Sundarrajan, S. Mukherjee, and S. Ramakrishna, Tissue Eng., Part A 17, 1363 (2011).
I. H. Jaafar, M. M. Ammar, S. S. Jedlicka, R. A. Pearson, and J. P. Coulter, J. Mater. Sci. 45, 2525 (2010).
R. E. Neisiany, S. N. Khorasani, M. Naeimirad, J. K. Y. Lee, and S. Ramakrishna, Macromol. Mater. Eng. 302, 1600551 (2017).
R. Esmaeely Neisiany, J. K. Y. Lee, S. Nouri Khorasani, R. Bagheri, and S. Ramakrishna, J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 59, 456 (2018).
Y. Du, J. Ge, Y. Shao, P. X. Ma, X. Chen, and B. Lei, J. Mater. Chem. B 3, 2986 (2015).
S. Salehi, M. Fathi, S. H. Javanmard, T. Bahners, J. S. Gutmann, S. Ergün, K. P. Steuhl, and T. A. Fuchsluger, Macromol. Mater. Eng. 299, 455 (2014).
Z. Li and C. Wang, One-Dimensional Nanostructures: Electrospinning Technique and Unique Nanofibers (Springer–Verlag, Berlin; Heidelberg, 2013).
M. G. McKee, G. L. Wilkes, R. H. Colby, and T. E. Long, Macromolecules 37, 1760 (2004).
A. Anindyajati, Jurnal Teknosains 8, 168 (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fatemeh Jafari, Khorasani, S.N., Alihosseini, F. et al. Development of an Electrospun Scaffold for Retinal Tissue Engineering. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 62, 290–298 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1560090420030069
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1560090420030069