Abstract
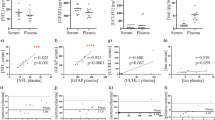
Dopaminergic nigrostriatal denervation and widespread intracellular α-synuclein accumulation are neuropathologic hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease (PD). A constellation of peripheral processes, including metabolic and inflammatory changes, are thought to contribute to neurodegeneration. In the present study, we sought to obtain insight into the multifaceted pathophysiology of PD through the application of a multi-marker discovery approach. Fifty older adults aged 70+, 20 with PD and 30 age-matched controls were enrolled as part of the EXosomes in PArkiNson Disease (EXPAND) study. A panel of 68 circulating mediators of inflammation, neurogenesis and neural plasticity, and amino acid metabolism was assayed. Biomarker selection was accomplished through sequential and orthogonalized covariance selection (SO-CovSel), a multi-platform regression method developed to handle highly correlated variables organized in multi-block datasets. The SO-CovSel model with the best prediction ability using the smallest number of variables was built with seven biomolecules. The model allowed correct classification of 94.2 ± 3.1% participants with PD and 100% controls. The biomarker profile of older adults with PD was defined by higher circulating levels of interleukin (IL) 8, macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1β, phosphoethanolamine, and proline, and by lower concentrations of citrulline, IL9, and MIP-1α. Our innovative approach allowed identifying and evaluating the classification performance of a set of potential biomarkers for PD in older adults. Future studies are warranted to establish whether these biomolecules could serve as biomarkers for PD as well as unveil new targets for interventions.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmadi Rastegar D, Ho N, Halliday GM, Dzamko N. Parkinson’s progression prediction using machine learning and serum cytokines. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2019;5:14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41531-019-0086-4.
Alecu I, Bennett SAL. Dysregulated lipid metabolism and its role in α-synucleinopathy in Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:328. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00328.
Antonini A, Abbruzzese G, Ferini-Strambi L, Tilley B, Huang J, Stebbins GT, et al. Validation of the Italian version of the Movement Disorder Society--unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale. Neurol Sci. 2013;34:683–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-1112-z.
Beck GC, Brinkkoetter P, Hanusch C, et al. Clinical review: immunomodulatory effects of dopamine in general inflammation. Crit Care. 2004;8:485–91. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc2879.
Biancolillo A, Næs T. The sequential and orthogonalized PLS regression for multiblock regression. In: Cocchi M, editor. Data fusion methodology and applications, vol. 31. Amsterdam: Elsevier Inc.; 2019. p. 157–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63984-4.00006-5.
Biancolillo A, Marini F, Roger J. SO-CovSel: a novel method for variable selection in a multiblock framework. J Chemom. 2019:e3120. https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.3120.
Breuillard C, Cynober L, Moinard C. Citrulline and nitrogen homeostasis: an overview. Amino Acids. 2015;47:685–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-1932-2.
Caldwell RB, Toque HA, Narayanan SP, Caldwell RW. Arginase: an old enzyme with new tricks. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2015;36:395–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2015.03.006.
Calvani R, Picca A, Marini F, et al. A distinct pattern of circulating amino acids characterizes older persons with physical frailty and sarcopenia: results from the BIOSPHERE study. Nutrients. 2018;10:1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111691.
Calzada E, Onguka O, Claypool SM. Phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2016;321:29–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ircmb.2015.10.001.
Chen R, Snyder M. Promise of personalized omics to precision medicine. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2013;5:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/WSBM.1198.
Chen-Plotkin AS, Albin R, Alcalay R, et al. Finding useful biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10:eaam6003. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aam6003.
Collins LM, Toulouse A, Connor TJ, Nolan YM. Contributions of central and systemic inflammation to the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology. 2012;62:2154–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.01.028.
Davidson WS, Jonas A, Clayton DF, George JM. Stabilization of alpha-synuclein secondary structure upon binding to synthetic membranes. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:9443–9. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.16.9443.
Deleidi M, Gasser T. The role of inflammation in sporadic and familial Parkinson’s disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70:4259–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1352-y.
Dickson DW. Neuropathology of Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2018;46:S30–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.07.033.
Elyaman W, Khoury SJ. Th9 cells in the pathogenesis of EAE and multiple sclerosis. Semin Immunopathol. 2017;39:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-016-0604-y.
Elyaman W, Bradshaw EM, Uyttenhove C, Dardalhon V, Awasthi A, Imitola J, et al. IL-9 induces differentiation of TH17 cells and enhances function of FoxP3+ natural regulatory T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:12885–90. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0812530106.
Emamzadeh FN, Surguchov A. Parkinson’s disease: biomarkers, treatment, and risk factors. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:612. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00612.
