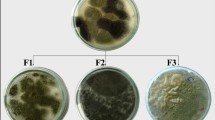
Abstract
Gamma spectrometry is applied for measurement of natural radioactivity by Hyper-pure germanium (HPGe) systems during the application of bioleaching optimum conditions in ore and waste samples. The bioleaching of the ore sample using isolated fungus A. lentulus indicate that the bioleaching efficiency of 234U, 232Th are higher than 238U, 230Th and 235U which may attributed to the effect α-recoil rate for 234U, organic matter, clays or iron oxide and or/lower activity concentration of 232Th. The immobilization of 238U, 235U, 230Th, 214Pb, and 214Bi in ore and waste samples could be result from high organic matter content, iron, and manganese oxides, in addition to the role of microbes that can resist leaching by their cellular compounds. The high mobility of some radionuclides in waste samples may be resulted from the leaching process of the original rocks using acid solution that clean the grain surfaces leaving spaces around the grains and this permit the organic acids to reach the inner parts of the grains during bioleaching processes leading to the high mobility 234U, 232Th and to lesser extent 238U and 235U. The radionuclides 226Ra, 214Pb and 214Bi were found almost totally in the residue of two sample (Q and W) indicating to be associated with radium sulphate or relatively insoluble mineral phases like alumina silicates and refractory oxides.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
H. Hamidian, B. Rezai, S. A. Milani, F. Vahabzade, and S. Z. Shafaie, “Microbial leaching of uranium ore,” Asian J. Chem. 21, 5808–5820 (2009).
G. M. Pires, S. Rodrigues, M. I. Gomes, Sustainable Solid Waste Collection and Management (Springer Int., Switzerland, 2019).
G. F. Knoll, Radiation Detection and Measurement, 3rd ed. (Wiley, New York, USA, 2000).
M. A. E. Abdel-Rahman and S. A. El-Mongy, “Analysis of radioactivity levels and hazard assessment of black sand samples from rashid area,” Egypt. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 49, 1752–1757 (2017).
A. K. Sam, “The state of disequilibrium between U and Th series isotopes in marine sediments from the sudanese Red Sea coast,” Radiochemistry 45, 90–95 (2003).
El. Walley and N. Dine, “Study of natural radioactivity and the state of radioactive disequilibrium in u-series for rock samples, North Eastern Desert, Egypt,” Appl. Rad. Isotopes 66, 75–80 (2007).
M. A. E. Rahman and S. A. El-Mongy, “Ore leashing processing for yellow cake production and assay of their uranium content by radiometric analysis,” Zeitschr. Anorg. Allgem. Chem. 644, 29–32 (2018).
M. R. Khattab, H. Tuovinen, J. Lehto, I. E. El Assay, M. G. El Feky, and M. A. Abd El-Rahman, “Determination of uranium in egyptian graniteic ore by gamma, alpha, and mass spectrometry,” Instrum. Sci. Technol. 45, 338–348 (2017).
R. M. Anjos, R. Veiga, T. Soares, A. M. A. Santos, J. G. Aguiar, M. H. B. O. Frasca, J. A. P. Brage, D. Uzeda, L. Mangia, A. Facure, B. Mosquera, C. Carvalho, and P. R. S. Gomes, “Natural radionuclide distribution in brazilian commercial granites,” Radiat. Meas. 39, 245–253 (2005).
S. Saeed, H. N. Bhatti, and T. M. Bhatti, “Bioleaching studies of rock phosphate using aspergillus niger,” J. Biol. Sci. 2, 76–78 (2002).
H. Hanane, B. Brahim, M. Hafidi, A. Lebrihi, M. J. Virolle, and Y. Ouhdouch, “Screening for rock phosphate solubilizing actinomycetes from moroccan phosphate mines,” Appl. Soil Ecol. 38, 12–19 (2008).
IAE Agency, Preparation and Certification of IAEA Gamma Spectrometry Reference Materials, RGU-1, RGTh-1 and RGK-1 (Int. Atomic Energy Agency, 1987).
Ch. Thom and K. B. Raper, A Manual of the Aspergilli (Williams and Wilkinc, Baltiore, 1945).
United Nations Sci. Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, UNSCEAR Report to General Assembly, Annex B: Report to General Assembly with Scientific Annexes, Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation, United Nations Sales Publ. No. E.10.Xi.3 (United Nations, New York, 2008), Vol. 1.
J. Adloff and K. Roessler, “Recoil and transmutation effects in the migration behaviour of actinides,” Radiochim. Acta 52–53, 269–274 (1991).
H. Tuovinen, E. Pohjolainen, D. Vesterbacka, K. Kaksonen, J. Virkanen, D. Solatie, J. Lehto, and D. Read, “Release of radionuclides from waste rock and tailings at a former pilot uranium mine in eastern finland,” Boreal Environ. Res. 21, 471–480 (2016).
J. Schaller, A. Weiske, and E. G. Dudel, “Effects of gamma-sterilization on DOC, uranium and arsenic remobilization from organic and microbial rich stream sediments,” Sci. Total Environ. 409, 3211–3214 (2011).
J. Falandysz, M. Chudzińska, D. Baralkiewicz, M. Drewnowska, and A. Hanć, “Toxic elements and bio-metals in cantharellus mushrooms from Poland and China,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 24, 11472–11482 (2017).
D. Desideri, C. Roselli, and L. Feduzi, and M. Assunta Meli, “Monitoring the atmospheric stability by using radon concentration measurements: a study in a Central Italy site,” J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 270, 523–530 (2006).
B. Alicja and S. Bogdan, “Activity disequilibrium between (234)U and (238)U isotopes in natural environment,” J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 300, 719–727 (2014).
X. Wang, N. Planavsky, A. Hofmann, E. E. Saupe, B. P. de Corte, P. Philippot, S. V. LaLonde, and N. E. Jemison, “A mesoarchean shift in uranium isotope systematics,” Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 238, 438–452 (2018).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank Prof. Dr. Mohamed El-Feky, Head of Geochemical Exploration Department, Nuclear materials authority (NMA) and Prof. Dr. Afaf Nada, Women’s College for Arts, Science and Education, Ain Shams University, for their help and assistance during the preparation of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nareman Harpy, Abdel-Rahman, M.A., Sallam, A.M. et al. The Significance of Mobilization and Immobilization of Specific Radionuclides for Optimum Bioleaching Conditions Using Aspergillus lentulus. Phys. Part. Nuclei Lett. 17, 253–259 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1547477120020077
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1547477120020077