Abstract
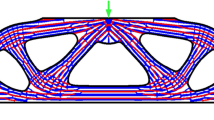
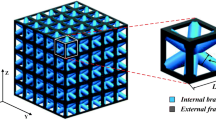
A numerical method is presented to generate hierarchical infills for additive manufacturing, using homogenization and optimization. Given the shape and the allowed stages of grading, the macroscopic properties of each level of the hierarchical infill are computed through numerical homogenization. Then, a multi-material optimization problem is formulated to find the distribution of the prescribed discrete set of candidates that maximizes the structural stiffness of the object to be printed for a limited volume fraction. The formulation is endowed with an additional overturning constraint to achieve objects that resist gravity in a stable configuration. Numerical simulations, addressing the design of a self-supporting orthotropic rhombic infill and a stiff isotropic triangular one, are shown.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chu, C., Graf, G., Rosen, D.W.: Design for additive manufacturing of cellular structures. Comput. Aided Design Appl. 5(5), 686–696 (2008)
Allaire, G., Bogosel, B.: Optimizing supports for additive manufacturing. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 58(6), 2493–2515 (2018)
Bruggi, M., Parolini, N., Regazzoni, F., Verani, M.: Topology optimization with a time-integral cost functional. Finite Elem. Anal. Design 140, 11–22 (2018)
Groen, J.P., Sigmund, O.: Homogenization-based topology optimization for high-resolution manufacturable microstructures. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 113(8), 1148–1163 (2018)
Allaire, G., Geoffroy-Donders, P., Pantz, O.: Topology optimization of modulated and oriented periodic microstructures by the homogenization method. Comput. Math. Appl. 78(7), 2197–2229 (2019)
Lewiński, T., Sokół, T., Graczykowski, C.: Michell structures. Springer, Berlin (2018)
Eschenauer, H.A., Olhoff, N.: Topology optimization of continuum structures: a review. Appl. Mech. Rev. 54(4), 331–390 (2001)
Liu, J., Gaynor, A.T., Chen, S., Kang, Z., Suresh, K., Takezawa, A., Li, L., Kato, J., Tang, J., Wang, C.C.L., Cheng, L., Liang, X., To, A.C.: Current and future trends in topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 57(6), 2457–2483 (2018)
Meng, L., Zhang, W., Quan, D., Shi, G., Tang, L., Hou, Y., Breitkopf, P., Zhu, J., Gao, T.: From topology optimization design to additive manufacturing: Today’s success and tomorrow’s roadmap. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-019-09331-1
Plocher, J., Panesar, A.: Review on design and structural optimisation in additive manufacturing: towards next-generation lightweight structures. Mater. Design (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-019-09331-1
Wu, J., Wang, C.C.L., Zhang, X., Westermann, R.: Self-supporting rhombic infill structures for additive manufacturing. CAD Comput. Aided Design 80, 32–42 (2016)
Wu, J., Aage, N., Westermann, R., Sigmund, O.: Infill optimization for additive manufacturing-approaching bone-like porous structures. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 24(2), 1127–1140 (2018)
Wu, Z., Xia, L., Wang, S., Shi, T.: Topology optimization of hierarchical lattice structures with substructuring. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 345, 602–617 (2019)
Alzahrani, M., Choi, S., Rosen, D.W.: Design of truss-like cellular structures using relative density mapping method. Mater. Design 85, 349–360 (2015)
Cheng, L., Bai, J., To, A.C.: Functionally graded lattice structure topology optimization for the design of additive manufactured components with stress constraints. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 344, 334–359 (2019)
Han, Y., Lu, W.F.: A novel design method for nonuniform lattice structures based on topology optimization. J. Mech. Design. Trans. ASME (2018). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4040546
Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Daynes, S., Zhang, H., Feih, S., Wang, M.Y.: Design of graded lattice structure with optimized mesostructures for additive manufacturing. Mater. Design 142, 114–123 (2018)
Panesar, A., Abdi, M., Hickman, D., Ashcroft, I.: Strategies for functionally graded lattice structures derived using topology optimisation for additive manufacturing. Additive Manuf. 19, 81–94 (2018)
Sigmund, O., Aage, N., Andreassen, E.: On the (non-)optimality of michell structures. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 54(2), 361–373 (2016)
Gibiansky, L.V., Sigmund, O.: Multiphase composites with extremal bulk modulus. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 48(3), 461–498 (2000)
Stegmann, J., Lund, E.: Discrete material optimization of general composite shell structures. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 62(14), 2009–2027 (2005)
Svanberg, K.: The method of moving asymptotes-a new method for structural optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 24(2), 359–373 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.1620240207
