Abstract
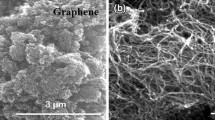
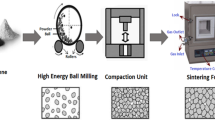
Processing and characterization of graphene (Gr)-reinforced aluminium alloy 7075 (AA7075) microcomposites and nanocomposites are reported in this work. Composites are fabricated by mechanical alloying process at wet conditions. The bulk composites are prepared by uniaxial die pressing to get higher densification and sintered in an inert atmosphere. Density of the nanocomposites is higher than the microcomposites due to the reduction of grain size by increased milling time. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis confirms graphene interaction with the AA7075 matrix lattice spaces. The effective distribution of graphene with aluminium alloy is further confirmed by the Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) analysis. The hardness of the composites proportionally increases with the graphene addition owing to grain refinement. Wear morphology is characterized using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM). Microcomposites reveal abrasive and ploughing wear mechanism of material removal from the surface. Nanocomposites show adhesive wear with delamination and particle pull-out from the material surface.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Das DK, Mishra PC, Singh S, Thakur RK (2014) Properties of ceramic-reinforced aluminium matrix composites—a review. Int J Mech Mat Eng 9:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40712-014-0012-9
Carvalho O, Miranda G, Soares D, Silva FS (2016) Carbon nanotube dispersion in aluminium matrix composites—quantification and influence on strength. Mech Adv Mater Struct 23:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2014.929766
Javadi A, Mirdamadi S, Faghihisani M, Shakhesi S, Soltani R (2013) Well-dispersion of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in aluminum matrix composites by controlling the mixing process. Fullerenes Nanotubes Carbon Nanostruct 21:436–447. https://doi.org/10.1080/1536383X.2011.629758
Min-Feng Y, Laurie O, Dyer MJ, Moloni K, Kelly TF, Ruoff RS (2000) Strength and breaking mechanism of multiwalled carbon nanotubes under tensile load. Science 287:637–640. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5453.637
Dhand V, Rhee KY, Kim HJ, Jung DH (2013) A comprehensive review of graphene nanocomposites: research status and trends. J Nanomater 158:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/763953
Liu J, Fernandez B, Rodriguez P, Naher S, Brabazon D (2016) Powder processing methodology for production of graphene oxide reinforced aluminium matrix composites. Adv Mater Process Technol 2(4):437–450. https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2016.1244389
Seol JH, Jo I, Moore AL, Lindsay L, Aitken ZH, Pettes MT, Li X, Yao Z, Huang R, Broido D, Mingo N, Ruoff RS, Shi L (2010) Two-dimensional phonon transport in supported graphene. Science 328:213–216. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1184014
Balandin AA (2011) Thermal properties of graphene and nanostructured carbon materials. Nat Mater 10:569–581. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3064
Nieto A, Bisht A, Lahiri D, Zhang C, Agarwal A (2017) Graphene reinforced metal and ceramic matrix composites: a review. Int Mater Rev 62:241–302. https://doi.org/10.1080/09506608.2016.1219481
Yu YX (2014) A dispersion-corrected DFT study on adsorption of battery active materials anthraquinone and its derivatives on monolayer graphene and h-BN. J Mater Chem A 2:8910–8917. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta00103f
Yu YX (2014) Binding energy and work function of organic electrode materials phenanthraquinone, pyromellitic dianhydride and their derivatives adsorbed on graphene. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:16267–16275. https://doi.org/10.1021/am504452a
Hu Z, Tong G, Lin D, Chen C, Guo H, Xu J, Zhou L (2016) Graphene-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites—a review. Mater Sci Technol 32:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2015.1104018
Gao C, Zhan B, Chen L, Li X (2017) A micromechanical model of graphene-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites with consideration of graphene orientations. Compos Sci Technol 152:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.09.010
Suthar J, Patel KM (2018) Processing issues, machining and applications of aluminum metal matrix composites. Mater Manuf Process 33:499–527. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1401713
Senthil Saravanan MS, Sivaprasad K, Susila P, Babu K (2011) Anisotropy models in precise crystallite size determination of mechanically alloyed powders. Phys B Condens Matter 406:165–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.10.023
Chu K, Jia C (2014) Enhanced strength in bulk grapheme–copper composites. Physica Status Solidi 211:184–190. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201330051
Zhang J, Chen Z, Zhao J, Jiang Z (2018) Microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminium–graphene composite powders produced by mechanical milling. Mech Adv Mater Mod Process 4:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40759-018-0037-5
Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Dommett GH, Kohlhaas KM, Zimney EJ, Stach EA, Piner RD, Nguyen ST, Ruoff RS (2006) Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 442:282–286. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04969
Prashantha Kumar HG, Anthony Xavior M (2017) Encapsulation and microwave hybrid processing of Al 6061-graphene-sic composites. Mater Manuf Process 33:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1279320
Naseer A, Ahmad F, Aslam M, Guan BH, Harun WSW, Muhamad N, Rafi Raza M, German RM (2019) A review of processing techniques for graphene-reinforced metal matrix composites. Mater Manuf Process 34:957–985. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2019.1615080
Bains PS, Sidhu SS, Payal HS (2015) Fabrication and machining of metal matrix composites: a review. Mater Manuf Process 31:553–573. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1025976
