Abstract
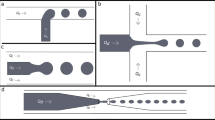
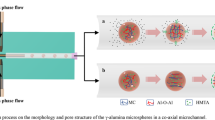
The hydrogel microspheres of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/ glutaraldehyde (GA) used as embolic agent can be applied in the embolization therapy. The mechanical properties and size precision of the hydrogel microspheres have a strong influence on its clinical application. In this work, the microfluidic technology was employed in the preparation of size-controlled PVA/GA hydrogel microspheres, and a novel in-situ gelation system was proposed. The influences of cross-linker (GA) content and the total content of PVA and GA in the dispersed phase, and catalyst content in the continuous phase on the compressive strength and deformation of PVA/GA gel microspheres were investigated in detail. Also, the kinetic behaviours of the formation of PVA/GA hydrogel microspheres in the microfluidic system were studied, and the results indicated that the gelation processes based on microfluidics accord to first-order reaction.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed EM (2015) Hydrogel: preparation, characterization, and applications: a review. J Adv Res 6(2):105–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2013.07.006
Kenawy E, Kamoun EA, Eldin MSM, El-Meligy MA (2014) Physically crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol)-hydroxyethyl starch blend hydrogel membranes: synthesis and characterization for biomedical applications. Arab J Chem 7(3):372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.05.026
Kamoun EA, Chen X, Mohy Eldin MS, Kenawy E-RS (2015) Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels for wound dressing applications: a review of remarkably blended polymers. Arab J Chem 8(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.07.005
Li XQ, Gong PW, Li YZ, Yu JF, Wang F, Li XA, Fan ZJ, Wang ZF (2019) Double-carrier drug delivery system based on polyurethane-polyvinyl alcohol/layered double hydroxide nanocomposite hydrogel. Mater Lett 243:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.01.151
Dai HJ, Zhang H, Ma L, Zhou HY, Yu Y, Guo T, Zhang YH, Huang HH (2019) Green pH/magnetic sensitive hydrogels based on pineapple peel cellulose and polyvinyl alcohol: synthesis, characterization and naringin prolonged release. Carbohydr Polym 209:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.014
Yang X, Liu Q, Chen X, Yu F, Zhu ZJCP (2008) Investigation of PVA/ws-chitosan hydrogels prepared by combined γ-irradiation and freeze-thawing. Carbohydr Polym 73(3):401–408
Baker MI, Walsh SP, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD (2012) A review of polyvinyl alcohol and its uses in cartilage and orthopedic applications. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 100(5):1451–1457. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.32694
Chen Y-P, Zhang J-L, Zou Y, Wu Y-L (2019) Recent advances on polymeric beads or hydrogels as embolization agents for improved Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE). Frontiers in chemistry 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00408
Hu J, Albadawi H, Chong BW, Deipolyi AR, Sheth RA, Khademhosseini A, Oklu R (2019) Advances in biomaterials and Technologies for Vascular Embolization. Adv Mater 31(33). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201901071
Doucet J, Kiri L, O'Connell K, Kehoe S, Lewandowski RJ, Liu DM, Abraham RJ, Boyd D (2018) Advances in degradable embolic microspheres: a state of the art review. J Funct Biomater 9(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb9010014
Keussen I, Bengtsson J, Gavier-Widen D, Karlstam E (2018) Uterine artery embolization in a sheep model: biodegradable versus non-degradable microspheres. Acta Radiol 59(10):1210–1217. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185118757575
Cha WI, Hyon SH, Oka M, Ikada Y (1996) Mechanical and wear properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. Macromol Symp 109:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.19961090111
Chen G, Wei R, Huang X, Wang F, Chen Z (2019) Synthesis and assessment of sodium alginate-modified silk fibroin microspheres as potential hepatic arterial embolization agent. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.122
Bolto B, Tran T, Hoang M, Xie Z (2009) Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes. Prog Polym Sci 34(9):969–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.05.003
Tripathi S, Mehrotra GK, Dutta PK (2009) Physicochemical and bioactivity of cross-linked chitosan-PVA film for food packaging applications. Int J Biol Macromol 45(4):372–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2009.07.006
Kurkuri MD, Aminabhavi TM (2004) Poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(acrylic acid) sequential interpenetrating network pH-sensitive microspheres for the delivery of diclofenac sodium to the intestine. J Control Release 96(1):9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2003.12.025
Rao KSVK, Naidu BVK, Subha MCS, Sairam M, Aminabhavi TM (2006) Novel chitosan-based pH-sensitive interpenetrating network microgels for the controlled release of cefadroxil. Carbohydr Polym 66(3):333–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.03.025
EdS Jr C, Pereira MM, Mansur HS (2009) Properties and biocompatibility of chitosan films modified by blending with PVA and chemically crosslinked. J Mater Sci Mater Med 20(2):553–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-008-3627-7
Wang T, Turhan M, Gunasekaran S (2004) Selected properties of pH-sensitive, biodegradable chitosan-poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel. Polym Int 53(7):911–918. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.1461
Zhai ML, Yoshii F, Kume T, Hashim K (2002) Syntheses of PVA/starch grafted hydrogels by irradiation. Carbohydr Polym 50(3):295–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0144-8617(02)00031-0
Akhtar MF, Hanif M, Ranjha NM (2016) Methods of synthesis of hydrogels ... A review. Saudi Pharm J 24(5):554–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2015.03.022
Berger J, Reist M, Mayer JM, Felt O, Peppas NA, Gurny R (2004) Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 57(1):19–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0939-6411(03)00161-9
