Abstract
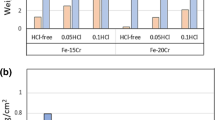
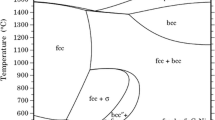
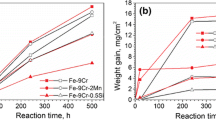
Chlorine-induced high-temperature corrosion is a major problem for structural materials used in incinerators because of the release of hydrochloride during waste combustion. In this work, the effect of HCl additions (0.05 and 0.1 vol%) to a N2–10CO2–10H2O gas on the oxidation of binary ferritic Fe—(15, 20, 25 and 30 wt%) Cr alloys was investigated at 650 °C. The addition of HCl significantly increased the rate of weight gain during reaction. Thick multi-layered iron-rich oxide scales formed on Fe-15Cr in all gases. Increasing Cr content increased the tendency for Cr2O3 scale formation, leading to complete protection for Fe-25Cr in HCl-free gas, but a level of 30Cr was required in the presence of HCl. Mechanisms underlying the effect of chlorine on the critical Cr concentration required for protective chromia formation are explored.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.-H. Lee, N. J. Themelis, and M. J. Castaldi. Combating Corrosion in WTE Facilities: Theory and Experience. in 14th Annual North American Waste-to-Energy Conference. American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection (2006).
D. Mudgal, S. Singh, and S. Prakash, Corrosion problems in incinerators and biomass-fuel-fired boilers. International Journal of Corrosion, 2014, 2014.
D. J. Young, High temperature oxidation and corrosion of metals, (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2016).
G. Lai, Waste-to-Energy Boilers and Waste Incinerators. High-Temperature Corrosion and Materials Applications (2007), p. 335–358.
T. T. Sharobem, Mitigation of High Temperature Corrosion in Waste-to-Energy Power Plants, (Columbia University, New York, 2017).
H. P. Nielsen, F. Frandsen, K. Dam-Johansen and L. Baxter, The implications of chlorine-associated corrosion on the operation of biomass-fired boilers. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science26, (3), 2000 (283–298).
H. Grabke, E. Reese and M. Spiegel, The effects of chlorides, hydrogen chloride, and sulfur dioxide in the oxidation of steels below deposits. Corrosion Science37, (7), 1995 (1023–1043).
M. J. McNallan, W. W. Liang, S. H. Kim, and C. T. Kang, High Temperature Corrosion, in NACE-6 (Houston, TX, 1983), p. 316–321.
J. Liu and M. McNallan, Effects of temperature variations on oxidation of iron-20% chromium alloys at 1200 K in Ar-20% O2-Cl2 gas mixtures. Materials and Corrosion50, (5), 1999 (253–260).
T. D. Nguyen, J. Zhang and D. J. Young, Water vapour effects on corrosion of Fe–Cr and Fe–Cr–Ni alloys containing cerium and manganese in CO2 gas at 818°C. Corrosion Science89, 2014 (220–235).
T. D. Nguyen, J. Zhang and D. J. Young, Effects of silicon and water vapour on corrosion of Fe–20Cr and Fe–20Cr–20Ni alloys in CO2 at 650°C. Oxidation of Metals87, (3–4), 2017 (541–573).
T. Gheno, D. Monceau, J. Zhang and D. J. Young, Carburisation of ferritic Fe–Cr alloys by low carbon activity gases. Corrosion Science53, (9), 2011 (2767–2777).
P. E. Liley, G. H. Thomson, D. G. Friend, T. E. Daubert, and E. Buck, Physical and Chemical Data, in Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook, Chemical Engineering (The McGraw-Hill, 2008).
T. Gheno, Oxidation and carburisation of model chromia-forming alloys in carbon dioxide, in School of Materials Science. Ph.D. Thesis (University of New South Wales, 2012).
R. Bender and M. Schütze, The role of alloying elements in commercial alloys for corrosion resistance in oxidizing-chloridizing atmospheres. Part I: Literature evaluation and thermodynamic calculations on phase stabilities. Materials and Corrosion54, (8), 2003 (567–586).
R. Bender and M. Schütze, The role of alloying elements in commercial alloys for corrosion resistance in oxidizing-chloridizing atmospheres. Part II: Experimental investigations. Materials and Corrosion54, (9), 2003 (652–686).
Y. Kawahara, High temperature corrosion mechanisms and effect of alloying elements for materials used in waste incineration environment. Corrosion Science44, (2), 2002 (223–245).
Y. Ihara, H. Ohgame, K. Sakiyama and K. Hashimoto, The corrosion behaviour of iron in hydrogen chloride gas and gas mixtures of hydrogen chloride and oxygen at high temperatures. Corrosion Science21, (12), 1981 (805–817).
M. Montgomery and A. Karlsson, In-situ corrosion investigation at Masnedø CHP plant: a straw-fired power plant. Materials and Corrosion50, (10), 1999 (579–584).
