Abstract
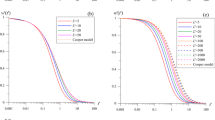
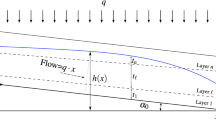
A semianalytic and approximate analytical solution is given to the problem of slug test in a partially penetrating well in a confined or unconfined anisotropic aquifer. An asymptotic solution is given to the problem of slug test in a partially penetrating well in an unconfined aquifer. The latter solution, unlike the semiempiric Bouwer–Rice method, takes into account hydraulic conductivity anisotropy and skin effect. Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm was used to develop a method for determining hydraulic conductivity anisotropy and skin effect based on data of slug tests in partially penetrating wells in confined or unconfined aquifer.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Vasilevskii, V.N., Umrikhin, I.D., Kamenetskii, S.G., Saitov, A.U., and Kuz’min, V.M., Vremennoe rukovodstvo po issledovaniyu skvazhin “ekspress-metodami” (Provisional Guide on Studying Wells by Slug Tests), Moscow: VNII, 1964.
Verigin, N.N., Vasil’ev, S.V., Sarkisyan, V.S., and Sherzhukov, B.S., Gidrodinamicheskie i fiziko-khimicheskie svoistva gornykh porod (Hydrodynamic and Physicochemical Properties of Rocks), Moscow: Nedra, 1977.
Gamayunov, N.I. and Sherzhukov, B.S., Field determination of granite permeability, Inzh.-Fiz. Zh., 1961, vol. 4, no. 10, pp. 71–78.
Kamenetskii, S.G., Two problems of the theory of flow of an elastic fluid in an elastic porous medium, in Tr. VNII. Razrabotka neftyanykh mestorozhdenii i podzemnaya gidrodinamika (Trans. VNII. Development of Oil Deposits and Subsurface Hydrodynamics), Moscow: Gostoptekhizdat, 1959, no. 19, pp. 134–145.
Kamenetskii, S.G. and Saitov, A.U., Slug test for studying piezometric nonflowing wells, Neftepromysl. Delo, 1963, no. 8, pp. 8–11.
Krylov, A.P., Glogovskii, M.M., Mirchink, M.F., Nikolaevskii, N.M., and Charnyi, I.A., Nauchnye osnovy razrabotki neftyanykh mestorozhdenii (Scientific Principles of Oil Deposit Development), Moscow: Gostoptekhizdat, 1948.
Lekhov, S.M. and Lekhov, M.V., Methods for calculating and reasons of erroneous results of slug tests in well, Inzh. Izysk., 2017, no. 2, pp. 38–50.
Morozov, P.E., Determination of the reservoir parameters by slug test in a horizontal well, Neftepromysl. Delo, 2018, no. 11, pp. 36–42.
Morozov, P.E., Semianalytical solution for unsteady fluid flow to a partially penetrating well, Uch. Zap. Kazan. Gos. Univ. Ser. Fiz.-Mat. Nauki, 2017, vol. 159, Book 3, pp. 340–353.
Khein, A.L., Transient fluid flow toward a well with an open bottom, partially penetrating the bed, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1953, vol. 91, no. 3, pp. 467–470.
Sherzhukov, B.S., Determining the resistance of partially penetrating wells (skin-effect) based on data of instantaneous filling or pumping and pumping with constant rate, in Tr. lab. inzhenernoi gidrogeol. VNII VODGEO (Trans. Lab. Eng. Hydrogeol.), Moscow: Stroiizdat, 1972, issue 6, pp. 193–209.
Sherzhukov, B.S. and Gamayunov, N.I., Method for estimating the hydrogeological parameters of aquifers when tested by a pilot well, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Razved., Geol. Razved., 1964, no. 5, pp. 105–111.
Bouwer, H. and Rice, R.C., A slug test for determining hydraulic conductivity of unconfined aquifers with completely or partially penetrating wells, Water Resour. Res., 1976, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 423–428.
Butler, J.J., Jr., The Design, Performance, and Analysis of Slug Tests, Boca Raton, FL: Lewis Publishers, 1998.
Chang, C.C. and Chen, C.S., An integral transform approach for a mixed boundary problem involving a flowing partially penetrating well with infinitesimal well skin, Water Resour. Res., 2002, vol. 38, no. 6, pp. 1071–1077.
Cooper, H., Bredehoeft, J.D. and Papadopulos, I.S., Response of a finite-diameter well to an instantaneous charge of water, Water Resour. Res., 1967, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 263–269.
Dougherty, D. and Babu, D., Flow to a partially penetrating well in a double-porosity reservoir, Water Resour. Res., 1984, vol. 20, no. 8, p. 1116–1122.
Hantush, M.S., Hydraulics of wells, in Advances in Hydroscience, Chow, V.T., Ed., N.Y.: Acad. Press, 1964, vol. 1, pp. 281–432.
Hyder, Z. and Butler, J.J., Jr., Slug tests in unconfined formations: an assessment of the Bouwer and Rice technique, Ground Water, 1995, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 16–22.
Hyder, Z., Butler, J.J., Jr., McElwee, C.D., and Liu, W., Slug tests in partially penetrating wells, Water Resour. Res., 1994, vol. 30, no. 11, pp. 2945–2957.
Paradis, D. and Lefebvre, R., Single-well interference slug tests to assess the vertical hydraulic conductivity of unconsolidated aquifers, J. Hydrol., 2013, vol. 478, pp. 102–118.
Peres, A.M., Omur, M., and Reynolds, A.C., A new analysis procedure for determining aquifer properties from slug test data, Water Resour. Res., 1989, vol. 25, no. 7, pp. 1591–1602.
Perina, T. and Lee, T.C., General well function for pumping from a confined, leaky, or unconfined aquifer, J. Hydrol., 2006, vol. 317, nos. 3–4, pp. 239–260.
Ramey, H.J., Jr. and Agarwal, R.G., Annulus unloading rates as influenced by wellbore storage and skin effect, SPE J., 1972, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 253–462.
Rushing, J.A., A semianalytical model for horizontal well slug testing in confined aquifers, PhD Dissertation, Texas: Texas A&M Univ., 1997, 133 p.
Sageev, A., Slug test analysis, Water Resour. Res., 1986, vol. 22, no. 8, pp. 11 323–1333.
Yeh, H.D., Chen, Y.J., and Yan, S.Y., Semi-analytical solution for a slug test in partially penetrating wells including the effect of finite-thickness skin, Hydrol. Processes, 2008, vol. 22, no. 18, pp. 3741–3748.
Zlotnik, V.A., Interpretation of slug and packer tests in anisotropic aquifers, Ground Water, 1994, vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 761–766.
Zlotnik, V.A., Goss, D., and Duffield, G.M., General steady-state shape factor for a partially penetrating well, Ground Water, 2010, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 111–116.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by G. Krichevets
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morozov, P.E. Assessing the Hydraulic Conductivity Anisotropy and Skin-Effect Based on Data of Slug Tests in Partially Penetrating Wells . Water Resour 47, 430–437 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807820030124
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807820030124