Barber EA, Turasan H, Gezer PG, Devina D, Liu GL, Kokini J (2019) Effect of plasticizing and crosslinking at room temperature on microstructure replication using soft lithography on zein films. J Food Eng 250:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2019.01.018
Villanueva-Flores F, Miranda-Hernandez M, Flores-Flores JO, Porras-Sanjuanico A, Hu HL, Perez-Martinez L, Ramirez OT, Palomares LA (2019) Poly(vinyl alcohol co-vinyl acetate) as a novel scaffold for mammalian cell culture and controlled drug release. J Mater Sci 54(10):7867–7882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03402-1
de Luna MS, Ascione C, Santillo C, Verdolotti L, Lavorgna M, Buonocore GG, Castaldo R, Filippone G, Xia H, Ambrosio L (2019) Optimization of dye adsorption capacity and mechanical strength of chitosan aerogels through crosslinking strategy and graphene oxide addition. Carbohydr Polym 211:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.02.002
Hsiao C-J, Lin J-F, Wen H-Y, Lin Y-M, Yang C-H, Huang K-S, Shaw J-F (2020) Enhancement of the stability of chlorophyll using chlorophyll-encapsulated polycaprolactone microparticles based on droplet microfluidics. Food Chem:306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125300
Ha Eun L, Kyu Hwan C, Xia M, Dong Woo K, Bum Jun P (2020) Interactions between polystyrene particles with diameters of several tens to hundreds of micrometers at the oil-water interface. J Colloid Interface Sci 560:838–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.10.095
Operti MC, Dolen Y, Keulen J, van Dinther EAW, Figdor CG, Tagit O (2019) Microfluidics-assisted size tuning and biological evaluation of PLGA particles. Pharmaceutics 11(11):590. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110590
Chen WY, Kim JH, Zhang D, Lee KH, Cangelosi GA, Soelberg SD, Furlong CE, Chung JH, Shen AQ (2013) Microfluidic one-step synthesis of alginate microspheres immobilized with antibodies. J R Soc Interface 10(88):20130566. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2013.0566
Mazutis L, Vasiliauskas R, Weitz DA (2015) Microfluidic production of alginate hydrogel particles for antibody encapsulation and release. Macromol Biosci 15(12):1641–1646. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201500226
Anseth KS, Bowman CN, BrannonPeppas L (1996) Mechanical properties of hydrogels and their experimental determination. Biomaterials 17(17):1647–1657. https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-9612(96)87644-7
Jabrail FH, Ahmad AZ, Gupta KC (2016) Synthesis and characterization of pH responsive polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels with chitosan and poly-acrylonitrile. J Polym Mater 33(3):539–553
Mansur HS, Sadahira CM, Souza AN, Mansur AAP (2008) FTIR spectroscopy characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel with different hydrolysis degree and chemically crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. Mater Sci Eng C Biomim Supramol Syst 28(4):539–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2007.10.088
Serra C, Berton N, Bouquey M, Prat L, Hadziioannou G (2007) A predictive approach of the influence of the operating parameters on the size of polymer particles synthesized in a simplified microfluidic system. Langmuir 23(14):7745–7750. https://doi.org/10.1021/la063289s
Xiang L, Ya-Ting Y, Cao-Fei F, Qun-Ying H, Liu-Si S, Zhen-Qi C, Serra CC (2014) A microfluidic-assisted fabrication of size-controlled Porose CeO2 microspheres as an analog production of nuclear fuel beads. Adv Sci Technol 94:55–68. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AST.94.55
Ye B, Miao J-L, Li J-L, Zhao Z-C, Chang Z, Serra CA (2013) Fabrication of size-controlled CeO2 microparticles by a microfluidic sol-gel process as an analog preparation of ceramic nuclear fuel particles. J Nucl Sci Technol 50(8):774–780. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223131.2013.796897
Chang Z, Serra CA, Bouquey M, Prat L, Hadziioannou G (2009) Co-axial capillaries microfluidic device for synthesizing size- and morphology-controlled polymer core-polymer shell particles. Lab Chip 9(20):3007–3011. https://doi.org/10.1039/b913703c
Chang Z, Serra CA, Bouquey M, Kraus I, Li S, Koehler JM (2010) Multiscale materials from microcontinuous-flow synthesis: ZnO and au nanoparticle-filled uniform and homogeneous polymer microbeads. Nanotechnology 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/21/1/015605
Hidaka K, Nakamura M, Osuga K, Miyazaki H, Wada S (2010) Elastic characteristics of microspherical embolic agents used for vascular interventional radiology. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 3(7):497–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2010.05.004
Peppas NA, Mikos AG (1986) Preparation methods and structure of hydrogels. Hydrogels Med Pharm 1:1–27
Xu JY, Liu X, Ren XY, Gao GH (2018) The role of chemical and physical crosslinking in different deformation stages of hybrid hydrogels. Eur Polym J 100:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.01.020
Du L, Huang Y, Zhang Q, Zhou Y, Huang J, Yan L, Yu Z, Qin A, Yang H, Chen M, Lang L, Bian B, Li X, Fu J (2019) Synthesis and assessment of drug-eluting microspheres for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Acta Biomater 88:370–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2019.02.035
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (grant numbers 2017YFE0300504) and the National Nature Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 21978279). Also, the authors thank the Key Research and Development Projects in Anhui Province of the People’s Republic of China (No. 201904a05020048) for financial support in the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Article Highlights
Fabrication of PVA/GA hydrogel microspheres by a novel in-situ gelation reaction in microfluidics.
Precise size control of embolic microspheres with a very narrow size distribution.
PVA/GA hydrogel formation kinetics of a first order reaction in microfluidic preparation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, D., Guo, L., Wang, Y. et al. Novel synthesis of PVA/GA hydrogel microspheres based on microfluidic technology. J Flow Chem 10, 551–562 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41981-020-00101-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41981-020-00101-w