Abstract
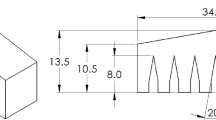
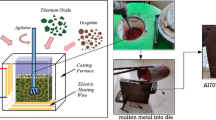
Surface micro-texturing has been proven an effective way to reduce friction and wear for tribological applications. In current work, we propose a low cost hot sintering method to apply micro-texturing on an advanced bearing polymer material. In step 1 of this method, one face of the mold was micro-textured using a micro-casting method, in step 2 the cured Aromatic Thermosetting coPolyester (ATSP) powder was filled in the mold. In step 3, the filled mold was placed in a hot press for a 2-h hot sintering process, and in step 4, the final textured bulk ATSP was completed after cooling down. Subsequently, the micro-textured ATSP bulk material was machined to 6.35 mm diameter pins for pin-on-disk configuration tribologcial studies at different speeds with a contact pressure of 9.1 MPa, under boundary lubrication conditions. Compared with plain untextured flat pins, the micro-textured pins could effectively reduce friction at speeds lower than 1.90 m/s: 14% reduction in average. Scanning electron microscopy was utilized for morphological studies of the micro-textured mold, and micro-textured ATSP samples, before and after the tribological experiments.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yilbas, B., Ali, H., Khaled, M., Al-Aqeeli, N., Abu-Dheir, N., & Varanasi, K. (2015). Characteristics of laser textured silicon surface and effect of mud adhesion on hydrophobicity. Applied Surface Science,351, 880–888.
Schneider, B. W., Lal, N. N., Baker-Finch, S., & White, T. P. (2014). Pyramidal surface textures for light trapping and antireflection in perovskite-on-silicon tandem solar cells. Optics Express,22(106), A1422–A1430.
Tang, M.-K., Huang, X.-J., Yu, J.-G., Li, X.-W., & Zhang, Q.-X. (2016). The effect of textured surfaces with different roughness structures on the tribological properties of Al alloy. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance,25(10), 4115–4125.
Etsion, I., & Halperin, G. (2002). A laser surface textured hydrostatic mechanical seal. Tribology Transactions,45(3), 430–434.
Kligerman, Y., Etsion, I., & Shinkarenko, A. (2005). Improving tribological performance of piston rings by partial surface texturing. Journal of Tribology,127(3), 632–638.
Kang, Z., Fu, Y., Chen, Y., Ji, J., Fu, H., Wang, S., et al. (2018). Experimental investigation of concave and convex micro-textures for improving anti-adhesion property of cutting tool in dry finish cutting. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology,5(5), 583–591.
Wei, Y., Kim, M.-R., Lee, D.-W., Park, C., & Park, S. S. (2017). Effects of micro textured sapphire tool regarding cutting forces in turning operations. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology,4(2), 141–147.
Lian, Y., Chen, H., Mu, C., Deng, J., & Lei, S. (2018). Experimental investigation and mechanism analysis of tungsten disulfide soft coated micro-nano textured self-lubricating dry cutting tools. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology,5(2), 219–230.
Morris, N. J., Rahnejat, H., & Rahmani, R. (2011). Tribology of partial pad journal bearings with textured surfaces.
Marian, V. G., Gabriel, D., Knoll, G., & Filippone, S. (2011). Theoretical and experimental analysis of a laser textured thrust bearing. Tribology Letters,44(3), 335.
Suh, A. Y., Lee, S.-C., & Polycarpou, A. A. (2002) Textured sliders as means to reduce adhesion in ultra low flying head disk interfaces. In ASME/STLE 2002 international joint tribology conference (pp. 51–55). American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Polycarpou, A. A., Boutaghou, Z.-E., Burbank, D. P., Gui, J., Hanchi, J. V., Stover, L. E., et al. (2003). Slider for disc storage system. US Patent, US6603639B1.
Zhou, L., Kato, K., Vurens, G., & Talke, F. (2003). The effect of slider surface texture on flyability and lubricant migration under near contact conditions. Tribology International,36(4–6), 269–277.
Vladescu, S.-C., Olver, A. V., Pegg, I. G., & Reddyhoff, T. (2015). The effects of surface texture in reciprocating contacts–An experimental study. Tribology International,82, 28–42.
