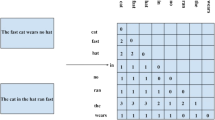
Abstract
Sentiment analysis, an application of machine learning in business is the process of identifying and cataloging comments, reviews, tweets, feedback, and even random rants according to the tone or sentiments conveyed by it. The data is analysed using machine learning approach of Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) rating the sentiments on a scale ranging from −100 to 100. A new proposed activation function is used for LSTM giving best results as compared to the existing Artificial Neural Network (ANN) techniques. Depending upon the mined opinion, the business intelligence tools evaluate the products or services of a company eventually resulting in the increase of the sales of that company. The results clearly show that BI extracted from SA is quite instrumental in driving business effectiveness and innovation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adventures of Don Quixote de la Mancha. (2018, August 08) url:https://play.google.com/store/books/details/Miguel_de_Cervantes_Saavedra_Adventures_of_Don_Qui?id=_6YZAAAAYAAJ&showAllReviews=true.
Agarap AF, Grafilon P (2018) Statistical analysis on E-commerce reviews, with sentiment classification using bidirectional recurrent neural network (RNN). arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.03687
Ain QT, Ali M, Riaz A, Noureen A, Kamran M, Hayat B, Rehman A (2017) Sentiment analysis using deep learning techniques: a review. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 8(6):424
Chen H, Chiang RH, Storey VC (2012) Business intelligence and analytics: from big data to big impact. MIS Q 36(4):1165
Customer Review (2018, August 06) Amazon.com reviews, customer review. url:https://www.amazon.com/gp/customer-reviews/R2VHSIW4YVZWRR/ ref=cm_cr_arp_d_rvw_ttl?ie=UTF8&ASIN=B01F3KV47E.
Customer Review (2018, August 06) Amazon.com reviews, customer review. url:https://www.amazon.com/gp/customer-reviews/R3T81JTO3RJDJR/ ref=cm_cr_arp_d_rvw_ttl?ie=UTF8&ASIN=B009PN70AQ
Customer Review (2018, August 06) Amazon.com reviews, customer review. url:https://www.amazon.com/gp/customer-reviews/R39PGHD1HK1CIR/ ref=cm_cr_arp_d_rvw_ttl?ie=UTF8&ASIN=B010TWAU2Q.
Daassi-Gnaba H, Oussar Y (2015) External vs. internal svm-rfe: the svm-rfe method revisited and applied to emotion recognition. Neural Network World 25(1):75
Dr. Batra's Hair Fall Control Shampoo, 200ml. (2018, June 25), Review url:https://www.amazon.in/Dr- Batras-Control-Shampoo-200ml/product-reviews/B01N290KTP/.
Dr. Batra's Hair Fall Control Shampoo, 200ml. (2018, June 25), Review url:https://www.snapdeal.com/product/dr-batras-hair-fall- control/635480126010
Dr. Batra's Hair Fall Control Shampoo,oil 200 ml. (2018, June 25), Review url:https://www.flipkart.com/dr-batra-s-hair-fall-control-shampoo-oil-200-ml/product-reviews/itmf3xfvcqyjfwzw?pid=SMPESY43MWZ397YQ.
Ebadati OME, Mortazavi MT (2018) An efficient hybrid machine learning method for time series stock market forecasting. Neural Network World 28(1):41–55
Ebrahimi M, Yazdavar AH, Sheth A (2017) Challenges of sentiment analysis for dynamic events. IEEE Intell Syst 32(5):70–75
Fang X, Zhan J (2015) Sentiment analysis using product review data. Journal of Big Data 2(1):5
Feyzbakhsh SA, Matsui M (1999, October) Adam-eve genetic algorithm as a function optimizer. In IEEE SMC'99 Conference Proceedings. 1999 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (Cat. No. 99CH37028) (Vol. 1, pp. 613-624). IEEE
Gers FA, Schmidhuber E (2001) LSTM recurrent networks learn simple context-free and context-sensitive languages. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12(6):1333–1340
Gers FA, Schmidhuber J, Cummins F (1999) Learning to forget: continual prediction with LSTM
Gupta, S. (2018, August 06) Applications of sentiment analysis in business. Url: https://dzone.com/articles/applications-of-sentiment-analysis-in-business.
He R, McAuley J (2016, April) Ups and downs: modeling the visual evolution of fashion trends with one-class collaborative filtering. In proceedings of the 25th international conference on world wide web (pp. 507-517). International world wide web conferences steering committee
Hochreiter S (1998) The vanishing gradient problem during learning recurrent neural nets and problem solutions. International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems 6(02):107–116
Huang JP, Wang XA, Zhao Y, Xin C, Xiang H (2018) Large earthquake magnitude prediction in Taiwan based on deep learning neural network. Neural Network World 28(2):149–160
Ilayaraja S (2018, June 26) ilayaraja97/keras-contrib: Keras community contributions url:https://github.com/ilayaraja97/keras-contrib
Jadav BM, Vaghela VB (2016) Sentiment analysis using support vector machine based on feature selection and semantic analysis. International Journal of Computer Applications, 146(13)
Maas AL, Daly RE, Pham PT, Huang D, Ng AY, Potts C (2011, June) Learning word vectors for sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics: Human language technologies-volume 1 (pp. 142-150). Association for Computational Linguistics
MajorLeagueJesus (2018, June 26) Rreview Counter-Strike: Global Offensive url:https://steamcommunity.com/id/MajorLeagueJesus/recommended/730/.
Mautner P, Moucek R (2012) Processing and categorization of Czech written documents using neural networks. Neural Network World 22(1):53–66
Mikolov T, Chen K, Corrado G, Dean J (2013) Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781
Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado GS, Dean J (2013) Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 3111-3119)
Pennington J, Socher R, Manning C (2014, October) Glove: global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP) (pp. 1532-1543)
Plaza L, de Albornoz JC (2012) Sentiment analysis in business intelligence: a survey. In Customer Relationship Management and the Social and Semantic Web: Enabling Cliens Conexus (pp. 231-252). IGI global
Pulver A, Lyu S (2017, May) LSTM with working memory. In 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (pp. 845-851). IEEE
Saggion H, Funk A (2009) Extracting opinions and facts for business intelligence. RNTI Journal, E (17), 119, 146
Seibold M, Jacobs D, Kemper A (2012) Operational business intelligence: processing mixed workloads. It Professional 15(5):16–21
Singh B, Kushwaha N, Vyas OP (2016, November) An interpretation of sentiment analysis for enrichment of business intelligence. In 2016 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON) (pp. 18-23). IEEE
Standard search API – Twitter (2018, June 28) Twitter, url:https://www.developer.twitter.com/en/docs/tweets/search/api-reference/get-search-tweets.
Taboada M, Brooke J, Tofiloski M, Voll K, Stede M (2011) Lexicon-based methods for sentiment analysis. Computational linguistics 37(2):267–307
The Homoeopathic Clinic by Dr. Riyanka Bhardwaj- Homeopathy Doctor in Greater Noida. (2018, August 08) url:https://www.google.com/search?q=The+Homoeopathic+Clinic+by+Dr.+Riyanka+Bhardwaj-+Homeopathy+Doctor+in+Greater+Noida+reviews.
Xie Z (2012, October) A non-linear approximation of the sigmoid function based on FPGA. In 2012 IEEE Fifth International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI) (pp. 221-223). IEEE
Acknowledgments
The authors are sincerely thankful to the potential reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sreesurya, I., Rathi, H., Jain, P. et al. Hypex: A Tool for Extracting Business Intelligence from Sentiment Analysis using Enhanced LSTM. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 35641–35663 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08930-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08930-6