Abstract
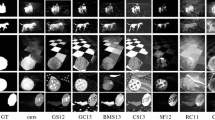
Saliency detection aims to automatically highlight the most important area in an image. Traditional saliency detection methods based on absorbing Markov chain only take into account boundary nodes and often lead to incorrect saliency detection when the boundaries have salient objects. In order to address this limitation and enhance saliency detection performance, this paper proposes a novel task-independent saliency detection method based on the bidirectional absorbing Markov chains that jointly exploits not only the boundary information but also the foreground prior and background prior cues. More specifically, the input image is first segmented into number of superpixels, and the four boundary nodes (duplicated as virtual nodes) are selected. Subsequently, the absorption time upon transition node’s random walk to the absorbing state is calculated to obtain the foreground possibility. Simultaneously, foreground prior (as the virtual absorbing nodes) is used to calculate the absorption time and get the background possibility. In addition, the two aforementioned results are fused to form a combined saliency map which is further optimized by using a cost function. Finally, the superpixel-level saliency results are optimized by a regularized random walks ranking model at multi-scale. The comparative experimental results on four benchmark datasets reveal superior performance of our proposed method over state-of-the-art methods reported in the literature. The experiments show that the proposed method is efficient and can be applicable to the bottom-up image saliency detection and other visual processing tasks.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F, Susstrunk S. Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: IEEE conference on Computer vision and pattern recognition; 2009. p. 1597–1604.
Achanta R, Shaji A, Smith K, Lucchi A, Fua P, Süsstrunk S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2012;34(11):2274–2282.
Alpert S, Galun M, Brandt A, Basri R. Image segmentation by probabilistic bottom-up aggregation and cue integration. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2012;34(2):315–327.
Borji A. Boosting bottom-up and top-down visual features for saliency estimation. In: IEEE conference on Computer vision and pattern recognition; 2012. p. 438–445.
Charles M, Grinstead J, Snell L. Introduction to probability. Providence: American Mathematical Society; 1997.
Chen C, Li Y, Li S, Qin H, Hao A. A novel bottom-up saliency detection method for video with dynamic background. IEEE Signal Process Lett 2018;25(2):154–158.
Cheng MM, Zhang GX, Mitra NJ, Huang X, Hu SM. Global contrast based salient region detection. In: IEEE Computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2011. p. 409–416.
Cholakkal H, Johnson J, Rajan D. Backtracking ScSPM image classifier for weakly supervised top-down saliency. In: Proceedings of IEEE conf. on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2016. p. 5278–5287.
Du J, Li W, Xiao B, Nawaz Q. Medical image fusion by combining parallel features on multi-scale local extrema scheme. Knowl-Based Syst 2016;113:4–12.
Duan L, Wu C, Miao J, Qing L, Fu Y. Visual saliency detection by spatially weighted dissimilarity. In: Proceedings of IEEE conf. on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2011. p. 473–480.
Fang Y, Lin W, Lau CT, Lee BS. 2011. A visual attention model combining top-down and bottom-up mechanisms for salient object detection. In: IEEE international conference on Acoustics, speech and signal processing; 2011. p. 1293–1296.
Goferman S, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A. Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2012;34(10):1915–1926.
Gopalakrishnan V, Hu Y, Rajan D. Random walks on graphs for salient object detection in images. IEEE Trans Image Process 2010;19(12):3232–3242.
He S, Lau RW, Yang Q. Exemplar-driven top-down saliency detection via deep association. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2016. p. 5723–5732.
Hu W, Hu R, Xie N, Ling H, Maybank S. Image classification using multiscale information fusion based on saliency driven nonlinear diffusion filtering. IEEE Trans Image Process 2014;23(4):1513–1526.
Hussain CA, Rao DV, Masthani SA. Robust pre-processing technique based on saliency detection for content based image retrieval systems. Procedia Comput Sci 2016;85:571–580.
Itti L, Koch C. Computational modelling of visual attention. Nature Rev Neurosci 2001;2(3):194–203.
Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 1998;20(11):1254–1259.
Jiang B, Zhang L, Lu H, Yang C, Yang MH. Saliency detection via absorbing Markov chain. In: Proceedings of IEEE int. Conf. on computer vision; 2013. p. 1665–1672.
Jiang H, Wang J, Yuan Z, Wu Y, Zheng N, Li S. 2013. Salient object detection: a discriminative regional feature integration approach. In: IEEE conference on Computer vision and pattern recognition; 2013. p. 2083–2090.
Lee G, Tai YW, Kim J. Eld-net: an efficient deep learning architecture for accurate saliency detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2018;40(7):1599–1610.
Li C, Yuan Y, Cai W, Xia Y, Dagan Feng D. Robust saliency detection via regularized random walks ranking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2015. p. 2710–2717.
Li G, Yu Y. Deep contrast learning for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2016. p. 478–487.
Li X, Lu H, Zhang L, Ruan X, Yang MH. Saliency detection via dense and sparse reconstruction. In: Proceedings of IEEE int. Conf. on computer vision; 2013. p. 2976–2983.
Liu T, Yuan Z, Sun J, Wang J, Zheng N, Tang X, Shum H. Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2011;33(2):353–367.
Margolin R, Tal A, Zelnik-Manor L. What makes a patch distinct?. In: IEEE conference on Computer vision and pattern recognition; 2013. p. 1139–1146.