Lu, W., Zhang, P., Liu, X., Zhai, W., Zhou, M., Luo, J., et al. (2017). Influence of surface topography on torsional fretting wear under flat-on-flat contact. Tribology International,109, 367–372.
Zhang, P., Lu, W., Liu, X., Zhai, W., Zhou, M., & Zeng, W. (2018). Torsional fretting and torsional sliding wear behaviors of CuNiAl against 42CrMo4 under dry condition. Tribology International,118, 11–19.
Ramesh, A., Akram, W., Mishra, S. P., Cannon, A. H., Polycarpou, A. A., & King, W. P. (2013). Friction characteristics of microtextured surfaces under mixed and hydrodynamic lubrication. Tribology International,57, 170–176.
Nanbu, T., Ren, N., Yasuda, Y., Zhu, D., & Wang, Q. J. (2008). Micro-textures in concentrated conformal-contact lubrication: Effects of texture bottom shape and surface relative motion. Tribology Letters,29(3), 241–252.
Pettersson, U., & Jacobson, S. (2003). Influence of surface texture on boundary lubricated sliding contacts. Tribology International,36(11), 857–864.
Usami, H., Sato, T., Kanda, Y., & Nishio, S. (2017) Applicability of interrupted micro cutting process “Tilling” as surface texturing. In Key Engineering Materials (Vol. 749, pp. 241–245). Trans Tech Pub.
Syahputra, H. P., & Ko, T. J. (2013). Application of image processing to micro-milling process for surface texturing. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,14(9), 1507–1512.
Nakano, M., Korenaga, A., Korenaga, A., Miyake, K., Murakami, T., Ando, Y., et al. (2007). Applying micro-texture to cast iron surfaces to reduce the friction coefficient under lubricated conditions. Tribology Letters,28(2), 131–137.
Hao, X., Pei, S., Wang, L., Xu, H., He, N., & Lu, B. (2015). Microtexture fabrication on cylindrical metallic surfaces and its application to a rotor-bearing system. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,78(5–8), 1021–1029.
Cannon, A. H., & King, W. P. (2009). Casting metal microstructures from a flexible and reusable mold. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering,19(9), 095016.
Cannon, A. H., & King, W. P. (2010). Microstructured metal molds fabricated via investment casting. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering,20(2), 025025.
Nielsen, T. K., Olsen, B. B., Nørregaard, J., Kristensen, A., Smistrup, K., & Søgaard, E. (2016). Injection molding tools with micro/nano-meter pattern. US Patent, US9268215B2.
Zhang, B., Huang, W., Wang, J., & Wang, X. (2013). Comparison of the effects of surface texture on the surfaces of steel and UHMWPE. Tribology International,65, 138–145.
Pettersson, U., & Jacobson, S. (2006). Tribological texturing of steel surfaces with a novel diamond embossing tool technique. Tribology International,39(7), 695–700.
Xu, S., An, S. O. J., Atsushi, D., & Castagne, S. (2016). Development of low-cost deformation-based micro surface texturing system for friction reduction. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,17(8), 1059–1065.
Shum, P., Zhou, Z., & Li, K. (2014). To increase the hydrophobicity, non-stickiness and wear resistance of DLC surface by surface texturing using a laser ablation process. Tribology International,78, 1–6.
Mishra, S. P., & Polycarpou, A. A. (2011). Tribological studies of unpolished laser surface textures under starved lubrication conditions for use in air-conditioning and refrigeration compressors. Tribology International,44(12), 1890–1901.
Wahab, J., Ghazali, M. J., Yusoff, W., & Sajuri, Z. (2016). Enhancing material performance through laser surface texturing: a review. Transactions of the IMF,94(4), 193–198.
Fan, H., Zhang, Y., Hu, T., Song, J., Ding, Q., & Hu, L. (2015). Surface composition–lubrication design of Al2O3/Ni laminated composites—Part I: Tribological synergy effect of micro–dimpled texture and diamond–like carbon films in a water environment. Tribology International,84, 142–151.
