Abstract
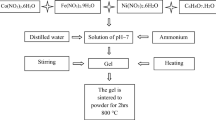
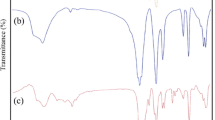
In this study, the effect of vanadium addition on the structural and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite (Co1−xVxFe2O4; where x = 0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20, and 0.25) prepared by a novel sol–gel autocombustion method was investigated. The formation of cubic spinel structure (space group Fd3m) was confirmed by X-ray diffraction in combination of Rietveld structure refinement analysis and transform infrared spectroscopic spectrum (FT-IR) analyses. Also, phase and elemental analyses confirmed that an inevitable secondary phase of hematite along with the spinel phase appears by addition of vanadium; therefore, a nanocomposite was formed in the sample containing vanadium. However, the SEM observations in combination of the results obtained by Rietveld structure refinement analysis showed that the presence of vanadium can affect the size of synthesized cobalt ferrite. VSM measurements showed that saturation magnetization and coercivity values are strongly dependent on the vanadium content and particle size, so that the maximum value of coercivity was obtained equal to ~916 Oe for Co0.85V0.15Fe2O4.

Highlights
-
Effect of vanadium ions addition on the magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite.
-
Effect of adding these ions on morphology and agglomeration of the nanoparticles.
-
The evolution of structural properties by using the Rietveld method.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shobana MK, Kwon H, Choe H (2012) Structural studies on the yttrium-doped cobalt ferrite powders synthesized by sol-gel combustion method. J Magn Magn Mater 324:2245–2248
Afshari M, Rouhani Isfahani A, Hasani S, Davar F, Jahanbani Ardakani K (2019) Effect of apple cider vinegar agent on the microstructure, phase evolution, and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Int J Appl Ceram Technol 16:1612–1621
Xie T, Xu L, Liu C (2012) Synthesis and properties of composite magnetic material SrCoxFe12-xO 19 (x=0-0.3). Powder Technol 232:87–92
Rouhani AR, Esmaeil‐Khanian AH, Davar F, Hasani S (2018) The effect of agarose content on the morphology, phase evolution, and magnetic properties of CoFe 2 O 4 nanoparticles prepared by sol‐gel autocombustion method. Int J Appl Ceram Technol 15:758–765
Ayyappan S, Philip J, Raj B (2009) A facile method to control the size and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys 115:712–717
Meng X et al. (2009) Mössbauer study of cobalt ferrite nanocrystals substituted with rare-earth Y3+ions. J Magn Magn Mater 321:1155–1158
Mohamed RM, Rashad MM, Haraz FA, Sigmund W (2010) Structure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite powders synthesized using organic acid precursor method. J Magn Magn Mater 332:2058–2064
Zubair A et al. (2017) Structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Eu-doped CoFe2O4nano-ferrites. Results Phys 7:3203–3208
Senthil VP et al. (2018) Study of structural and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanostructures. Chem Phys Lett 695:19–23
Lima AC et al. (2015) The effect of Sr2+ on the structure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. Mater Lett 145:56–58
Sharifi I, Shokrollahi H (2012) Nanostructural, magnetic and Mössbauer studies of nanosized Co1-xZnxFe2O4synthesized by co-precipitation. J Magn Magn Mater 324:2397–2403
Gabal MA, Al-Juaid AA, El-Rashed S, Hussein MA (2017) Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized CoFe2O4via facile methods: a comparative study. Mater Res Bull 89:68–78
Amiri S, Shokrollahi H (2013) The role of cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles in medical science. Mater Sci Eng C 33:1–8
Chae KP, Lee JG, Kim WK, Lee YB (2002) Magnetic properties of ti-doped CoFe2O4 films. J Magn Magn Mater 248:236–240
Ansari SM et al. (2018) Controlled surface/interface structure and spin enabled superior properties and biocompatibility of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 459:788–801
Amiri S, Shokrollahi H (2013) Magnetic and structural properties of RE doped Co-ferrite (RE=Nd, Eu, and Gd) nano-particles synthesized by co-precipitation. J Magn Magn Mater 345:18–23
Sharifi I, Shokrollahi H, Doroodmand MM, Safi R (2012) Magnetic and structural studies on CoFe 2O 4 nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation, normal micelles and reverse micelles methods. J Magn Magn Mater 324:1854–1861
Chae KP, Lee JG, Kweon HS, Lee YB (2004) The crystallographic, magnetic properties of Al, Ti doped CoFe2O4powders grown by sol-gel method. J Magn Magn Mater 283:103–108
Sanpo N, Wang J, Berndt CC (2013) Sol-gel synthesized copper-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J Nano Res 22:95–106