Murabito F, Spampinato C, Palazzo S, Giordano D, Pogorelov K, Riegler M. Top-down saliency detection driven by visual classification. Comput Vis Image Underst 2018;172:67–76.
Peng H, Li B, Ling H, Hu W, Xiong W, Maybank SJ. Salient object detection via structured matrix decomposition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2017;39(4):818–832.
Perazzi F, Krähenbühl P, Pritch Y, Hornung A. Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE conf. on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2012. p. 733–740.
Rahtu E, Kannala J, Salo M, Heikkilä J. Segmenting salient objects from images and videos. In: Proceedings of European conf. on computer vision; 2010. p. 366–379.
de San Roman PP, Benois-Pineau J, Domenger JP, Paclet F, Cataert D, De Rugy A. Saliency driven object recognition in egocentric videos with deep CNN: toward application in assistance to neuroprostheses. Comput Vis Image Underst 2017;164:82–91.
Sun J, Xie J, Liu J, Sikora T. Image adaptation and dynamic browsing based on two-layer saliency combination. IEEE Trans Broadcast 2013;59(4):602–613.
Sun J, Lu H, Liu X. Saliency region detection based on Markov absorption probabilities. IEEE Trans Image Process 2015;24(5):1639–1649.
Tong N, Lu H, Zhang L, Ruan X. Saliency detection with multi-scale superpixels. IEEE Signal Process Lett 2014;21(9):1035–1039.
Tu WC, He S, Yang Q, Chien SY. Real-time salient object detection with a minimum spanning tree. In: Proceedings of IEEE conf. on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2016. p. 2334–2342.
Tu Z, Zheng A, Yang E, Luo B, Hussain A. A biologically inspired vision-based approach for detecting multiple moving objects in complex outdoor scenes. Cogn Comput 2015;7(5):539–551.
Wang L, Wang L, Lu H, Zhang P, Ruan X. Saliency detection with recurrent fully convolutional networks. In: European conference on computer vision; 2016. p. 825–841.
Wang W, Shen J, Porikli F. Saliency-aware geodesic video object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2015. p. 3395–3402.
Wang X, Lv Q, Wang B, Zhang L. Airport detection in remote sensing images: a method based on saliency map. Cogn Neurodyn 2013;7(2):143–154.
Wang Z, Ren J, Zhang D, Sun M, Jiang J. A deep-learning based feature hybrid framework for spatiotemporal saliency detection inside videos. Neurocomputing 2018;287:68–83.
Xie Y, Lu H. Visual saliency detection based on Bayesian model. In: Proceedings of the 18th IEEE int. Conf. on image processing; 2011. p. 645–648.
Xie Y, Lu H, Yang MH. Bayesian saliency via low and mid level cues. IEEE Trans Image Process 2013; 22(5):1689–1698.
Yan Q, Xu L, Shi J, Jia J. Hierarchical saliency detection. In: IEEE conference on Computer vision and pattern recognition; 2013. p. 1155–1162.
Yan Y, Ren J, Zhao H, Sun G, Wang Z, Zheng J, Marshall S, Soraghan J. Cognitive fusion of thermal and visible imagery for effective detection and tracking of pedestrians in videos. Cogn Comput 2018; 10(1):94–104.
Yang C, Zhang L, Lu H. Graph-regularized saliency detection with convex-hull-based center prior. IEEE Signal Process Lett 2013;20(7):637–640.
Yang W, Li D, Wang S, Lu S, Yang J. Saliency-based color image segmentation in foreign fiber detection. Math Comput Model 2013;58(3-4):852–858.
Yuan Y, Li D, Meng MQH. Automatic polyp detection via a novel unified bottom-up and top-down saliency approach. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 2018;22(4):1250–1260.
Zhan J, Zhao H, Zheng P, Wu H, Wang L. Salient superpixel visual tracking with graph model and iterative segmentation. Cognitive Computation. 2019:1–12.
Zhang J, Sclaroff S. Saliency detection: a boolean map approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision; 2013. p. 153–160.
Zhang L, Ai J, Jiang B, Lu H, Li X. Saliency detection via absorbing Markov chain with learnt transition probability. IEEE Trans Image Process 2018;27(2):987–998.
Zhang Q, Luo D, Li W, Shi Y, Lin J. Two-stage absorbing Markov chain for salient object detection. In: IEEE international conference on Image processing; 2017. p. 895–899.
Zhang W, Xiong Q, Shi W, Chen S. Region saliency detection via multi-feature on absorbing Markov chain. Vis Comput 2016;32(3):275–287.
Zhao R, Ouyang W, Li H, Wang X. Saliency detection by multi-context deep learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2015. p. 1265–1274.
Zhu G, Wang Q, Yuan Y. Tag-saliency: Combining bottom-up and top-down information for saliency detection. Comput Vis Image Underst 2014;118:40–49.
Zhu W, Liang S, Wei Y, Sun J. Saliency optimization from robust background detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE conf. on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2014. p. 2814–2821.
Funding
This work was supported by China Scholarship Council, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 913203002), the Pilot Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDA08040109), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Grant No. ACAIM190302), and Universities Joint Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Detection Science and Technology in Anhui Province (Grant No. 2019GDTCZD02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). Additional informed consent was obtained from all patients for which identifying information is included in this article.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, F., Kong, B., Li, J. et al. Robust Visual Saliency Optimization Based on Bidirectional Markov Chains. Cogn Comput 13, 69–80 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-020-09724-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-020-09724-6