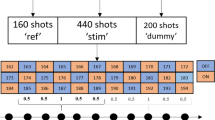
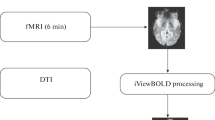
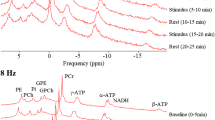
Abstract—Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain; it plays an important role in various types of synaptic plasticity and pathology. In the present work, proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) and two modified MEGA-PRESS pulse sequences, that is, –GABAMEGA-PRESS and +GABAMEGA-PRESS, were used to investigate the effect of visual stimulation on the GABA level in the human visual cortex in vivo. With –GABAMEGA-PRESS, it was possible to acquire the 1H-NMR signal of methylated protons of GABA with the chemical shift δ = 3.01 ppm without the signals from macromolecules. When +GABAMEGA-PRESS was used, the GABA signal was a superposition of resonances of methylene protons of GABA and macromolecules. The effect of constant visual stimulation on the level of N-acetylaspartate and total level of glutamate and glutamine was also estimated. Constant visual stimulation had no effect on the levels of N-acetylaspartate and glutamine in the visual cortex. The –GABA signal intensity decreased with a statistically significant decrease in the level of GABA signal intensity leading to inactivation of GABA synthesis. No statistically significant changes in the intensity of the +GABA resonance were found, probably due to the effect of visual stimulation on macromolecules. In order to test this hypothesis, a signal from macromolecules was acquired using a specifically designed inversion-recovery pulse sequence. It was shown that the intensity of this signal is unaffected by visual stimulation and the absence of changes in the intensity of the +GABA signal during the stimulation has to be considered as the masking effect of macromolecular signal.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. A. Lewis, D. W. Volk, and T. Hashimoto, Psychopharmacology 174 (1), 143 (2004).
G. Sanacora, G. F. Mason, D. L. Rothman, et al., Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 56 (11), 1043 (1999).
A. W. Goddard, G. F. Mason, A. Almai, et al., Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 58 (6), 556 (2001).
O. A. Petroff and D. L. Rothman, Mol. Neurobiol. 16 (1), 97 (1998).
L. K. Bak, A. Schousboe, and H. S. Waagepetersen, J. Neurochem. 98 (3), 641 (2006).
A. Floyer-Lea, M. Wylezinska, T. Kincses, and P. M. Matthews, J. Neurochem. 95 (3), 1639 (2006).
R. A. E. Edden, S. D. Muthukumaraswamy, T. C. A. Freeman, and K. D. Singh, J. Neurosci. 29 (50), 15721 (2009).
P. A. Bottomley, Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 508 (1), 333 (1987).
J. Frahm, K. D. Merboldt, and W. Hanicke, J. Magn. Reson. 72 (3), 502 (1987).
P. K. Bhattacharyya, M. D. Phillips, L. A. Stone, and M. J. Lowe, Magn. Reson. Imaging 29 (3), 374 (2011).
V. Govindaraju, K. Young, and A. A. Maudsley, NMR Biomed. 13 (3), 129 (2000).
M. Mescher, H. Merkle, J. D. Kirsch, et al., NMR Biomed. 11 (6), 266 (1998).
S. J. Kish, T. L. Perry, and S. Hansen, J. Neurochem. 32 (6), 1629 (1979).
R. A. Edden, N. A. Puts, and P. B. Barker, Magn. Reson. Med. 68 (3), 657 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.24391
D. C. Shungu, X. Mao, R. Gonzales, et al., NMR Biomed. 29 (7), 932 (2016).
M. Považan, G. Hangel, B. Strasser, et al., Neuroimage 121, 126 (2015).
L. Michels, E. Martin, P. Klaver, et al., PloS One 7 (4), e31933 (2012).
R. J. Maddock, G. A. Casazza, D. H. Fernandez, and M. I. Maddock, J. Neurosci. 36 (8), 2449 (2016).
R. Mekle, S. Kuhn, H. Pfeiffer, et al., NMR Biomed. 30 (2), e3672 (2017).
C. Chen, H. P. Sigurdsson, S. Pepes, et al., NeuroImage 156, 207 (2017).
P. Bednařik, I. Tkač, F. Giove, et al., J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 35 (4), 601 (2015).
K. Kurcyus, E. Annac, N. M. Hanning, et al., J. Neurosci. 38 (46), 9967 (2018).
P. E. Menshchikov, N. A. Semenova, T. A. Akhadov, et al., Biophysics (Moscow) 62 (6), 1009 (2017).
A. V. Manzhurtsev, N. A. Semenova, M. V. Ubminskii, et al., Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Khim., No. 6, 1630 (2016).
R. A. De Graaf, In Vivo NMR Spectroscopy: Principles and Techniques (Wiley, 2019).
http://www.gabamrs.com.
S. Cavassila, S. Deval, C. Huegen, et al., NMR Biomed. 14 (4), 278 (2001).
https://www.stat.auckland.ac.nz/~wild/ChanceEnc/ Ch10.wilcoxon.pdf.
S. Mangia, I. Tkac, R. Gruetter, et al., J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 27 (5), 1055 (2007).
B. Schaller, R. Mekle, L. Xin, et al., J. Neurosci. Res. 91 (8), 1076 (2013).
A. Schousboe and U. Sonnewald, Glutamate/-GABAglutamine Cycle (Springer International, 2016).
Y. Lin, M. C. Stephenson, L. Xin, et al., J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 32 (8), 1484 (2012).
R. C. G. Landim, R. A. Edden, B. Foerster, et al., Magn. Reson. Imaging 34 (3), 239 (2016).
K. L. Behar and T. Ogino, Magn. Reson. Med. 30 (1), 38 (1993).
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 18-13-00030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of compliance with standards of research involving humans as subjects. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional committee of the Clinical and Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology (Moscow Healthcare Department) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study.
Additional information
Translated by E. Makeeva
Abbreviations: GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; MRS, magnetic resonance spectroscopy; PS, pulse sequence; NAA, N-acetylaspartate; tCr, phosphocreatin; Glx, total glutamine and glutamate; FSP, frequency-selective pulse; SNR, signal/noise ratio.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yakovlev, A., Manzhurtsev, A., Menshchikov, P. et al. The Effect of Visual Stimulation on GABA and Macromolecule Levels in the Human Brain in vivo. BIOPHYSICS 65, 51–57 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350920010248
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350920010248