Abstract
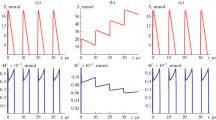
A kinetic model describing the dynamics of synaptic “discharge” taking into account the kinetics of the injection of the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft, the pH-dependence of the catalytic activity of the enzyme, and diffusion withdrawal of protons is proposed. The model provides a physicochemical explanation for a number of important physiological phenomena, such as the neuromuscular paralysis, the molecular mechanism of neurological memory, and the effect of some neurotoxins and drugs.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Varfolomeev, S.D., Semenova, N.A., Bykov, V.I., et al., Kinetics of chemical processes in the human brain. Modeling of the BOLD-signal at f-MRT research, Dokl. Akad. Nauk, 2019, vol. 488, no. 2, pp. 39–43.
Varfolomeev, S.D., Semenova, N.A., Ublinskiy, M.V., et al., fMRI and MR-spectroscopy in research on triggering and autostabilization of N-acetylaspartate, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2019, vol. 729, pp. 84–91.
Sergeev, P.V., Shimanovskii, N.L., and Petrov, V.N., Retseptory fiziologicheski aktivnykh veshchestv (Receptors of Physiologically Active Compounds), 2nd ed., Volgograd: Sem’ Vetrov; 1999.
Rozengart, E.V., Basova, N.E., Moralev, S.N., et al., Research on cholinesterases in the Soviet Union and Russia: a historical perspective, Chem.-Biol. Interact., 2013, vol. 203, no. 1, pp. 3–9.
Rosenberry, T.L., Mallender, W.D., Thomas, P.J., et al., A steric blockade model for inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by peripheral site ligands and substrate, Chem.-Biol. Interact., 1999, vol. 119–120, pp. 85–97.
Hasselmo, M.E., The role of acetylcholine in learning and memory, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 2006, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 710–715.
Titov, S.A., Neurochemical bases of memory, in Neirokhimiya (Neurochemistry), Ashmarin, I.P., Stukalov, P.V., and Eshchenko, N.D., Eds., Moscow: Inst. Biomed. Khim. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk, 1996, pp. 370–414.
Lushchekina, S.V., Schopfer, L.M., Grigorenko, B.L., et al., Optimization of cholinesterase-based catalytic bioscavengers against organophosphorus agents, Front. Pharmacol., 2018, vol. 9, no. 211, pp. 1–13.
Nemukhin, A.V., Kulakova, A.M., Lushchekina, S.V., et al., Simulation of chemical reactions in the active centers of cholinesterase by quantum theory methods, Vestn. Mosk. Univ., Ser. 2:Khim., 2015, vol. 56, no. 6, pp. 343–347.
Nemukhin, A.V., Grigorenko, B.L., Morozov, D.I., et al., On quantum mechanical-molecular mechanical (QM/MM) approaches to model hydrolysis of acetylcholine by acetylcholinesterase, Chem.-Biol. Interact., 2013, vol. 203, no. 1, pp. 51–56.
Lushchekina, S., Gubaydullina, A., Polomskih, V., et al., QM/MM of ChE-catalyzed reactions with special attention to OP inhibition, FEBS J., 2013, vol. 280, suppl. 1, pp. 164–174.
Reed, M.C., Lieb, A., and Nijhout, H.F., The biological significance of substrate inhibition: a mechanism with diverse functions, BioEssays, 2010, vol. 32, pp. 422–429.
Tai, K., Bond, S.D., MacMillan, H.R., et al., Finite element simulations of acetylcholine diffusion in neuromuscular junctions, Biophys. J., 2003, vol. 84, no. 4, pp. 2234–2241.
Aidoo, A. and Ward, K., Spatio-temporal concentration of acetylcholine in vertebrate synaptic cleft, Math. Comp. Model., 2006, vol. 44, pp. 952–962.
Middendorf, H.D., Di Cola, D., Cavatorta, F., et al., Water dynamics in charged and uncharged polysaccharide gels by quasi-elastic neutron scattering, Biophys. Chem., 1994, vol. 47, pp. 145–153.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 18-13-00030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by M. Batrukova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varfolomeev, S.D., Bykov, V.I. & Tsybenova, S.B. Kinetics of Chemical Processes in the Human Brain. Proton Blockade of Acetylcholinesterase and pH-Impulse in the Mechanism of Functioning of the Cholinergic Synapse. Dokl Biochem Biophys 491, 85–88 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672920020155
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672920020155