Figura M, Kuśmierska K, Bucior E, Szlufik S, Koziorowski D, Jamrozik Z, et al. Serum amino acid profile in patients with Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0191670. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191670.
GBD 2015 Neurological Disorders Collaborator Group. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders during 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16:877–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30299-5.
GBD 2016 Parkinson’s Disease Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:939–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30295-3.
Giunta S. Is inflammaging an auto[innate]immunity subclinical syndrome? Immun Ageing. 2006;3:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4933-3-12.
Grozdanov V, Bliederhaeuser C, Ruf WP, Roth V, Fundel-Clemens K, Zondler L, et al. Inflammatory dysregulation of blood monocytes in Parkinson’s disease patients. Acta Neuropathol. 2014;128:651–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1345-4.
Hatano T, Saiki S, Okuzumi A, et al. Identification of novel biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease by metabolomic technologies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2016;87:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2014-309676.
Havelund JF, Andersen AD, Binzer M, Blaabjerg M, Heegaard NHH, Stenager E, et al. Changes in kynurenine pathway metabolism in Parkinson patients with L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. J Neurochem. 2017;142:756–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14104.
He R, Yan X, Guo J, Xu Q, Tang B, Sun Q. Recent advances in biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:305. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00305.
Hou Y, Dan X, Babbar M, Wei Y, Hasselbalch SG, Croteau DL, et al. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15:565–81. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-019-0244-7.
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992;55:181–4. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.55.3.181.
Justice JN, Ferrucci L, Newman AB, Aroda VR, Bahnson JL, Divers J, et al. A framework for selection of blood-based biomarkers for geroscience-guided clinical trials: report from the TAME Biomarkers Workgroup. GeroScience. 2018;40:419–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-018-0042-y.
Kim R, Kim H-J, Kim A, Jang M, Kim A, Kim Y, et al. Peripheral blood inflammatory markers in early Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Neurosci. 2018;58:30–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2018.10.079.
Kori M, Aydln B, Unal S, et al. Metabolic biomarkers and neurodegeneration: a pathway enrichment analysis of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. OMICS. 2016;20:645–61. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2016.0106.
Kulisevsky J, Oliveira L, Fox SH. Update in therapeutic strategies for Parkinsonʼs disease. Curr Opin Neurol. 2018;31:439–47. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0000000000000579.
Kustrimovic N, Comi C, Magistrelli L, Rasini E, Legnaro M, Bombelli R, et al. Parkinson’s disease patients have a complex phenotypic and functional Th1 bias: cross-sectional studies of CD4+ Th1/Th2/T17 and Treg in drug-naïve and drug-treated patients. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15:205. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1248-8.
Lashuel HA, Overk CR, Oueslati A, Masliah E. The many faces of α-synuclein: from structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013;14:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3406.
LeWitt PA, Li J, Lu M, Guo L, Auinger P, Parkinson Study Group–DATATOP Investigators. Metabolomic biomarkers as strong correlates of Parkinson disease progression. Neurology. 2017;88:862–9. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003663.
Loscalzo J, Barabasi A-L. Systems biology and the future of medicine. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2011;3:619–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/wsbm.144.
Martinez-Martin P. Hoehn and Yahr staging scale. In: Kompoliti K, Verhagen Metman L, editors. Encyclopedia of movement disorders. Amsterdam: Elsevier Inc.; 2010. p. 23–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-374105-9.00034-4.
Marzetti E, Picca A, Marini F, Biancolillo A, Coelho-Junior HJ, Gervasoni J, et al. Inflammatory signatures in older persons with physical frailty and sarcopenia: the frailty “cytokinome” at its core. Exp Gerontol. 2019;122:129–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2019.04.019.
Mercado NM, Collier TJ, Sortwell CE, Steece-Collier K. BDNF in the aged brain: translational implications for Parkinson’s disease. Austin Neurol Neurosci. 2017;2:1021.
Okazawa H, Murata M, Watanabe M, Kamei M, Kanazawa I. Dopaminergic stimulation up-regulates the in vivo expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the striatum. FEBS Lett. 1992;313:138–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(92)81430-t.
Patel D, Witt SN. Ethanolamine and phosphatidylethanolamine: partners in health and disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:4829180. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4829180.
Pattarini R, Smeyne RJ, Morgan JI. Temporal mRNA profiles of inflammatory mediators in the murine 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrimidine model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. 2007;145:654–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.12.030.
Perrin FE, Lacroix S, Avilés-Trigueros M, David S. Involvement of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha and interleukin-1beta in Wallerian degeneration. Brain. 2005;128:854–66. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh407.
Picca A, Calvani R, Landi G, Marini F, Biancolillo A, Gervasoni J, et al. Circulating amino acid signature in older people with Parkinson’s disease: a metabolic complement to the EXosomes in PArkiNson Disease (EXPAND) study. Exp Gerontol. 2019a;128:110766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2019.110766.
