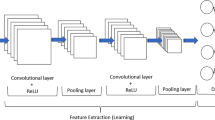
Abstract—Soybean phenology is strongly influenced by temperature and day length, and phenological records clearly reflect the changes in climatic conditions. A model including three artificial neural networks was designed to predict the time intervals between sowing, emergence, flowering, and maturity as dependent on climatic factors. Ensemble regression models were constructed to predict the yield, seed protein, and oil content in soybean. Data on maturation were analyzed for early-maturing soybean accessions phenotyped at two experimental stations of Vavilov Institute of Plant Genetic Resources in the North-Caucasian and Northwestern regions of Russia. The model was implemented in Python using the Keras and TensorFlow packages.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. G. Paptsov, S. A. Shilovskaya, A. V. Kolesnikov, et al., Adaptation of Russian Agriculture to Global Climate Change (Oxfam International, 2015). http:// www.oxfam.ru/upload/iblock/f96/f9622b41f4854994-5438f2292f509d14.pdf. Cited January 6, 2019.
J. E. Olesen, T.R. Carter, C.H. Diaz-Ambrona, et al., Eur. J. Agron. 34 (2), 96 (2011).
T. Carter and K. Makinen, Approaches to Climate Change Impact, Adaptation and Vulnerability Assessment: Towards a Classification Framework to Serve Decision-Making: MEDIATION 2.1 (Finnish Environment Institute, Helsinki, Finland, 2011).
A. D. Richardson, R. S. Anderson, M. Altaf Arain, et al., Global Change Biol. 18 (2) 566 (2012).
K. N. Kozlov, L. Yu. Novikova, I. V. Seferova, and M. G. Samsonova, Biophysics (Moscow) 63 (1), 136 (2018).
D. J. Major, et al., Crop Sci. 15, 174 (1975).
T. Hodges and V. French, Agronomy J. 77 (3), 500 (1985).
P. Pedersen, et al., Agronomy J. 96, 556 (2004).
T. D. Setiyono, et al., Field Crops Res. 100 (2–3), 257 (2007).
L. Yu. Novikova, I. V. Seferova, and K. N. Kozlov, Biophysics (Moscow) 63 (6) 956 (2018).
M. Abdipour, et al., J. Am. Oil Chemists’ Soc. 95 (3), 283 (2018).
M. Kaul, R. L. Hill, and C. Walthall, Agricult. Syst. 85 (1), 1 (2005).
A. Bagherzadeh, et al., Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2 (2), (2016).
D. A. Elizondo, R. W. McClendon, and G. Hoogenboom, Trans. ASAE 37 (3), 981 (1994).
N. I. Korsakov, O. P. Adamova, V. I. Budalova, et al., Methodological Guidelines for Studies on Collections of Legume Grain Crops (N. I. Vavilov Research Institute of Plant Industry, Leningrad, 1990) [in Russian].
L. Shelchko, et al., CMEA International Classification of the Genus Glycine Willd. (CMEA Scientific Council on Collections of Wild and Cultivated Plant Species, N. I. Vavilov Research Institute of Plant Industry, Leningrad, 1990) [in Russian].
O. D. Taratuhin, L. Yu. Novikova, I. V. Seferova, and K. N. Kozlov, Biophysics (Moscow) 64 (3) 440 (2019).
M. Feurer, A. Klein, K. Eggensperger, et al. in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Ed. by C. Cortes (Curran Assoc., 2015), pp. 2962–2970.
M. Srinivasa Rao, P. Swathi, C.A. Rama Rao, et al., PLoS One 10 (2), e0116762 (2015).
P. G. Jones and P. K. Thornton, Agricult. Forest Meteorol. 86 (1–2), 127 (1997).
P. G. Jones and P. K. Thornton, Agricult. Forest Meteorol. 97 (3), 213 (1999).
P. G. Jones and P. K. Thornton, Agron. J. 92, 445 (2000).
P. G. Jones and A. L. Jones, MarkSim: A Computer Tool That Generates Simulated Weather Data for Crop Modeling and Risk Assessment (CIAT, 2002).
D. P. van Vuuren, et al., Clim. Change 109 (1–2), 5 (2011).
F. Pedregosa, et al., J. Machine Learning Res. 12, 2825 (2011).
F. Chollet, et al., Keras (GitHub, 2015). https://https://github.com/keras-team/keras.
M. Abadi, et al., in Proc. 12th USENIX Conf. on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (Savannah, GA, USA, 2016), pp. 265–283.
K. Kozlov, A. M. Samsonov, and M. Samsonova, Peer J. Comp. Sci. 2, e74 (2016).
R. Storn and K. Price, J. Global Optim. 11, 341 (1997).
M. O’Neill and C. Ryan, IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 5 (4), 349 (2001).
L. Yu. Novikova, I. V. Seferova, A. Yu. Nekrasov, et al., Vavilov. Zh. Genet. Selekts. 22 (6) 708 (2018).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Computations were performed at the Polytechnic Supercomputer Center of St. Petersburg State University and a cluster of University of Southern California.
Initial data were obtained on the basis of the unique research tool Collection of Plant Genetic Resources (Vavilov Institute of Plant Genetic Resources).
Funding
This work was supported by the Federal Grant Program (project no. 14.575.21.0136 dated September 26, 2017, unique project identifier RFMEFI57517X0136).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by T. Tkacheva
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taratuhin, O.D., Novikova, L.Y., Seferova, I.V. et al. An Artificial Neural Network Model to Predict the Phenology of Early-Maturing Soybean Varieties from Climatic Factors. BIOPHYSICS 65, 106–117 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350920010200
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350920010200