Ji G, Tang S, Xu B, Gu B, Du Y (2003) Synthesis of CoFe2O4 nanowire arrays by sol-gel template method. Chem Phys Lett 379:484–489
Toksha BG, Shirsath SE, Patange SM, Jadhav KM (2008) Structural investigations and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel auto combustion method. Solid State Commun 147:479–483
Patankar KK, Ghone DM, Mathe VL, Kaushik SD (2018) Structural and physical property study of sol–gel synthesized CoFe2-xHoxO4 nano ferrites. J Magn Magn Mater 454:71–77
Ramakrishna A, Murali N, Mammo TW, Samatha K, Veeraiah V (2018) Structural and DC electrical resistivity, magnetic properties of Co0.5M0.5Fe2O4(M = Ni, Zn, and Mg) ferrite nanoparticles. Phys B Condens Matter 534:134–140
Sajjia M, Benyounis KY, Olabi AG (2012) The simulation and optimization of heat treatment of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by the sol–gel technique. Powder Technol 222:143–151
Mund HS, Ahuja BL (2017) Structural and magnetic properties of Mg doped cobalt ferrite nano particles prepared by sol-gel method. Mater Res Bull 85:228–233
Gowreesan S, Kumar AR (2018) Synthesis, structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of spinel structure of Ca2+substitute in Cobalt ferrites (Co1−xCaxFe2O4). Chin J Phys 56:1262–1272
Kumar R, Kar M (2016) Lattice strain induced magnetism in substituted nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 416:335–341
Ghasemi A (2015) Compositional dependence of magnetization reversal mechanism, magnetic interaction and Curie temperature of Co1-xSrxFe2O4 spinel thin film. J Alloy Compd 645:467–477
Chae KP, Kim WK, Lee JG, Lee YB (2001) Magnetic properties of Ti-doped ultrafine CoFe2O4 powder grown by the sol gel method. Hyperfine Interact 136–137:65–72
Heiba ZK, Mohamed MB, Ahmed SI (2017) Cation distribution correlated with magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles defective by vanadium doping. J Magn Magn Mater 441:409–416
Balavijayalakshmi J, Sudha T (2017) Effect of Cr3+ substitution on structural and magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles. Springe Proc Phys 189:289–297
Ansari MMN, Khan S (2017) Structural, electrical and optical properties of sol-gel synthesized cobalt substituted MnFe2O4nanoparticles. Phys B Condens Matter 520:21–27
Mozaffari M, Amighian J, Darsheshdar E (2014) Magnetic and structural studies of nickel-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles, synthesized by the sol-gel method. J Magn Magn Mater 350:19–22
Chandra Sekhar B et al. (2016) Magnetic and magnetostrictive properties of Cu substituted Co-ferrites. J Magn Magn Mater 398:59–63
Yadav RS et al. (2015) Magnetic properties of Co1−x Znx Fe2 O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by starch-assisted sol–gel autocombustion method and its ball milling. J Magn Magn Mater 378:190–199
Ben Ali M et al. (2016) Effect of zinc concentration on the structural and magnetic properties of mixed Co-Zn ferrites nanoparticles synthesized by sol/gel method. J Magn Magn Mater 398:20–25
Zandi Khajeh MA, Shokrollahi H, Avazpour L, Toroghinejad MR (2015) Study on the effect of sol–gel parameters using the Taguchi technique to achieve the optimal crystallite size and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite powders. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 76:271–278
Yadav RS et al. (2015) Magnetic properties of dysprosium-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by starch-assisted sol-gel auto-combustion method. J Supercond Nov Magn 28:2097–2107
Karimi Z et al. (2014) Magnetic and structural properties of nano sized Dy-doped cobalt ferrite synthesized by co-precipitation. J Magn Magn Mater 361:150–156
Gonsalves LR, Mojumdar SC, Verenkar VMS (2011) Synthesis and characterization of Co0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 nanoparticles. J Therm Anal Calorim 104:869–873
Naik CC, Gaonkar SK, Furtado I, Salker AV (2018) Effect of Cu2+ substitution on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of cobalt ferrite with its enhanced antimicrobial property. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29:14746–14761
Kumari S, Kumar V, Kumar P, Kar M, Kumar L (2015) Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline yttrium substituted cobalt ferrite synthesized by the citrate precursor technique. Adv Powder Technol 26:213–223
Ranjani M, Jesurani S, Priyadharshini M, Vennila S (2016) Sol-gel synthesis and characterization of zinc substituted cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles. Int J Eng Res Technol 5:882–886
Falsafi F et al. (2017) Sm-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: a novel sensing material for conductometric hydrogen leak sensor. Ceram Int 43:1029–1037