Picca A, Coelho-Junior HJ, Cesari M, Marini F, Miccheli A, Gervasoni J, et al. The metabolomics side of frailty: toward personalized medicine for the aged. Exp Gerontol. 2019b;126:110692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2019.110692.
Picca A, Guerra F, Calvani R, et al. Mitochondrial-derived vesicles as candidate biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease: rationale, design and methods of the EXosomes in PArkiNson Disease (EXPAND) study. Int J Mol Sci. 2019c;20:2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102373.
Picca A, Ponziani FR, Calvani R, et al. Gut microbial, inflammatory and metabolic signatures in older people with physical frailty and sarcopenia: results from the BIOSPHERE study. Nutrients. 2019d;12:65. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010065.
Picca A, Guerra F, Calvani R, et al. Mitochondrial signatures in circulating extracellular vesicles of older adults with Parkinson’s disease: results from the EXosomes in PArkiNson’s Disease (EXPAND) study. J Clin Med. 2020;9:504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020504.
Poewe W, Seppi K, Tanner CM, et al. Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2017;3:17013. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.13.
Posavi M, Diaz-Ortiz M, Liu B, Swanson CR, Skrinak RT, Hernandez-Con P, et al. Characterization of Parkinson’s disease using blood-based biomarkers: a multicohort proteomic analysis. PLoS Med. 2019;16:e1002931. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002931.
Qin X-Y, Zhang S-P, Cao C, Loh YP, Cheng Y. Aberrations in peripheral inflammatory cytokine levels in Parkinson disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2016;73:1316–24. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.2742.
Rahmani F, Saghazadeh A, Rahmani M, Teixeira AL, Rezaei N, Aghamollaii V, et al. Plasma levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with Parkinson disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Res. 2019;1704:127–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.10.006.
Reale M, Iarlori C, Thomas A, et al. Peripheral cytokines profile in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav Immun. 2009;23:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2008.07.003.
Saresella M, Calabrese E, Marventano I, et al. Increased activity of Th-17 and Th-9 lymphocytes and a skewing of the post-thymic differentiation pathway are seen in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Behav Immun. 2011;25:539–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2010.12.004.
Scalzo P, Kümmer A, Bretas TL, Cardoso F, Teixeira AL. Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor correlate with motor impairment in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. 2010;257:540–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5357-2.
Sommer A, Winner B, Prots I. The Trojan horse-neuroinflammatory impact of T cells in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurodegener. 2017;12:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-017-0222-8.
Sprott RL. Biomarkers of aging and disease: introduction and definitions. Exp Gerontol. 2010;45:2–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2009.07.008.
Stoessel D, Schulte C, Teixeira dos Santos MC, et al. Promising metabolite profiles in the plasma and CSF of early clinical Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00051.
Tomlinson CL, Stowe R, Patel S, Rick C, Gray R, Clarke CE. Systematic review of levodopa dose equivalency reporting in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2010;25:2649–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23429.
van der Veen JN, Kennelly JP, Wan S, Vance JE, Vance DE, Jacobs RL. The critical role of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017;1859:1558–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.04.006.
Yabuki Y, Shioda N, Yamamoto Y, Shigano M, Kumagai K, Morita M, et al. Oral l-citrulline administration improves memory deficits following transient brain ischemia through cerebrovascular protection. Brain Res. 2013;1520:157–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2013.05.011.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by Innovative Medicine Initiative-Joint Undertaking (IMI-JU no. 115621), the non-profit research foundation “Centro Studi Achille e Linda Lorenzon,” and by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES; Finance Code 001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.P. and R.C. conceived and developed the study. A.R.B., H.J.C.-J., G.L., and M.R.L.M. coordinated participant recruitment and assessment. A.A., J.G., S.P., and A.Pr. developed and conducted metabolomics analysis. M.B. and A.P. performed immunoassays for cytokine quantification. A.B. and F.M. developed and packaged MATLAB scripts for the SO-CovSel algorithm. R.B., M.C., E.M., and A.U. contributed critical input towards study design and manuscript development. All authors edited and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The study was conducted in agreement with legal requirements and international norms (Declaration of Helsinki 1964). The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Rome, Italy (protocol no. 0045298/17).
Consent to participate
Prior to enrolment, all participants provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(XLSX 29 kb)
About this article
Cite this article
Calvani, R., Picca, A., Landi, G. et al. A novel multi-marker discovery approach identifies new serum biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease in older people: an EXosomes in PArkiNson Disease (EXPAND) ancillary study. GeroScience 42, 1323–1334 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-020-00192-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-020-00192-2