Abstract
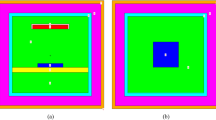
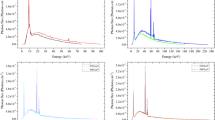
In the in-service radiographic testing of water-filled pipes, the interaction of radiation with water diminishes the quality of the transmitted radiation to cause severe degradation in the radiographic sensitivity. In this paper, simulation work was carried out to investigate the radiographic testing of a water-filled pipe using X-ray and Ir-192 gamma source. The radiation reaching the film was studied, and accordingly, an approach to improve the radiographic sensitivity by optimizing the radiographic screen to control the scattered radiation was proposed. The approach showed promising indications, so the experimental work was proceeded using X-ray to validate the simulation results. The sensitivity, measured by the visibility of the Image Quality Indicator, was better in the radiographs obtained utilizing the proposed approach than that offered in the test used the standard screens.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
International Atomic Energy Agency, Industrial Radiography: Manual for the Syllabi Contained in IAEA-TECDOC-628 “Training Guidelines in Non-destructive Testing Techniques”, Vienna, Austria: IAEA, 1992, Training Ser. no. 3.
Nondestructive Testing Handbook, Bossi, R.H., Iddings, F.A., Wheeler, G.C., and Moore, P.O., Eds.,Vol. 4: Radiographic Testing, Columbus, OH: Am. Soc. Nondestr. Test., 2002, 3rd ed.
GE Inspection Technologies, Industrial Radiography-Image Forming Techniques, General Electric Co., 2007.
Orphan, V.J., Utilization of Real-Time X-Radiography for In-Service Inspection of Nuclear Reactor Piping: Feasibility Investigation, Final Report, La Jolla, CA: Science Applications, Inc., 1978.
Freeman, W. E. and McDonald, D.E., US development in radiological methods, Int. J. Pressure Vessels Piping, 1987, vol. 28, pp. 139–162.
Kolbuck, V., In service weld X-ray method for thick fittings on large diameter liquid filled pipelines, in Proc. Int. Pipeline Conf., Calgary, Canada, 2004.
Kolbuck, V., X-ray method liquid filled pipeline, in Int. Pipeline Conf., Canada, October 4–8, 2004.
Bremnes, O., Modeling the influence of the water level on radiographic inspection of pipes, in ECNDT, Berlin, 2006.
http://fismed.ciemat.es/GAMOS, Cited June 2017.
American Society of Mechanical Engineers, ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Sec. V, Art. 2, 2016 ed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tariq O. Mousa, Mohammed, M.S. & Aljohani, M.S. Optimizing Radiographic Sensitivity in the In-Service Testing of Pipes. Russ J Nondestruct Test 56, 92–99 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106183092001009X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S106183092001009X