Rajput AB, Hazra S, Ghosh NN (2013) Synthesis and characterisation of pure single-phase CoFe2O4 nanopowder via a simple aqueous solution-based EDTA-precursor route. J Exp Nanosci 8:629–639
Hashemi SM, Hasani S, Jahanbani Ardakani K, Davar F (2019) The effect of simultaneous addition of ethylene glycol and agarose on the structural and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by the sol-gel auto-combustion method. J Magn Magn Mater 492:165714
Prathapani S, Vinitha M, Jayaraman TV, Das D (2014) Effect of Er doping on the structural and magnetic properties of cobalt-ferrite. J Appl Phys 115:1–4
Maisnam M et al. (2004) Magnetic properties of vanadium-substituted lithium zinc titanium ferrite. Mater Lett 58:2412–2414
Cullity BD (1978) Elements of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley Publishing Co. Reading, MA
Scherrer P (1918) Determination of size and inner structure of colloidal particles by X-ray (Bestimmung der Grösse und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen). Nachrichten von der Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften zu Göttingen. Math. Phys. Kl 1918:98–100
Šepelák V, Tkáčová K, Boldyrev VV, Wiβmann S, Becker KD (1997) Mechanically induced cation redistribution in ZnFe2O4 and its thermal stability. Phys B Condens Matter 234–236:617–619
Jain GC, Das BK, Tripathi RB, Narayan R (1979) Influence of V2O5 on the densification and the magnetic properties of Ni—Zn ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 14:80–86
Bachmann HG, Barnes WH (1961) Bonding in the trigonal bipyramidal coordination polyhedra of V2O5 and of certain other structures containing pentavalent vanadium. Z für Krist 115:215–230
Kaiser M (2010) Magnetic and dielectric properties of low vanadium doped nickel–zinc–copper ferrites. J Phys Chem Solids 71:1451–1457
Jain G, Das B, Tripathi R, Narayan R (1982) Influence of V2O5 addition on electrical conductivity and magnetic properties of Ni-Zn ferrites. IEEE Trans Magn 18:776–778
Hanke I, Zenger M (1977) Mn-Zn-ferrite MIT Sn/Ti-mischsubstitution Mn-Zn ferrites with combined Sn-Ti substitutions. J Magn Magn Mater 4:120–128
Anjum S, Tufail R, Rashid K, Zia R, Riaz S (2017) Effect of cobalt doping on crystallinity, stability, magnetic and optical properties of magnetic iron oxide nano-particles. J Magn Magn Mater 432:198–207
Kulal SR et al. (2012) Synthesis of Dy doped Co-Zn ferrite by sol-gel auto combustion method and its characterization. Mater Lett 84:169–172
Hashhash A, Kaiser M (2015) Influence of Ce-substitution on structural, magnetic and electrical properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J Electron Mater 45:462–472
Mazen SA, Abu-Elsaad NI, Nawara AS (2015) Influence of silicon substitution and annealing temperature on the microstructure and magnetic properties of lithium ferrite. J Alloy Compd 648:690–697
Yadav RS et al. (2015) Magnetic properties of Co1-xZnxFe2O4spinel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by starch-assisted sol-gel autocombustion method and its ball milling. J Magn Magn Mater 378:190–199
Topkaya R, Baykal A, Demir A (2013) Yafet-Kittel-type magnetic order in Zn-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with uniaxial anisotropy. J Nanoparticle Res 15:1359
Palareti G et al. (2016) Comparison between different D-Dimer cutoff values to assess the individual risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism: analysis of results obtained in the DULCIS study. Int J Lab Hematol 38:42–49
Tatarchuk TR et al. (2018) Effect of cobalt substitution on structural, elastic, magnetic and optical properties of zinc ferrite nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 731:1256–1266
Gurav SK, Shirsath SE, Kadam RH, Mane DR (2013) Low temperature synthesis of Li0.5ZrxCoxFe2.5-2xO4 powder and their characterizations. Powder Technol 235:485–492
Hasani S et al. (2014) Nano/sub-micron crystallization of Fe-Co-7.15V alloy by thermo-mechanical process to improve magnetic properties. Mater Sci Eng B 190:96–103
Somaiah N, Jayaraman TV, Joy PA, Das D (2012) Magnetic and magnetoelastic properties of Zn-doped cobalt-ferrites - CoFe2-xZnxO4(x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3). J Magn Magn Mater 324:2286–2291
Srinivasamurthy KM et al. (2018) Tuning of ferrimagnetic nature and hyperfine interaction of Ni2+ doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for power transformer applications. Ceram Int 44:9194–9203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imanipour, P., Hasani, S., Seifoddini, A. et al. The possibility of vanadium substitution on Co lattice sites in CoFe2O4 synthesized by sol–gel autocombustion method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 95, 157–167 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05316-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05316-w