D. J. Young, T. D. Nguyen, P. Felfer, J. Zhang and J. M. Cairney, Penetration of protective chromia scales by carbon. Scripta Materialia77, 2014 (29–32).
K. Strafford, P. Datta and G. Forster, High-temperature chloridation of binary Fe-Cr alloys at 1000°C. Materials Science and Engineering: A120, 1989 (61–68).
A. Zahs, M. Spiegel and H. J. Grabke, Chloridation and oxidation of iron, chromium, nickel and their alloys in chloridizing and oxidizing atmospheres at 400–700°C. Corrosion Science42, (6), 2000 (1093–1122).
T. Dudziak, Steam Oxidation of Fe-Based Materials, in High Temperature Corrosion (IntechOpen, Pakistan, 2016), p. 15.
G. Gibbs, M. Wootton, W. Price and K. Hodgson, Scale stresses during protective and breakaway corrosion of iron and rimming steel in CO2. Oxidation of Metals7, (3), 1973 (185–200).
J. Robertson and M. Manning, Criteria for formation of single layer, duplex, and breakaway scales on steels. Materials Science and Technology4, (12), 1988 (1064–1071).
F. Rouillard, G. Moine, L. Martinelli and J. Ruiz, Corrosion of 9Cr steel in CO2 at intermediate temperature I: mechanism of void-induced duplex oxide formation. Oxidation of Metals77, (1–2), 2012 (27–55).
L. Martinelli, F. Balbaud-Célérier, A. Terlain, S. Bosonnet, G. Picard and G. Santarini, Oxidation mechanism of an Fe–9Cr–1Mo steel by liquid Pb–Bi eutectic alloy at 470 C (Part II). Corrosion Science50, (9), 2008 (2537–2548).
Y. Sato and D. J. Young, High-Temperature corrosion of iron at 900°C in atmospheres containing HCl and H2O. Oxidation of Metals55, (3–4), 2001 (243–260).
C. Tedmon Jr., The effect of oxide volatilization on the oxidation kinetics of Cr and Fe-Cr alloys. Journal of the Electrochemical Society113, (8), 1966 (766).
E. Potter, Mechanism of magnetite growth on low-carbon steel in steam and aqueous solutions up to 550°C, in Proceedings of 2nd International Congress on Metallic Corrosion (Houston, TX, 1963).
C. Wagner, Reaktionstypen bei der Oxydation von Legierungen. Zeitschrift für Elektrochemie, Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für physikalische Chemie63, (7), 1959 (772–782).
R. Rapp, The transition from internal to external oxidation and the formation of interruption bands in silver-indium alloys. Acta Metallurgica9, (8), 1961 (730–741).
J. Takada and M. Adachi, Determination of diffusion coefficient of oxygen in α-iron from internal oxidation measurements in Fe-Si alloys. Journal of Materials Science21, (6), 1986 (2133–2137).
J. Takada, S. Yamamoto, S. Kikuchi and M. Adachi, Determination of diffusion coefficient of oxygen in γ-iron from measurements of internal oxidation in Fe-Al alloys. Metallurgical Transactions A17, (2), 1986 (221–229).
R. Braun and M. Feller-Kniepmeier, Diffusion of chromium in α-iron. Physica Status Solidi90, (2), 1985 (553–561).
J. H. Swisher and E. T. Turkdogan, Transactions of the Metallurgical Society of AIME239, 1967 (426–431).
C. Wagner, Theoretical analysis of the diffusion processes determining the oxidation rate of alloys. Journal of the Electrochemical Society99, (10), 1952 (369–380).
C. Yu, T. D. Nguyen, J. Zhang and D. J. Young, Sulfur effect on corrosion behavior of Fe-20Cr-(Mn, Si) and Fe-20Ni-20Cr-(Mn, Si) in CO2-H2O at 650°C. Journal of The Electrochemical Society163, (3), 2016 (C106–C115).
D. Gaskell, An introduction to transport phenomena in materials engineering, (Momentum Press, New York, 2012).
T. Nguyen, J. Zhang and D. Young, Effect of Si on corrosion of Fe-Cr and Fe-Cr-Ni alloys in wet CO2 gas. Corrosion Science and Technology14, (3), 2015 (127–131).
T. D. Nguyen, J. Zhang and D. J. Young, Water vapor effects on corrosion of Fe–Cr and Fe–Cr–Ni alloys containing silicon in CO2 gas at 818°C. Oxidation of Metals83, (5–6), 2015 (575–594).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Dr.-Ing. Michael Schütze, DECHEMA-Forschungsinstitut, for valuable discussion and final manuscript checking. Financial support by Australian Research Council under the Discovery Scheme is highly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aye, K.K., Zhang, J. & Young, D.J. Effect of Hydrogen Chloride on Corrosion Behaviour of Fe–Cr Alloys in Wet CO2 Gas at 650 °C. Oxid Met 94, 51–80 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-020-09978-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-020-09978-3