Abstract
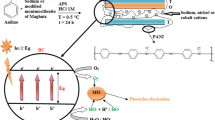
The present study focuses on the use of waste coal fly ash (CFA) for preparing magnetic photocatalyst (MnFe2O4/CFA) and its application of dye degradation from water. The MnFe2O4/CFA photocatalyst was synthesized through a facile hydrothermal method and characterized by various techniques for its structural, morphological, and photocatalytic properties. The MnFe2O4/CFA nanocomposite was used for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue (MB) under sunlight. Detailed studies for various parameters such as pH, catalyst dose, initial dye concentration, oxidant concentration, and time on photocatalytic degradation were analyzed. The degradation efficiency reached ~ 100% under sunlight within 30 min by the MnFe2O4/CFA nanocomposite. The degradation/removal efficiency of MB was found in the order MnFe2O4/CFA (99.9%) > CFA (61%) > MnFe2O4 (56%) under optimum conditions for composite at pH = 3, composite dose 60 mg/L, and oxidant dose 0.8 mM. The MnFe2O4/CFA is a promising visible-light-active photocatalyst and can be reused several times without significant loss in photocatalytic degradation efficiency.
Graphic abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abroshan E, Farhadi S, Zabardasti A (2018) Novel magnetically separable Ag3PO4/MnFe2O4 nanocomposite and its high photocatalytic degradation performance for organic dyes under solar-light irradiation. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 178:154–163
Ambashta RD, Sillanpää M (2010) Water purification using magnetic assistance: a review. J Hazard Mater 180:38–49
Baldrian P, Merhautová V, Gabriel J, Nerud F, Stopka P, Hrubý M, Beneš MJ (2006) Decolorization of synthetic dyes by hydrogen peroxide with heterogeneous catalysis by mixed iron oxides. Appl Catal B Environ 66:258–264
Banerjee S, Sharma GC, Chattopadhyaya M, Sharma YC (2014) Kinetic and equilibrium modeling for the adsorptive removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions on of activated fly ash (AFSH). J Environ Chem Eng 2:1870–1880
Bora LV, Mewada RK (2017) Visible/solar light active photocatalysts for organic effluent treatment: fundamentals, mechanisms and parametric review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:1393–1421
Chatterjee D, Ruj B, Mahata A (2001) Adsorption and photocatalysis of colour removal from waste water using flyash and sunlight. Catal Commun 2:113–117
Devi E, Soibam I (2017) Structural and optical characterization of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Adv Mater Proc 2:93–96
Duta A, Visa M (2015) Simultaneous removal of two industrial dyes by adsorption and photocatalysis on a fly-ash–TiO2 composite. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 306:21–30
Fu Y, Xiong P, Chen H, Sun X, Wang X (2012) High photocatalytic activity of magnetically separable manganese ferrite–graphene heteroarchitectures. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:725–731
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A, Madkour FF (2017) Testing the advanced oxidation processes on the degradation of Direct Blue 86 dye in wastewater. Egyp J Aqua Res 43:11–19
Ibrahim I, Ali IO, Salama TM, Bahgat A, Mohamed MM (2016) Synthesis of magnetically recyclable spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M = Zn Co, Mn) nanocrystals engineered by sol gel-hydrothermal technology: high catalytic performances for nitroarenes reduction. Appl Catal B Environ 181:389–402
Joshi MK, Pant HR, Liao N, Kim JH, Kim HJ, Park CH, Kim CS (2015) In-situ deposition of silver–iron oxide nanoparticles on the surface of fly ash for water purification. J Colloid Interface Sci 453:159–168
Kefeni KK, Mamba BB, Msagati TA (2017) Application of spinel ferrite nanoparticles in water and wastewater treatment: a review. Sep Purif Technol 188:399–422