Arabnejad, S., Pasini, D.: Mechanical properties of lattice materials via asymptotic homogenization and comparison with alternative homogenization methods. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 77, 249–262 (2013)
Noor, A.K.: Continuum modeling for repetitive lattice structures. Appl. Mech. Rev. 41(7), 285–297 (1988)
Kumar, R.S., McDowell, D.L.: Generalized continuum modeling of 2-D periodic cellular solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41(26), 7399–7422 (2004)
Hassani, B., Hinton, E.: A review of homogenization and topology optimization I—Homogenization theory for media with periodic structure. Comput. Struct. 69(6), 707–717 (1998)
Theerakittayakorn, K., Nanakorn, P., Sam, P., Suttakul, P.: Exact forms of effective elastic properties of frame-like periodic cellular solids. Arch. Appl. Mech. 86(8), 1465–1482 (2016)
Vigliotti, A., Pasini, D.: Linear multiscale analysis and finite element validation of stretching and bending dominated lattice materials. Mech. Mater. 46, 57–68 (2012)
Andreassen, E., Andreasen, C.S.: How to determine composite material properties using numerical homogenization. Comput. Mater. Sci. 83, 488–495 (2014)
Timoshenko, S.P., Goodier, J.N.: Theory of elasticity, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, Singapore (1970)
Bendsøe, M.P., Sigmund, O.: Topology optimization. Theory, methods and applications. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Kaw, K.: Mechanics of composite materials. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2006)
Vannucci, P.: Anisotropic elasticity. Springer, Berlin (2018)
Bendsøe, M.P., Kikuchi, N.: Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 71(2), 197–224 (1988)
Bruggi, M.: Conceptual design of diagrids and hexagrids by distribution of lattice structures. Front. Built Environ. 6, 80 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fbuil.2020.00080
Wang, M.Y., Wang, X.: “color” level sets: a multi-phase method for structural topology optimization with multiple materials. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 193(6–8), 469–496 (2004)
Sanders, E.D., Aguiló, M.A., Paulino, G.H.: Multi-material continuum topology optimization with arbitrary volume and mass constraints. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 340, 798–823 (2018)
Bruggi, M., Duysinx, P.: A stress-based approach to the optimal design of structures with unilateral behavior of material or supports. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 48(2), 311–326 (2013)
Christensen, P.W., Klarbring, A.: An introduction to structural optimization. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Sigmund, O., Maute, K.: Topology optimization approaches. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 48, 1031–1055 (2013)
Beckers, M.: Topology optimization using a dual method with discrete variables. Struct. Optim. 17, 14–24 (1999)
Stolpe, M., Bendsøe, M.: Global optima for the Zhou–Rozvany problem. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 43, 151–165 (2011)
Aage, N., Andreassen, E., Lazarov, B.: Topology optimization using PETSC: an easy-to-use, fully parallel, open source topology optimization framework. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 51, 565–572 (2013)
Bruggi, M.: Topology optimization with mixed finite elements on regular grids. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 305, 133–153 (2016)
Błachowski, B., Gutkowski, W.: Discrete structural optimization by removing redundant material. Eng. Optim. 40(7), 685–694 (2008)
Bourdin, B.: Filters in topology optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 50(9), 2143–2158 (2001)
Bruyneel, M., Duysinx, P.: Note on topology optimization of continuum structures including self-weight. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 29(4), 245–256 (2005)
Divakara Shetty, S., Shetty, N.: Investigation of mechanical properties and applications of polylactic acids—a review. Mater. Res. Exp. 6(11), 112002 (2019)
Wang, W., Wang, T.Y., Yang, Z., Liu, L., Tong, X., Tong, W., Deng, J., Chen, F., Liu, X.: Cost-effective printing of 3D objects with skin-frame structures. ACM Trans. Graph. 32(6), 1–10 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The financial support of Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research through PRIN Grant Number 2015JW9NJT is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Zenon Mróz.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruggi, M., Taliercio, A. Hierarchical Infills for Additive Manufacturing Through a Multiscale Approach. J Optim Theory Appl 187, 654–682 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-020-01685-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-020-01685-y
Keywords
- Structural optimization
- Additive manufacturing
- Hierarchical infill
- Homogenization
- Lattice structures
- Multiscale analysis