Lazzini, G., Gemini, L., Lutey, A., Kling, R., Romoli, L., Allegrini, M., et al. (2019). Surface morphologies in ultra-short pulsed laser processing of stainless-steel at high repetition rate. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,20, 1–10.
Coblas, D. G., Fatu, A., Maoui, A., & Hajjam, M. (2015). Manufacturing textured surfaces: State of art and recent developments. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology,229(1), 3–29.
Frich, D., Goranov, K., Schneggenburger, L., & Economy, J. (1996). Novel high-temperature aromatic copolyester thermosets: synthesis, characterization, and physical properties. Macromolecules,29(24), 7734–7739.
Lan, P., Meyer, J. L., Economy, J., & Polycarpou, A. A. (2016). Unlubricated tribological performance of aromatic thermosetting polyester (ATSP) coatings under different temperature conditions. Tribology Letters,61(1), 10.
Lan, P., Gheisari, R., Meyer, J. L., & Polycarpou, A. A. (2018). Tribological performance of aromatic thermosetting polyester (ATSP) coatings under cryogenic conditions. Wear,398, 47–55.
Lan, P., Meyer, J. L., Vaezian, B., & Polycarpou, A. A. (2016). Advanced polymeric coatings for tilting pad bearings with application in the oil and gas industry. Wear,354, 10–20.
Lan, P., Polychronopoulou, K., Zhang, Y., & Polycarpou, A. A. (2017). Three-body abrasive wear by (silica) sand of advanced polymeric coatings for tilting pad bearings. Wear,382, 40–50.
Lan, P., Polychronopoulou, K., Iaccino, L. L., Bao, X., & Polycarpou, A. A. (2018). Elevated-temperature and-pressure tribology of drilling fluids used in oil and gas extended-reach-drilling applications. SPE Journal,23(6), 12.
Demas, N. G., Zhang, J., Polycarpou, A. A., & Economy, J. (2008). Tribological characterization of aromatic thermosetting copolyester–PTFE blends in air conditioning compressor environment. Tribology Letters,29(3), 253–258.
Lan, P., & Polycarpou, A. A. (2018). High temperature and high pressure tribological experiments of advanced polymeric coatings in the presence of drilling mud for oil & gas applications. Tribology International,120, 218–225.
Economy, J., Polycarpou, A., & Meyer, J. (2017). Polymer coating system for improved tribological performance. US Patent, US9534138B2.
Bakir, M., Meyer, J. L., Economy, J., & Jasiuk, I. (2016). Heat-induced polycondensation reaction with self-generated blowing agent forming aromatic thermosetting copolyester foams. Macromolecules,49(17), 6489–6496.
Marty, F., Rousseau, L., Saadany, B., Mercier, B., Français, O., Mita, Y., et al. (2005). Advanced etching of silicon based on deep reactive ion etching for silicon high aspect ratio microstructures and three-dimensional micro-and nanostructures. Microelectronics Journal,36(7), 673–677.
Frich, D., Economy, J., & Goranov, K. (1997). Aromatic copolyester thermosets: High temperature adhesive properties. Polymer Engineering & Science,37(3), 541–548.
Meyer, J. L., Bakir, M., Lan, P., Economy, J., Jasiuk, I., Bonhomme, G., et al. (2019). Reversible bonding of aromatic thermosetting copolyesters for in-space assembly. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering,304(4), 1800647.
https://zeus.plmsc.psu.edu/~manias/MatSc597/roughness/definitions.html. Accessed October 24, 2019.
Vaezian, B., Meyer, J. L., & Economy, J. (2016). Processing of aromatic thermosetting copolyesters into foams and bulk parts: Characterization and mechanical properties. Polymers for Advanced Technologies,27(8), 1006–1013.
Acknowledgements
The SEM analysis and laser microscopic 3D image were carried out in the Center for Microanalysis of Materials at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, which is partially supported by the U.S. Department of Energy under Grant DEFG02-96-ER45439.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, P., Gheisari, R., Meyer, J.L. et al. Surface Micro-texturing by Hot Sintering for Advanced Bearing Polymers for Friction Reduction Under Boundary Lubrication. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 21, 1025–1034 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00274-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00274-y