Abstract
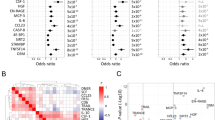
Stroke has a high incidence rate and often leads to permanent disability, particularly if it is not treated promptly. However, no blood biomarkers for early diagnosis are available to date. Therefore, we sought to detect stroke-specific blood biomarkers by identifying proteins associated with the underlying coagulation mechanism, which accounts for more than 80% of all stroke cases. Protein profiling was performed using blood samples from 16 healthy controls and 18 patients who suffered a stroke as the discovery set. We identified upregulated proteins (> 1.5-fold change and p value < 0.05) in patients who suffered a stroke relative to the corresponding levels in healthy controls by nano-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using data-independent acquisition based on sequential window acquisition of all theoretical mass spectra, which was developed to improve the consistency and accuracy of candidate proteins. Pathway analysis confirmed that the upregulated proteins were mainly involved in blood coagulation. Among these, we selected prothrombin, plasminogen, fibrinogen alpha-chain, and histidine-rich glycoprotein as candidate biomarkers. Multiple reaction monitoring analysis was performed on a validation set of 61 serum samples (31 healthy controls and 30 stroke patients) to assess the diagnostic value of the candidate biomarkers. All four proteins showed higher expression levels in patients with stroke than in healthy controls. The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve were greater than 0.9, confirming their clinical value. These four blood coagulation proteins may help in diagnosing stroke more accurately and quickly.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdullah W, Idris S, Bashkar S, Hassan R (2009) Role of fibrinolytic markers in acute stroke. Singap Med J 50:604
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE 3rd (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. Stroke 24:35–41
Adamson J, Beswick A, Ebrahim S (2004) Is stroke the most common cause of disability? J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 13:171–177
Aisina R, Mukhametova L (2014) Structure and function of plasminogen/plasmin system Russian. J Bioorgan Chem 40:590–605
Anjo SI, Santa C, Manadas B (2017) SWATH-MS as a tool for biomarker discovery: From basic research to clinical applications. Proteomics 17:1600278
Balogun IO, Roberts LN, Patel R, Pathansali R, Kalra L, Arya R (2016) Thrombin generation in acute ischaemic stroke. Stroke Res Treat 2016:7940680
Beretov J, Wasinger VC, Millar EK, Schwartz P, Graham PH, Li Y (2015) Proteomic analysis of urine to identify breast cancer biomarker candidates using a label-free LC-MS/MS approach. PLoS One 10:e0141876
Bertina RM (2009) The role of procoagulants and anticoagulants in the development of venous thromboembolism. Thromb Res 123:S41–S45
Boehme AK, Esenwa C, Elkind MS (2017) Stroke risk factors, genetics, and prevention. Circ Res 120:472–495
Chapin JC, Hajjar KA (2015) Fibrinolysis and the control of blood coagulation. Blood Rev 29:17–24
Chuang S-Y, Bai C-H, Chen W-H, Lien L-M, Pan W-H (2009) Fibrinogen independently predicts the development of ischemic stroke in a Taiwanese population: CVDFACTS study. Stroke 40:1578–1584
Colwell M, Ahmed N, Butkowski R (2017) Detection of histidine-rich glycoprotein and fibrinogen with nickel-enzyme conjugates: purification of rabbit HRG. Anal Biochem 525:67–72
Dagonnier M, Cooke IR, Faou P, Sidon TK, Dewey HM, Donnan GA, Howells DW (2017) Discovery and longitudinal evaluation of candidate biomarkers for ischaemic stroke by mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Biomark Insights 12:1177271917749216
Dawson J, Walters M, Delles C, Mischak H, Mullen W (2012) Urinary proteomics to support diagnosis of stroke. PLoS One 7:e35879
Di Napoli M, Singh P (2009) Is plasma fibrinogen useful in evaluating ischemic stroke patients? Why, how, and when. Am Heart Assoc,
Eidelman RS, Hennekens CH (2003) Fibrinogen: a predictor of stroke and marker of atherosclerosis. Oxford University Press 24:499–500
Han NY, Choi W, Park JM, Kim EH, Lee H, Hahm KB (2013) Label-free quantification for discovering novel biomarkers in the diagnosis and assessment of disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. J Dig Dis 14:166–174
Jickling GC, Sharp FR (2015) Biomarker panels in ischemic stroke. Stroke 46:915–920
Kim H et al (2013) Development of biomarkers for screening hepatocellular carcinoma using global data mining and multiple reaction monitoring. PLoS One 8:e63468
Lee S-J, Hong JM, Lee SE, Kang DR, Ovbiagele B, Demchuk AM, Lee JS (2017) Association of fibrinogen level with early neurological deterioration among acute ischemic stroke patients with diabetes. BMC Neurol 17:101