Sahoo B, Joseph J, Sharma A, Paul J (2016) Surface modification of aluminium by graphene impregnation. Mater Des 116:51–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.11.075
Raveen R, Yoganandh J, Sathieshkumar S, Neelakandeswari N (2019) Preparation and characterization of pulsed electrodeposited cobalt–graphene nanocomposite coatings. J Mater Des Appl 233:2469–2477. https://doi.org/10.1177/1464420719863462
Sharma P, Sharma S, Khanduja D (2015) On the use of ball milling for the production of ceramic powders. Mater Manuf Process 30:1370–1376. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1037904
Toozandehjani M, Matori KA, Ostovan F, Aziz SA, Mamat MS (2017) Effect of milling time on the microstructure, physical and mechanical properties of Al-Al2O3 nanocomposite synthesized by ball milling and powder metallurgy. Materials 10:1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10111232
German RM (2016) Sintering simplified: surface area, density, and grain size relations. Mater Sci Forum 835:50–75. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.835.50
Bastwros M, Kim GY, Zhu C, Zhang K, Wang S, Tang X, Wang X (2014) Effect of ball milling on graphene reinforced Al6061 composite fabricated by semi-solid sintering. Compos Part B Eng 60:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.12.043
Prabhu B, Suryanarayana C, An L, Vaidyanathan R (2006) Synthesis and characterization of high-volume fraction Al–Al2O3 nanocomposite powders by high-energy milling. Mater Sci Eng A 425:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.03.066
Torchynska TV, Filali BE (2017) Emission, defects, and structure of ZnO nanocrystal films obtained by electrochemical method Chapter 4. In: Thirumalai J (ed) Thin film processes—artifacts on surface phenomena and technological facets. InTech, London, pp 55–87. https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2017.344
Ipaz L, Aperador W, Caicedo J, Esteve J, Zambrano G (2012) A practical application of X-ray spectroscopy in Ti-Al-N and Cr-Al-N thin films chapter 2. In: Sharma SK (ed) X-ray spectroscopy. InTech, London, pp 21–38. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.4534.5123
Namazu. T (2008) Uniaxial Tensile Test for MEMS Materials. Chapter 4. In: Advanced Micro and Nanosystems; Reliability of MEMS, Wiley-VCH Verlag, Germany, pp 123–161. doi: 10.1002/9783527622139.ch4
Zheng R, Hao X, Yuan Y, Wang Z, Ameyama K, Ma C (2013) Effect of high volume fraction of B4C particles on the microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy based composites. J Alloy Comp 576:291–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.04.141
Rashad M, Pan F, Tang A, Asif M (2014) Effect of graphene nanoplatelets addition on mechanical properties of pure aluminum using a semi-powder method. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 24:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2014.03.012
Meyers MA, Mishra A, Benson DJ (2006) Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials. Prog Mater Sci 51:427–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2005.08.003
Archard JF (1953) Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J Appl Phys 24:981–988. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1721448
Sekhar R, Singh TP (2015) Mechanisms in turning of metal matrix composites: a review. J Mater Res Technol 4:197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2014.10.013
Zhang C, Yao D, Yin J, Zuo K, Xia Y, Liang H, Zeng Y (2019) Effects of β-Si3N4 whiskers addition on mechanical properties and tribological behaviors of Al matrix composites. Wear 430–431:145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2019.05.003
Liu ZY, Wang QZ, Xiao BL, Ma ZY (2010) Clustering model on the tensile strength of PM processed SiCp/Al composites. Compos Appl Sci Manuf 41:1686–1692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2010.08.007
Bastwros MH, Esawi AMK, Wifi A (2013) Friction and wear behaviour of Al–CNT composites. Wear 307:164–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2013.08.021
Adegbenjo AO, Obadele BA, Olubambi PA (2018) Densification, hardness and tribological characteristics of MWCNTs reinforced Ti6Al4V compacts consolidated by spark plasma sintering. J Alloy Comp 749:818–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.373
Diler EA, Ipek R (2013) Main and interaction effects of matrix particle size, reinforcement particle size and volume fraction on wear characteristics of Al-SiCp composites using central composite design. Compos Part B 50:371–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.02.001
Gao X, Yue H, Guo E, Zhang S, Wang B, Guan E, Song S, Zhang H (2018) Preparation and tribological properties of homogeneously dispersed graphene-reinforced aluminium matrix composites. Mater Sci Technol 34:1316–1322. https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2018.1446869
Khan MM, Dixit G (2017) Abrasive wear characteristics of silicon carbide particle reinforced zinc-based composite. Silicon India 10:1315–1327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9607-0
Chi H, Jiang L, Chen G, Qiao J, Lin X, Wu G (2016) The tribological behavior evolution of TiB2/Al composites from running-in stage to steady stage. Wear 368–369:304–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2016.10.003
Seenuvasaperumala AEP, Jayavel R (2017) Influence of calcium hexaboride reinforced magnesium composite for the mechanical and tribological behaviour. Tribol Int 111:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.02.042
Khun NW (2015) Scratch-induced wear behavior of aluminum alloy under dry and wet conditions. J Mechatron 3:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1166/jom.2015.1119
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj, R.R., Yoganandh, J., Saravanan, M.S.S. et al. Effect of graphene addition on the mechanical characteristics of AA7075 aluminium nanocomposites. Carbon Lett. 31, 125–136 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-020-00157-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-020-00157-7