Kumar KV, Ramamurthi V, Sivanesan S (2005) Modeling the mechanism involved during the sorption of methylene blue onto fly ash. J Colloid Interface Sci 284:14–21
Kumar A, Sharma G, Naushad M, Thakur S (2015) SPION/β-cyclodextrin core–shell nanostructures for oil spill remediation and organic pollutant removal from waste water. Chem Eng J 280:175–187
Kumar A et al (2017) Sustainable nano-hybrids of magnetic biochar supported g-C3N4/FeVO4 for solar powered degradation of noxious pollutants—synergism of adsorption, photocatalysis & photo-ozonation. J Clean Prod 165:431–451
Kumar A, Kumar A, Sharma G, Ala’a H, Naushad M, Ghfar AA, Stadler FJ (2018) Quaternary magnetic BiOCl/g-C3N4/Cu2O/Fe3O4 nano-junction for visible light and solar powered degradation of sulfamethoxazole from aqueous environment. Chem Eng J 334:462–478
Kwon J, Kim J-H, Kang S-H, Choi C-J, Rajesh JA, Ahn K-S (2017) Facile hydrothermal synthesis of cubic spinel AB2O4 type MnFe2O4 nanocrystallites and their electrochemical performance. Appl Surf Sci 413:83–91
Lai C et al (2019) Fabrication of novel magnetic MnFe2O4/bio-char composite and heterogeneous photo-Fenton degradation of tetracycline in near neutral pH. Chemosphere 224:910–921
Li N, Fu F, Lu J, Ding Z, Tang B, Pang J (2017) Facile preparation of magnetic mesoporous MnFe2O4@ SiO2–CTAB composites for Cr(VI) adsorption and reduction. Environ Pollut 220:1376–1385
Lopez-Lopez C, Martín-Pascual J, Martínez-Toledo M, Muñío M, Hontoria E, Poyatos J (2015) Kinetic modelling of TOC removal by HO/UV, photo-Fenton and heterogeneous photocatalysis processes to treat dye-containing wastewater. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:3255–3262
Mahmoodi NM (2014) Synthesis of magnetic carbon nanotube and photocatalytic dye degradation ability. Environ Monit Asses 186:5595–5604
Meeker RE (1965) Stabilization of hydrogen peroxide. Google Patents
Melián EP et al (2009) ZnO activation by using activated carbon as a support: characterisation and photoreactivity. Appl Catal A Gen 364:174–181
Mushtaq F, Zahid M, Bhatti IA, Nasir S, Hussain T (2019) Possible applications of coal fly ash in wastewater treatment. J Environ Manag 240:27–46
Naseri MG, Saion EB, Ahangar HA, Hashim M, Shaari AH (2011) Synthesis and characterization of manganese ferrite nanoparticles by thermal treatment method. J Mag Mater 323:1745–1749
Nguyen TD, Phan NH, Do MH, Ngo KT (2011) Magnetic Fe2O4 (M: Fe, Mn) activated carbons: fabrication, characterization and heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of methyl orange. J Hazard Mater 185:653–661
Ökte AN, Karamanis D (2013) A novel photoresponsive ZnO-flyash nanocomposite for environmental and energy applications. Appl Catal B Environ 142:538–552
Pant HR et al (2013) Antibacterial and photocatalytic properties of Ag/TiO2/ZnO nano-flowers prepared by facile one-pot hydrothermal process. Ceram Int 39:1503–1510
Saud PS et al (2015) Preparation and photocatalytic activity of fly ash incorporated TiO2 nanofibers for effective removal of organic pollutants. Ceram Int 41:1771–1777
Shao L, Ren Z, Zhang G, Chen L (2012) Facile synthesis, characterization of a MnFe2O4/activated carbon magnetic composite and its effectiveness in tetracycline removal. Mater Chem Phys 135:16–24
Sharma R, Bansal S, Singhal S (2015) Tailoring the photo-Fenton activity of spinel ferrites (MFe2O4) by incorporating different cations (M = Cu, Zn, Ni and Co) in the structure. RSC Adv 5:6006–6018
Sharma G et al (2018) Facile fabrication of Zr2Ni1Cu7 trimetallic nano-alloy and its composite with Si3N4 for visible light assisted photodegradation of methylene blue. J Mol Liq 272:170–179
Sonar SK, Niphadkar PS, Mayadevi S, Joshi PN (2014) Preparation and characterization of porous fly ash/NiFe2O4 composite: promising adsorbent for the removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution. Mater Chem Phys 148:371–379
