Abstract
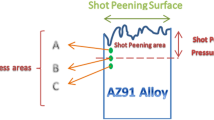
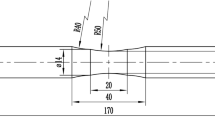
Shot peening is a treatment used to increase surface hardness and wear resistance. In this study, the effect of shot peening on the microstructure, hardness and wear resistance of AZ31 magnesium alloy was investigated. For this purpose, specimens were exposed to shot peening operation using steel pellets for periods of 20, 40, 60, and 80 min. Microstructures were investigated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-Ray diffraction (XRD). In addition, the Vickers method and the pin on disk method were used to measure the hardness and wear for testing, respectively. The results showed that the shot peening operation resulted in grain refining on the surface, in addition, the wear resistance increased with increasing shot peening time. This is because of grain refining on the surface and the micro strains created by shot peening. Assessment of surface wearing indicated the application of an adhesive wear mechanism on the untreated specimen and the abrasive wear mechanism in the shot peened specimens. Moreover, by increasing the duration of shot peening, the abrasive wear decreased due to increased hardness.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Laleh, M. and Kargar F., J. Alloys Compd., 2011, vol. 509, no. 37, p. 9150.
Fouad, Y. and El-Batanouny, M., AlexandriaEng. J., 2011, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 19–22.
Xu, C., Sheng, G., Sun, Y., Yuan, X., and Jiao, Y., Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 2018, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 28–34.
Laleh, M., Rouhaghdam, A.S., Shahrabi, T., and Shanghi, A., J. Alloys Compd., 2010, vol. 496, nos. 1–2, pp. 548–552.
Xu, K., Wang, A., Wang, Y., Dong, X., Zhang, X., and Huang, Z., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2009, vol. 256, no. 3, pp. 619–626.
Hwang, D.Y., Kim, Y.M., Park, D-Y., Yoo, B., and Shin, D.H., Electrochim. Acta, 2009, vol. 54, no. 23, pp. 5479–5485.
Mueller, K. and Mueller, S., J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, vol. 187, pp. 775–779.
Hassani-Gangaraj, S., Cho, K., Voigt, H.-J., Guagliano, M., and Schuh, C., Acta Mater., 2015, vol. 97, pp. 105–115.
Wang, Z., Tao, N., Tong, W., Lu, J., and Lu, K., Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, no. 14, pp. 4319–4329.
Tao, N., Wang, Z., Tong, W., Sui, M., Lu, J., and Lu, K., Acta Mater., 2002, vol. 50, no. 18, pp. 4603–4616.
Li, W., Liu, P., Ma, F., Liu, X., and Rong, Y., J. Alloys Compd., 2011, vol. 509, no. 2, pp. 518–522.
Barnett, M., Nave, M., and Bettles, C., Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2004, vol. 386, nos. 1–2, pp. 205–211.
Valiev, R., J. Mater. Sci., 2007, vol. 42, no. 5, pp. 1483–1490.
Hou, L.-F., Wei, Y.-H., Liu, B.-S., and Xu, B.-S., Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2008, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 1053–1057.
Révész, Á., Szommer, P., Szabó, P., and Varga, L., J. Alloys Compd., 2011, vol. 509, pp. S482–S485.
Revesz, A. and Takacs, L., J. Alloys Compd., 2007, vol. 441, nos. 1–2, pp. 111–114.
Lu, K. and Lu, J., Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2004, vol. 375, pp. 38–45.
Tao, N., Lu, K., Scr. Mater., 2009, vol. 60, no. 12, pp. 1039–1043.
Wei, Y.-H., Liu, B.-S., Hou, L.-F., Xu, B.-S., and Liu, G., J. Alloys Compd., 2008, vol. 452, no. 2, pp. 336–342.
Balusamy, T., Narayanan, T.S., and Ravichandran, K., Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, vol. 213, pp. 221–228.
Paydar, H., Amini, K., and Akhbarizadeh, A., Kovove Mater., 2014, vol. 52, pp. 163–169.
Bagherifard, S., Hickey, D.J., Fintová, S., Pastorek, F., Fernandez-Pariente, I., Bandini, M., et al., Acta Biomater., 2018, vol. 66, pp. 93–108.
Zhang, H., Hei, Z., Liu, G., Lu, J., and Lu, K., Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, no. 7, p. 1871.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haghighi, O., Amini, K. & Gharavi, F. Effect of Shot Peening Operation on the Microstructure and Wear Behavior of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 56, 164–168 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205120010098
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205120010098