Lobo MDP, Moreno FBMB, Souza GHMF, Verde SMML, Moreira RDA, Monteiro-Moreira ACDO (2017) Label-free proteome analysis of plasma from patients with breast cancer: stage-specific protein expression. Front Oncol 7:14
Ma Y, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Yang G-Y (2019) Significance of complement system in ischemic stroke: a comprehensive review. Aging Dis 10:429–462
Macko RF et al (1999) Elevated tissue plasminogen activator antigen and stroke risk: the stroke prevention in young women study. Stroke 30:7–11
Maino A, Rosendaal FR, Algra A, Peyvandi F, Siegerink B (2015) Hypercoagulability is a stronger risk factor for ischaemic stroke than for myocardial infarction: a systematic review. PLoS One 10:e0133523
Millán M, Dorado L, Dávalos A (2010) Fibrinolytic therapy in acute stroke. Curr Cardiol Rev 6:218–226
Opartkiattikul N (1999) Standardization of coagulation tests. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 30:79–85
Pan S, Zhan X, Su X, Guo L, Lv L, Su B (2011) Proteomic analysis of serum proteins in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with acupuncture. Exp Biol Med 236:325–333
Parker CE, Borchers CH (2014) Mass spectrometry based biomarker discovery, verification, and validation—quality assurance and control of protein biomarker assays. Mol Oncol 8:840–858
Poon IK, Patel KK, Davis DS, Parish CR, Hulett MD (2011) Histidine-rich glycoprotein: the Swiss Army knife of mammalian plasma. Blood 117:2093–2101
Rifai N, Gillette MA, Carr SA (2006) Protein biomarker discovery and validation: the long and uncertain path to clinical utility. Nat Biotechnol 24:971
Rothwell PM, Howard SC, Power DA, Gutnikov SA, Algra A, van Gijn J, Clark TG, Murphy MFG, Warlow CP (2004) Fibrinogen concentration and risk of ischemic stroke and acute coronary events in 5113 patients with transient ischemic attack and minor ischemic stroke. Stroke 35:2300–2305
Saadatnia M, Salehi M, Amini G, Miri NSA (2012) The impact of prothrombin (G20210A) gene mutation on stroke in youths. ARYA Atherosc 8:9
Sharma R et al. (2015) Proteomic signature of endothelial dysfunction identified in the serum of acute ischemic stroke patients by the iTRAQ-based LC–MS approach J Proteome Res 14:2466-2479
Stoll G, Kleinschnitz C, Nieswandt B (2008) Molecular mechanisms of thrombus formation in ischemic stroke: novel insights and targets for treatment. Blood 112:3555–3562
ten Cate H, Hemker HC (2016) Thrombin generation and atherothrombosis: what does the evidence indicate? J Am Heart Assoc 5:e003553
Thomas S, Hao L, Ricke WA, Li L (2016) Biomarker discovery in mass spectrometry-based urinary proteomics. PROTEOMICS–Clin Appl 10:358–370
Vu TT, Stafford AR, Leslie BA, Kim PY, Fredenburgh JC, Weitz JI (2011) Histidine-rich glycoprotein binds fibrin (ogen) with high affinity and competes with thrombin for binding to the γ′-chain. J Biol Chem 286:30314–30323
Wildsmith KR et al (2014) Identification of longitudinally dynamic biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease cerebrospinal fluid by targeted proteomics. Mol Neurodegener 9:22
Yakovlev S, Makogonenko E, Kurochkina N, Nieuwenhuizen W, Ingham K, Medved L (2000) Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin: mechanism of exposure of tPA-and plasminogen-binding sites. Biochemistry 39:15730–15741
Yannell KE, Ferreira CR, Tichy SE, Cooks RG (2018) Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM)-profiling with biomarker identification by LC-QTOF to characterize coronary artery disease. Analyst 143:5014–5022
Zimmermann-Ivol CG, Burkhard PR, Le Floch-Rohr J, Allard L, Hochstrasser DF, Sanchez J-C (2004) Fatty acid binding protein as a serum marker for the early diagnosis of stroke: a pilot study. Mol Cell Proteomics 3:66–72
Funding
This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the NRF funded by the Korean government, MSIP (Grant No. 2016M3A9B694241).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.L. and S.M. wrote the manuscript, created the figures and the table, and generated proteomic data. A.P., D.K., Y.J.L., H.J.K., H.C., M.S., S.J., J.G., and Y.T.J. performed sample preparation and generated proteomic data. H.G.K. conceived the study and was in charge of overall direction and planning. All the authors discussed the results and have approved the manuscript for publishing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
All samples were obtained from Eulji University, Daejeon, Korea. This study was approved by the local institutional review board (EMC 2016-03-019).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Mun, S., Park, A. et al. Proteomics Reveals Plasma Biomarkers for Ischemic Stroke Related to the Coagulation Cascade. J Mol Neurosci 70, 1321–1331 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01545-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01545-4