Styszko K, Szczurowski J, Czuma N, Makowska D, Kistler M (2018) Adsorptive removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from aqueous solutions by chemically treated fly ash. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:493–506
Tabasum A, Zahid M, Bhatti HN, Asghar M (2019) Fe3O4–GO composite as efficient heterogeneous photo-Fenton’s catalyst to degrade pesticides. Mater Res Express 6:015608
Tahir M, Ali S, Rizwan M (2019) A review on remediation of harmful dyes through visible light-driven WO3 photocatalytic nanomaterials. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:4975–4988
Türkeş E, Açıkel YS (2019) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic halloysite–chitosan nanocomposites: use in the removal of methylene blue in wastewaters. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:1282–1294
Uribe IO, Mosquera-Corral A, Rodicio JL, Esplugas S (2015) Advanced technologies for water treatment and reuse. AIChE J 61:3146–3158
Vignesh K, Suganthi A, Min B-K, Kang M (2014) Photocatalytic activity of magnetically recoverable MnFe2O4/g-C3N4/TiO2 nanocomposite under simulated solar light irradiation. J Mol Catal A Chem 395:373–383
Visa M, Bogatu C, Duta A (2010) Simultaneous adsorption of dyes and heavy metals from multicomponent solutions using fly ash. Appl Surf Sci 256:5486–5491
Visa M, Andronic L, Duta A (2015a) Fly ash-TiO2 nanocomposite material for multi-pollutants wastewater treatment. J Environ Manag 150:336–343
Visa M, Isac L, Duta A (2015b) New fly ash TiO2 composite for the sustainable treatment of wastewater with complex pollutants load. Appl Surf Sci 339:62–68
Wang X, Wang A, Ma J (2017) Visible-light-driven photocatalytic removal of antibiotics by newly designed C3N4@ MnFe2O4–graphene nanocomposites. J Hazard Mater 336:81–92
Wang N, Zhao Q, Xu H, Niu W, Ma L, Lan D, Hao L (2018) Adsorptive treatment of coking wastewater using raw coal fly ash: adsorption kinetic, thermodynamics and regeneration by Fenton process. Chemosphere 210:624–632
Wang N, Hu Q, Hao L, Zhao Q (2019) Degradation of acid organic 7 by modified coal fly ash-catalyzed Fenton-like process: kinetics and mechanism study. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:89–100
Yeole K, Kadam P, Mhaske S (2014) Synthesis and characterization of fly ash-zinc oxide nanocomposite. J Mater Res Technol 3:186–190
Zahid M, Nadeem N, Hanif MA, Bhatti IA, Bhatti HN, Mustafa G (2019) Metal ferrites and their graphene-based nanocomposites: synthesis, characterization, and applications in wastewater treatment. In: Zabel H, Farle M (eds) Magnetic nanostructures. Springer, Berlin, pp 181–212
Zhang M, Mao Y, Wang W, Yang S, Song Z, Zhao X (2016) Coal fly ash/CoFe2O4 composites: a magnetic adsorbent for the removal of malachite green from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 6:93564–93574
Zhou Y et al (2016) Photo-Fenton degradation of ammonia via a manganese–iron double-active component catalyst of graphene–manganese ferrite under visible light. Chem Eng J 283:266–275
Acknowledgements
Dr. Muhammad Zahid (corresponding author) is thankful to TWAS for the grant (Grant No. 15-410 under TWAS-COMSTECH Joint Research Grant) to partial purchase of chemicals and equipment being used in this study and the University of Agriculture Faisalabad, Pakistan, for providing the facilities to conduct this research. The authors would also like to acknowledge the Central Resource Laboratory, University of Peshawar and National Textile University Faisalabad to provide the characterization facilities for the composite materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mushtaq, F., Zahid, M., Mansha, A. et al. MnFe2O4/coal fly ash nanocomposite: a novel sunlight-active magnetic photocatalyst for dye degradation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 4233–4248 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02777-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02777-y